Domain, co-domain and image there are three different sets related to the study of a function. So, to understand what these sets are, we need to understand, first, what a function is.
Occupation is a set of ordered pairs (x, y), where each value of x is related to one, and only one, of the values of y, through a formation rule: y = f(x).
Examples of functions and non-functions:
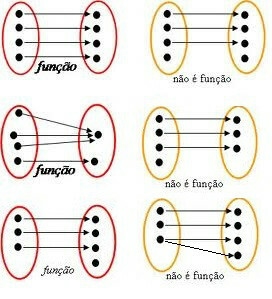
Now that we know what is and isn't a role, let's look at the domain, counterdomain, and image definitions.
What is domain, counter-domain and image
Domain
It is the set formed by all values of the variable x, for which the function exists, that is, those that have one, and only one, associated y-value.
Abbreviation: Sun (f).
dominion
It is the set formed by all the values that variable y can assume, that is, that may or may not be associated with the values of variable x.
Abbreviation: CD(f).
Image
It is a subset formed by all values of the counterdomain that have an association with some of the elements of variable x.
Abbreviation: Im (f).
- Free Online Inclusive Education Course
- Free Online Toy Library and Learning Course
- Free Online Math Games Course in Early Childhood Education
- Free Online Pedagogical Cultural Workshops Course

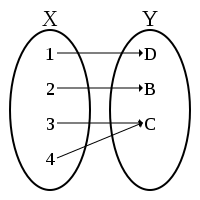
Example: Consider the sets X = {0, 1, 2, 3} and Y = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10} and the function defined by the following rule:
f: X → Y
y = f (x) = 3x
We have:
Domain: D(f) = X = {0, 1, 2, 3}.
Counterdomain: CD(f) = Y = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10}.
Image: Im (f) = { f (0), f (1), f (2), f (3) } = {0, 3, 6, 9}, because:
f (0) = 3.0 = 0
f(1) = 3. 1 = 3
f(2) = 3.2 = 6
f(3) = 3.3 = 9
To be a function, all domain elements must have one, and only one, corresponding element in the counterdomain. Note that this happens in the function above.
However, it is not necessary that all elements of the counterdomain have a counterpart in the domain. See, for example, that the values 1, 2, 4, 5, 7, 8, and 10 of set Y have no association with any value of X.
You may also be interested:
- First degree function (affiliated function)
- First degree function exercises (affine function)
- Trigonometric Functions - Sine, Cosine and Tangent
The password has been sent to your email.