At mitochondria they are cell organelles related to the process of cellular respiration. They are often referred to as the “powerhouses” of cells because, through the process of cellular respiration, a large amount of ATP is generated.
Read too: What is ATP?
→ Characteristics of mitochondria
At mitochondria are spherical or elongated organelles found in almost all eukaryotic cells, that is, cells that are characterized by the presence of genetic material surrounded by the nuclear membrane. in cells prokaryotes, mitochondria are not present.

O number of mitochondria varies from cell to cell, but typically hundreds of mitochondria are seen in a single cell. A larger number is seen in cells that exhibit high metabolic activity. In addition, mitochondria accumulate in places in the cytoplasm that spend more energy.
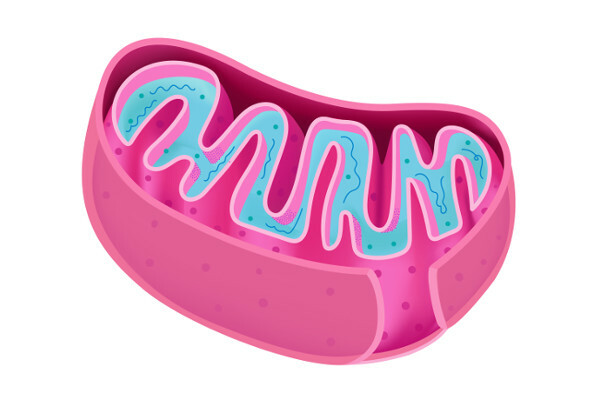
These organelles have a length ranging from 1.0 µm to 10 µm and width between 0.5 µm and 1.0 µm. They have two membranes: one
inner membrane, which has projections into its interior (mitochondrial crests), and a outermost membrane, which is smooth. Between the outer and the inner membrane, there is the so-called intermembranous space. The inner membrane, in turn, delimits an inner space, which contains the mitochondrial matrix.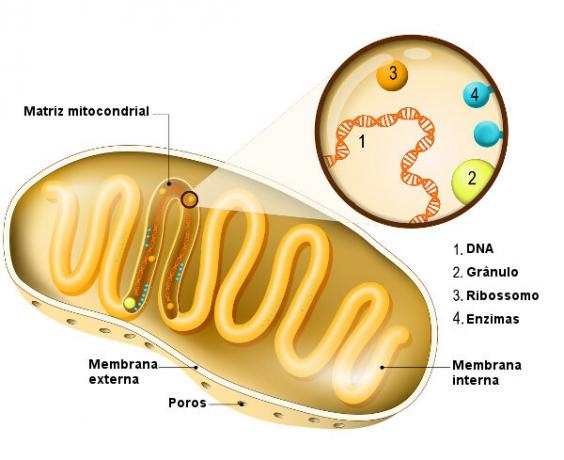
Mitochondrial crests are responsible for ensuring the increase in the surface of the inner membrane. On this crest, it is possible to perceive the presence of enzymes and also other components that are important in the process of cellular respiration. Cells that consume a lot of energy have mitochondria with lots of ridges.
In the mitochondrial matrix, there is a large amount of enzymes that act on cell respiration, other proteins, genetic material (DNA and RNA) and ribosomes. O DNA found in mitochondria is very similar to that of bacteria, appearing as double, circular filaments. You DNA strands they are synthesized in the organelle itself, and their duplication occurs without interference from nuclear DNA.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
As stated, RNA is also present in mitochondria. In these organelles, the ribosomal RNA, messenger RNA and transporter RNA. You ribosomes they are also found inside mitochondria, but are different from those found in the cell's cytoplasm. These mitochondrial ribosomes are smaller and closely resemble those of bacteria.
In mitochondria, some proteins are also synthesized, but in smaller amounts. Mitochondria are able to fuse and divide by binary fission, as well as prokaryotic organisms.
→ Functions of mitochondria
Mitochondria work like a site of the cellular respiration process. This metabolic process extracts energy stored in glucose and also in other organic fuels, with decomposition of these fuels, in the presence of oxygen, in carbon dioxide and water. The energy released is used to carry out various cellular activities, such as transport across the membrane.
If you want to understand the process of cellular respiration in more detail, access the text:Cellular respiration.
→ Origin of mitochondria
The origin of mitochondria, and also of chloroplasts, is explained through the endosymbiont theory. According to this theory, an ancestor of eukaryotic cells phagocytosed a small prokaryote aerobic ancestor (used oxygen to metabolize organic molecules), which began to live in its interior. This ancestral prokaryote was engulfed, but it was not digested by the cell and, as it provides an advantage to this cell began to live symbiotic, that is, in a relationship that benefited all involved.

Some features of mitochondria suggest that this theory is indeed correct, such as the presence of two membranes, the ability to divide like some prokaryotes, the presence of circular DNA and the presence of ribosomes similar to those of prokaryotes.
Read too:endosymbiotic theory
→ Mitochondria Summary
Mitochondria are found in eukaryotic cells.
Mitochondria are related to the cellular respiration process and are found in greater numbers in cells that have high metabolic activity.
Mitochondria are organelles that have a double membrane.
The innermost membrane of the mitochondria forms the mitochondrial ridges.
Mitochondrial ridges delimit the mitochondrial matrix, in which proteins, DNA, RNA and ribosomes are found.
The DNA of mitochondria is similar to that of bacteria.
The origin of mitochondria can be explained by the endosymbiotic theory.
By Ma. Vanessa dos Santos



