Atcells they can be defined as the structural and functional units of all living beings. These structures are alive, carry the genetic information of a particular organism and are capable of transmitting this information at the time of cell division.
According to the Cell Theory, all living organisms are made up of cells. In single-celled individuals, a single cell constitutes the entire body of the specimen; in multicellular beings, it takes several cells working together for the body to be formed. Man is an example of a multicellular organism, and bacteria are examples of unicellular beings.
When we look at the cells of different organisms, we can see that they have very different morphological characteristics. In our body, for example, there are over 100 different types of cells. It is worth noting, however, that, despite being visually distinct, when we analyze in detail their organization internal and its biochemical processes, we can conclude that they are quite similar, even in organisms many different.
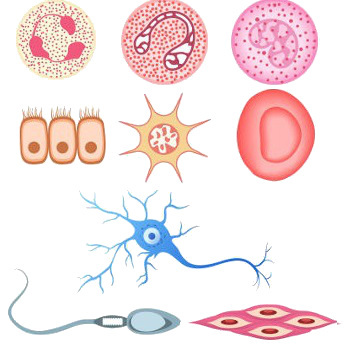
Different human cell types
→ What are the basic parts of a cell?
A cell is made up of some basic parts. We normally say that all cells have a plasma membrane, cytoplasm and nucleus. However, there are cells that do not have this last structure, an aspect that is even a way of differentiating two types of cells: the prokaryotes and the eukaryotes.
Prokaryotic cells are those that do not have a defined cell nucleus, therefore, the genetic material is dispersed in the cytoplasm. Eukaryotic cells, on the other hand, are those in which the genetic material is present in a cell nucleus surrounded by a double membrane. In addition to this crucial difference, we can also mention that prokaryotic cells do not have proteins called histones linked to their DNA, nor do they have membranous cytoplasmic organelles.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
THE plasma membraneand the cytoplasm, unlike the nucleus, is present in all cell types. The plasma membrane, which is characterized by being a phospholipid double layer, is extremely important for the cell, as it controls the passage of substances both inside and out. Due to this property of selecting what enters and leaves the cell, we say that it presents selective permeability.
O cytoplasm, in turn, it is a region delimited by the plasma membrane. This region consists of a matrix, called cytosol, which contains substances such as amino acids, energy nutrients and ions. Immersed in this matrix are cell organelles, structures responsible for controlling the cell's various activities.
→ What are cell organelles?
At cell organelles they are structures that function like small organs inside the cell. Each organelle performs a certain function and is essential for the proper functioning of the cell. There are several cell organelles, highlighting:
centriole
Chloroplast
Golgi complex
Lysosome
mitochondria
peroxisome
endoplasmic reticulum
ribosome
It is clear, therefore, that, despite being small, cells have a variety of complex biochemical structures and processes that are essential for the maintenance of life. Without the development of these small structures, life would not be possible.
By Ma. Vanessa dos Santos
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
SANTOS, Vanessa Sardinha dos. "What is cell?"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/o-que-e/biologia/o-que-e-celula.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.
