THE Venezuela is a country located on the American continent (specifically on the South America subcontinent) constituted mostly by continental areas and also by small islands, located in the Sea of the Caribbean. The islands of Las Aves, Los Roques, Orchila, Blanquilla, Los Hermanos and Margarita Island belong to the country.
Venezuela borders Guyana to the east, Brazil to the south and Colombia to the west. The country is considered rich in biodiversity and natural resources, known mainly for its oil reserves.
Data
Parents |
Venezuela — officially: Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela. |
capital |
Caracas |
Official language |
Spanish |
Government |
Presidential republic |
president |
Currently, Venezuela is experiencing a presidential crisis, in which the legitimacy of the position is under question, and this is being disputed by Nicolás Maduro and Juan Guaidó. |
Vice president |
Delcy Rodriguez |
Independence |
Colonized by the Spanish Empire. |
Area |
916 445 km2, being 0.3% constituted by water |
Population |
31,977,065 inhabitants |
Coin |
sovereign bolivar |
Gross Domestic Product |
Total: US$320 billion, according to the International Monetary Fund |
HDI |
0.761 - 78th position |
Timezone |
UTC-4 |

Venezuela is located on the American continent, in the South America subcontinent.
General features
→ History
Venezuela was colonized by the Spanish Empire. Before the arrival of the explorers, the Venezuelan territory was inhabited by different peoples. In 1498, Christopher Columbus arrived on the Venezuelan coast and, in 1530, the Spanish began the period of colonization. In 1808, the movements for the liberation of colonies exploited by Spain began. After years of resistance, Venezuelans became independent in 1811.
→ Major cities
Caracas, capital of Venezuela, it is the largest city in the country and the one with the highest concentration of inhabitants. They are also important cities in the country: Maracay, Valencia, Mérida and Ciudad Guayana.

Caracas is the largest city in Venezuela and the one with the highest population concentration.
→ Demography
The Venezuelan population is quite mixed. Colonization made possible the mixture of Amerindian, African and European peoples. The Venezuelan people have Spanish as their official language, and some inhabitants also speak indigenous languages.
THE demographic density of Venezuela is 33 inhabitants per km2. It is one of the most urbanized countries in Latin America. Approximately 85% of the population lives in urbanized areas, and most of the population is concentrated in the north of the country. The most populous cities are:
• Caracas: 5,298,364 inhabitants
• Maracaibo: 2,450,599 inhabitants
• Valencia: 2,044,323 inhabitants
It is worth noting that Venezuela has one of the highest rates of urban violence in the world. A United Nations study, through the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime, released that the country's homicide rate was 79 per 100,000 population in 2013, one of the highest in the country. world.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
→ Religion
The predominant religion in Venezuela is the Roman Catholicism, covering about 85.7% of the population. The second religion with the most followers is Protestantism, with a total of 12% of the population. Then there is a small group of Jews and Muslims.
→ Climate
The climate in Venezuela varies with altitude. The predominant climate is the tropical, with temperatures between 24 ºC and 36 ºC, marked by variations in rainy periods. In mountainous regions, temperatures drop drastically, reaching 8ºC, which is characteristic of temperate zones. Above two thousand meters of altitude, temperatures can be negative. Annual rainfall varies between 430 mm and 1000 mm. It usually rains more in the months between June and October.
→ Hydrography

The Orinoco is the main river in Venezuelan territory.
The main river in the country responsible for the drainage of the hydrographic system is the river Orinoco. This one has its source in Parima, close to the border with Brazil. It has numerous tributaries, such as the Caroní, Cassiquiare and Apure rivers. There are two large basins in the country: the Atlantic Basin and the Caribbean Basin.
→ Vegetation
Venezuela has almost half of its territory covered by humid forests and broad foliage. The country is considered one of the seventeen countries megadiverse (group of countries that concentrate great biodiversity). Features tropical florests low altitude, closed and mangrove forests. In the coastal regions, it is possible to find species of palm trees, and in the more arid regions, cacti are concentrated.
Read too: Vegetation Types

On the coast of Venezuela, it is possible to find species of palm trees.
→ Fauna and Flora
Venezuela has great biodiversity both in fauna and flora. The fauna is represented by species such as the manatee, the pink dolphin and the orinoco crocodile. There are, in Venezuela, around 1,417 birds, such as the ibis and the turpial. Many species are endemic (they only exist in that location).
The flora is especially represented by the yellow ipe. In addition, the country has about 25,000 species of orchids. Approximately 38% of the 21,000 plant species found in Venezuela are endemic, that is, exclusive to Venezuelan territory.
→ Relief
Venezuela's relief can be divided into three main regions: the high reliefs, the plains and the Guyana massif. The first is the high relief region, with an emphasis on the Andes Mountains. In the southern region are the plains, known as the Llanos region. The Guianas massif region has an average altitude of 400 meters. In this region, there are also important elevations, such as the Roraima and Guanay Guaca mountains.
→ Politics
Venezuela configures a Presidential republic based on the 1999 Constitution. States have their own governors and are elected for a four-year term. The main political parties are the Acción Democrática, the Partido Social Cristiano and the Partido Socialista Unidos de Venezuela.
Historically, Venezuela has experienced numerous political crises and some attempted coups. Currently, the country is experiencing an intense scenario of political crisis, in which the position of president, occupied by Nicolás Maduro, is questioned by the international community.
know more: Venezuela's entry into Mercosur
→ Economy
Venezuela has a mixed economy based on oil market. The country has the cheapest gasoline in the world. This is possible because the gasoline that reaches the consumer is subsidized by the government. Venezuela is one of the main exporters of Petroleum of the world.
The industrial sector represents about 17% of the GDP, and the agrarian sector represents about 3%. The country exports products such as rice, corn, fruits and beef, however, it is not self-sufficient in this sector.
also know: What are the sectors of the economy?
Venezuela Map
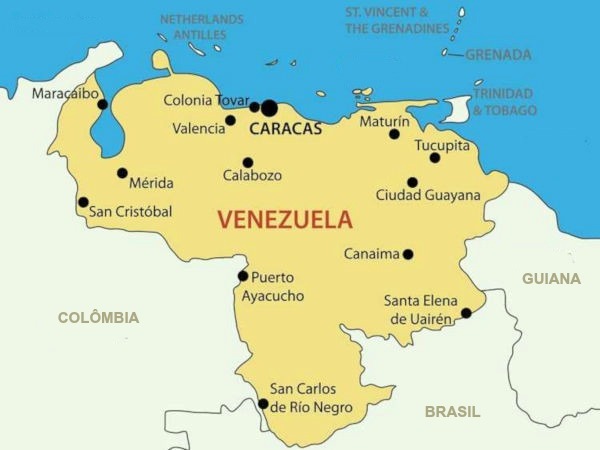
Venezuela is a country with little territorial extension, bordering other countries and the ocean.
Political and economic crisis in Venezuela
The crisis experienced in Venezuela has political and economic motivations and has been intensely reported in numerous media outlets. This dramatic crisis of humanitarian bias began in 2013 with the death of the former president of Venezuela, Hugo Chavez.
Chavez was succeeded by the current president, Nicolas Mature. Maduro intended to maintain a policy similar to that of Chávez, however, the scenario found in the country presented a different reality from that experienced by his predecessor.

Nicolás Maduro is the current president of Venezuela, however his position has been questioned and not recognized by some countries.*
Venezuela, in this period of transition between governments, presented high inflation rates, surpassing 800% per year. Oil barrel prices were well above average. Markets began to sell basic products at exorbitant prices, and the population began to live nightmare days.
THE instability lived in the Maduro government associated with the strong authoritarianism, the discontent of the population, the lack of basic supplies for survival, the high number of unemployed people and the poverty that has been created have forced Venezuela into a state of socioeconomic collapse.
The population began to protest, often violently, resulting in deaths. The political crisis worsened after a controversial election reelected Maduro to the presidency. However, some countries, such as the United States, Mexico and Brazil, did not recognize his success, accusing him of totalitarianism.
Read too:Crisis in Venezuela's economy and politics
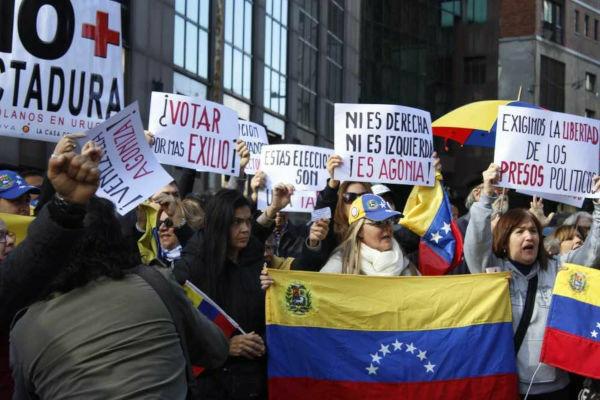

The Venezuelan population has organized numerous protests against the current government, accusing it of authoritarianism.**
What was bad before, got worse. According to the IMF (International Monetary Fund) inflation in 2018 reached 1,000,000%. The crisis worsened even more, Venezuelans began to live in miserable conditions, and many chose to leave the country in search of better living conditions. One of the main destinations is Brazil.
read more: Venezuelan immigration to Brazil
Currently, there is an intense debate regarding the legitimacy of the office of president. Some countries, such as Brazil and the United States, do not recognize the current government and appoint Juan Guaidó (who has declared himself interim president) as the country's new leader. Other countries, such as Russia and China, are in favor of Maduro.
________________
* Image credits: Marcos Salgado / Shutterstock
** Image Credits:sebastorg / Shutterstock
By Rafaela Sousa
Graduated in Geography