O Cardiovascular system, also called the circulatory system, it is the system responsible for ensuring the transport of blood throughout the body, thus allowing our cells to receive, for example, nutrients and oxygen. This system is formed by the heart and blood vessels.
→ Components of the cardiovascular system
The cardiovascular system is composed of the following structures:
Heart: organ responsible for ensuring the pumping of blood;
Blood vessels: they are tubes through which blood passes. The three main types of blood vessels are: arteries, veins and capillaries.
→ Heart

Note the main parts of the heart.
O heart of human beings, like that of other mammals, is a organmuscular formed by four chambers: two atria and two ventricles. The atria are the chambers responsible for guaranteeing the reception of blood in the heart, while the ventricles are the chambers responsible for guaranteeing the pumping of blood out of the heart.
On the left side of the heart, only blood rich in oxygen is seen, while on the right side, only blood rich in carbon dioxide is observed. In the heart, there is still the presence of
fourvalves that prevent the backflow of blood, thereby allowing a continuous flow.Read too: heart breath
The heart has three layers or tunics: the endocardium, the myocardium and the epicardium. The endocardium is the innermost layer. The myocardium is the middle layer, which is formed by striated cardiac muscle tissue, which is, therefore, responsible for ensuring that the blood is pumped properly due to the contractions muscle. The myocardium is the thickest layer of the heart. Finally, we have the epicardium, which is the outermost layer. It is in the epicardium that the fatty tissue layer that usually surrounds the organ accumulates.
The heart is able to contract as well as relax, the contraction of systole and the relaxation of diastole. When it contracts, it pumps blood and when it relaxes, it fills with blood. In humans, heartbeats originate in the heart itself. The region that originates the heartbeat is called the sinoatrial node and it is characterized as a cluster of cells that produce electrical impulses.
→ Blood vessels

Blood vessels are responsible for ensuring the transport of blood throughout the body.
Blood vessels are a large closed tube system where the blood circulates. The three main blood vessels found in the body are the arteries, veins and capillaries. See below some basic characteristics of these three vessels:
Arteries: Arteries are vessels that carry blood from the heart to the organs and tissues of the body. In these vessels, blood runs at high pressure. Arteries branch into arterioles.
Capillaries: They are very thin blood vessels that guarantee the exchange of substances between the blood and the tissues of the body.
Veins: Blood capillaries converge to the so-called venules, which converge to the veins. Veins are the vessels that ensure blood returns to the heart. In these vessels, blood flows at low pressure and to prevent blood reflux, the veins are equipped with valves.
Read too:Difference between vein, artery and capillary
→ Circulation in human beings
the blood reaches the heart through the right atrium through the veinsarmholes. This blood is rich in carbon dioxide and poor in oxygen. This deoxygenated blood then proceeds to the right ventricle. From the right ventricle, it is pumped to the lungs via the pulmonary arteries.
US lungs, the process of hematosis occurs, the blood until then rich in carbon dioxide receives oxygen from pulmonary respiration. Oxygen-rich blood returns to the heart via veinslungs, reaching this organ through the left atrium. From the atrium, it goes to the left ventricle.
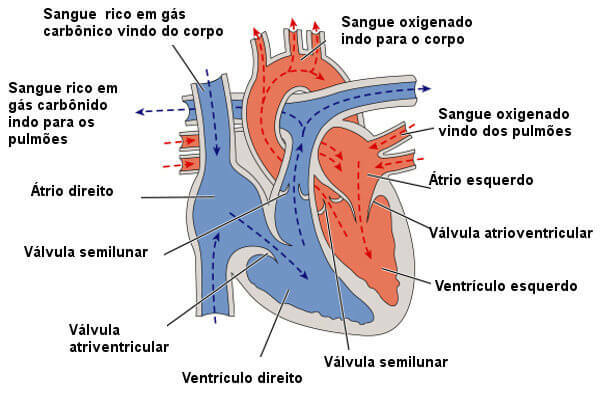
Observe how the blood flows in the heart.
From the left ventricle, blood flows to the body, leaving the heart through the aorta artery. The blood then travels to the various organs and tissues in the body. In capillaries, gas exchange takes place. The oxygen present in the blood passes to the tissues and the carbon dioxide produced in cellular respiration passes to the blood.
Capillaries come together to form venules, which form veins, which continue to carry oxygen-poor blood to the heart. The superior and inferior vena cava ensure that blood rich in carbon dioxide is taken to the right atrium.
Read too: Obesity and cardiovascular disease
→ Systemic and pulmonary circulation
Circulation in human beings is called dual circulation, since the presence of two circuits: systemic circulation or large circulation and pulmonary circulation or small circulation:
Systemic circulation or large circulation: It concerns the circuit that the blood makes starting from the heart towards the various tissues of the body and then returning to this organ. Upon reaching the lung, blood is driven to the body. In capillaries, gas exchange takes place, and the blood, now rich in carbon dioxide and poor in oxygen, returns to the heart.
Pulmonary circulation or small circulation: It concerns the circuit performed by blood from the heart to the lungs and its return to the heart. In this circuit, the oxygen-poor blood leaves the heart, travels to the lung, where it is oxygenated, and returns to the heart.
→ Exercise solved
Below is an exercise that addresses the cardiovascular system.
|
(Vunesp) It is very common to hear the following statement: "The arteries carry arterial blood, rich in oxygen, and the veins carry venous blood, poor in oxygen". However, this generalization is incorrect, as venous blood (that which runs in the veins) is not it is always poor in oxygen, and arterial blood (that which runs in the arteries) is not always rich in oxygen. Which of the vessels listed below could exemplify that this generalization does not occur in mammals? I. Vessels that exit the left ventricle of the heart. II. Vessels that reach the left atrium of the heart. III. Vessels that exit the right ventricle of the heart. IV. Vessels that reach the right atrium of the heart. Of the above statements, only: The) I and II B) I and III ç) II and IV d) II and III. and) II and IV |
Resolution: The arteries that carry blood rich in carbon dioxide are the pulmonary arteries, while the veins that carry blood rich in oxygen are the pulmonary veins. So the correct answer is letter D.
By Ma. Vanessa Sardinha dos Santos
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/biologia/sistema-circulatorio.htm
