Israel is a country of Middle East washed by the Mediterranean Sea. It has an area of 22 thousand km² and currently has a population of 8.6 million inhabitants. Its recognition as a State officially took place in 1948. The capital, however, is not an international consensus. Israel claims as such the city of Jerusalem, whose eastern portion is disputed by Palestine. The city of Tel Aviv, on the other hand, is home to many embassies from other countries and is recognized as a capital.
The Israeli territory has a very heterogeneous relief and climates ranging from temperate to arid in extensive desert regions. The country's economy is developed and diversified, with emphasis on the technological and industrial sectors. Furthermore, religious tourism emerges as an important economic activity.
Read too: Causes of conflicts between Palestine and Israel
Israel general data
Official name: State of Israel.
Gentile: Israeli.
Territorial extension: 22,072 km².
Location: Middle East.
Capital: Israel considers the city of Jerusalem as its capital, home to the seat of government. There is, however, no international consensus on this issue. The city of Tel Aviv is also considered the capital and is home to the headquarters of several international embassies.
Climate: temperate and semi-arid tropical.
Government: parliamentary democracy.
Administrative division: six districts.
Language: Hebrew (official).
-
Religions:
Judaism: 74,3%;
Islam: 17,8%;
christianity: 1,9%;
druse: 1.6%;
others: 4.4%.
Population: 8,656,000 inhabitants (UN, 2020).
Demographic density: 400 inhab./km² (UN, 2020).
Human Development Index (HDI): 0,919.
Coin: new Israeli shekel (NIS).
Gross Domestic Product (GDP): US$446.71 billion (IMF, 2021).
GDP per capita: US$ 47,600 (IMF, 2021).
Gini: 0.390 (World Bank, 2016).
Timezone: GMT +2 hours.
-
External relations:
UN;
OECD;
IMF;
world Bank.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
history of Israel
The creation of the State of Israel is quite recent, having taken place in the middle of the 20th century. The history of occupation of the region where he is currently located, however, began in the PPaleolithic period and it developed through numerous foreign occupations, imperial dominions, and territorial disputes. From the Roman Empire, the region became known as Palestine, and the direct conflict between Jews and Romans culminated in the expulsion of the first around 70 AD.
A few centuries later, in the year 636, the region became part of the Arab Muslim domain, which remained there until the turn of the 19th to the 20th century. This period also marked, on the other hand, the emergence of a movement, known as Zionism, which aimed the return of the Jews to the region.
The ideals of the Zionist movement also included the creation of a Jewish State, an idea that was gradually consolidating and gaining more supporters, notably during the Second World War (1939-1945). The events that made the creation of Israel they began, however, at an earlier time, shortly after the end of the First World War (1914-1918), which was when England advanced over the area and began to exercise its dominion over the region.
The period after the conflict heightened tensions between Jews and Palestinians (Muslim Arabs), leading to the occurrence of armed attacks and violent offensives by both sides for the exercise of control over those territories. The intermediation of the investees was carried out by the United Nations (UN), which, in 1947, started to the process of territorial division through the creation of the Special Committee for Palestine (UNSCOP, acronym in English). The following year, the State of Israel became official. Since then, the country started to annex new areas to its territory, which triggered a series of clashes with the Palestinians, a people that has remained stateless to date.
See too: Causes and context of the First Arab-Israeli War
Israel map
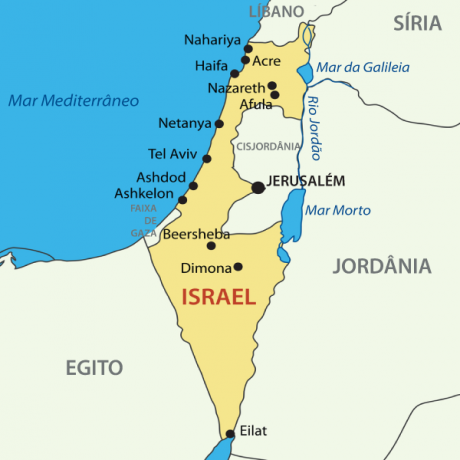
Israel geography
Israel it is a country in the middle east which currently occupies an area of 22,072 km². To the west the territory has an exit to the Mediterranean Sea, while bordering:
to the north, with the Lebanon;
to the east, with the Syria and with the Jordan, where the territory of the West Bank is also located;
and to the southwest, with the Egypt.
In the same region is a narrow territory called the Gaza Strip.
Eastern boundaries include the Sea of Galilee, the River Jordan and the Dead Sea. To the south, Israel has a narrow exit to the Red Sea, where the Gulf of Eilat or Aqaba is situated.
Israel climate
Israeli territory has very contrasting weather conditions, which is due to the influence of the Mediterranean Sea and the extensive desert areas that extend across the south of the country and also across much of the Middle East.
Thus, to the east and in the vicinity of the Negev Desert, arid and semiarid climates predominate, characterized by high temperatures and low rainfall. In Eilat, for example, the southernmost point of Israel, the maximums can reach 40º C and the annual rains accumulate only 34 mm.
In the coastal strip and in the higher regions, milder temperatures and considerable amounts of rain predominate, especially in the north of the country. In these areas, accumulation can reach up to 1,200 mm. Regarding temperatures, these can range from 4º C, in the cold months, to 30º C, in the hot period.
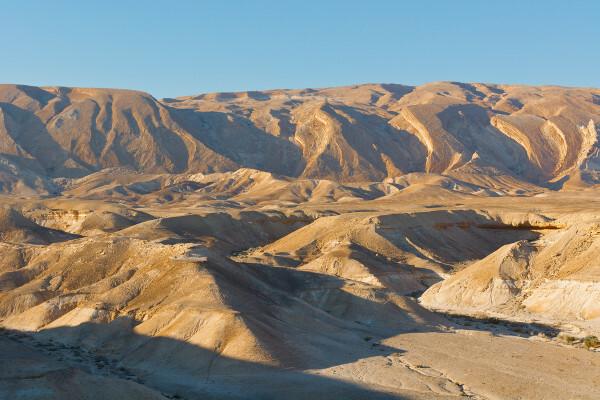
Israel relief
The Israeli relief can be divided into four different units. The first one is the coastal plain, located on the coastal strip with an exit to the Mediterranean. To the north is the mountainous region, which brings together the highest elevations in the country, where the Galilee Mountains and the Golan Heights are located. Along the eastern strip extends the Jordan River Valley, an area of geological fault that ends in the Gulf of Aqaba. The south of the country is characterized by depressions and plateaus.
Stay on Mount Hermon the highest point in Israel, at approximately 2,236 meters above sea level.

Vegetation of Israel
The vegetation cover of the the north of the country is made up of coniferous and oak forests., which gradually replaced the once dominant Lebanese cedar. From the center-north onwards, there are extensive areas planted with orchards and varied agricultural crops.
The higher lands are covered by smaller species such as wild shrubs and maquis, in addition to trees such as oaks. On the coast predominates the dune vegetation, while in the desert areas, to the south, the coverage is quite rare, although it is possible to observe the presence of date palms and pistachios in areas where there is groundwater availability.
Israel hydrography
The Jordan is the main river that runs through Israeli territory.. Also noteworthy are the Sea of Galilee, which consists of a 166 km² lake also located to the north, and the Dead Sea, which is partially located in Israel, to the south.
Read too: Nile River - the largest river in terms of territorial extension
Israel Demographics
Israel has a population of 8,656,000, according to UN information for 2020. This figure includes East Jerusalem, which is also claimed by Palestine as its capital. The population distribution in the country is 400 inhab./km², with the majority of Israelis concentrated near the coast and in the northern areas of the country. Southern Israel has very low demographic density, in view of the arid conditions provided by the presence of the Negev desert.
The country's population is predominantly urban, with a rate of 92.7%. The metropolitan region of Tel Aviv has more than one million inhabitants, while the city itself has a contingent of 435,000 people. Jerusalem, the capital claimed by Israel, today has 944,000 inhabitants. Also noteworthy is the city of Haifa, on the north coast, with 280 thousand inhabitants.

Jews represent 74.3% of the Israeli population, most of whom are natives of the country. The second most populous group is the Arabs, who represent 20.9% of the inhabitants. The remaining 4.7% are composed of other unspecified ethnic groups. The official language of Israel is Hebrew, being the most spoken language followed by Arabic.
It is worth mentioning the high HDI from the country, which is 0.919, 19th in the world ranking. Israel still has the 10th longest life expectancy on a world scale, which is 83.15 years old.
flag of israel

Israel's economy
The Israeli economy is well developed and diverse, centered on the service sector. It has an advanced technological base, which contributed to a rapid growth process from the early 2000s until 2013, when the effects of the global economic crisis hit the country. Israel's GDP growth in the period in question was due to the increase in exports, which are led by pharmaceuticals, medical instruments, refined oil, integrated circuits and diamonds.
The industry accounts for 21.5% of the GDP of Israel, which currently stands at US$446.71 billion (IMF, 2020). It consists of branches ranging from food, textile, wood, civil construction and petrochemicals to products of high technology, such as electronic instruments used by medicine, telecommunications, aviation and others. Despite the restricted area, mining also stands out with the production of diamonds and agricultural supplies, such as potassium nitrate and derivatives of Petroleum.
THE agricultural activity it is very dependent on irrigation, and its production is mainly focused on the domestic market supply. Among the main crops are potatoes, tomatoes, carrots, fruits and other foodstuffs. In addition, poultry and egg production, as well as milk, stand out.
It is also worth emphasizing the importance of tourism, especially religious, for the economy of that country, with emphasis on the pilgrimage of the faithful in the city of Jerusalem.
![Tourist activities linked to religious tourism are important income generators for Israel. [1]](/f/76b06776ed7233783497e49a74f18b1a.jpg)
Israeli culture
Israeli culture has great religious influence in its formation, notably of the Jewish faith. Traces of other nationalities can also be found in its various manifestations, such as Iraqis, Russians, Moroccans, Ethiopians and Poles. In addition to the religious aspect, expressed mainly in Israel, secular culture and modern customs and traditions are very well represented by Tel Aviv, one of the largest cultural centers in the country.
The main holidays and events celebrated follow the Hebrew religious calendar. In addition, the Remembrance Day of the Holocaust, in memory of the victims of that genocide, and Independence Day. The country is also home to the Holocaust Museum and Diaspora Museum, in the city of Tel Aviv. Israel also has a tradition in music and literature, whose works are produced mainly in Hebrew.
In gastronomy, the kosher cooking it is practiced by many members of the Jewish community. It is characterized by certain eating rules, such as prohibited food combinations, which are respected by religious. Some of the country's typical dishes are falafel (chickpea dumpling), msabahha, which has humus in its composition, and shakshuka, a preparation of eggs cooked in tomato sauce.
See too: What is cultural appropriation?
Israel Infrastructure
As an urbanized country, Israel has a extensive network of infrastructure to serve its population.UN data show us that almost all inhabitants have access to safe drinking water. The same happens with basic sanitation, whose networks serve 93% of Israelis. It is also noteworthy that a large and growing portion of the population, 81.58%, has access to the internet today.
Electricity, which reaches almost all of the country's inhabitants equally, comes mostly from fossil fuels, which represent 95% of installed capacity.
Displacements are made mainly through highwayss, which add up to 19,555 km, among which is Trans-Israel, which branches into several other roads. The railway network is much less dense and has 1,384 km of railways. With regard to air transport, the main connections are made through Ben-Gurion International Airport. Entries and exits by sea are via the ports of Eilat, Haifa, Hadera and Ashdod.
Israeli government
The Israeli government is of the type parliamentary democratic, in which the president represents the head of state, while the prime minister plays the role of head of government. The country's claimed capital is Jerusalem, home to the seat of the executive branch. A part of this city, however, is considered by the Palestinians as their capital. Tel Aviv is recognized by many in the international community as an Israeli capital.
Curiosities about Israel
Its name is derived from the ancient Kingdom of Israel, which, in turn, was based on the biblical text in which Jacob, considered the patriarch of the Jews, was named Israel.
The city of Jerusalem is today one of the main religious tourist destinations in the world and annually receives thousands of Jews, Christians and Muslims.
The Wailing Wall is one of Judaism's greatest sacred symbols and Jerusalem's main point of visitation.
It is not possible to dive in the Dead Sea, a body of water that is understood as part of Israeli territory. This is due to its high salinity. Furthermore, it is considered one of the lowest elevation points on the planet.
The biggest LGBTQ+ parade in the Middle East takes place in the city of Tel Aviv.
Image credit
[1] S1001 / Shutterstock
By Paloma Guitarrara
Geography teacher

