You nucleic acids can be defined as polymers (macromolecules formed from smaller units) composed of molecules known as nucleotides. The two existing nucleic acids are the deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) it's the ribonucleic acid (RNA). They are responsible for encoding and translating the information that determine the synthesis of the various proteins found in living beings.
Nucleic acid function
Nucleic acids are complex molecules responsible for store andtransmit the informationions geneticss, as well as ensure your translation. The storage and transmission of this information is guaranteed through DNA. Translation, in turn, is a role of RNA and is nothing more than the protein synthesis, which is guided by the genetic information provided by the DNA. Some RNA molecules also have enzymatic capacity, being known as ribozymes.
Read too: Biology concepts that should not be confused in Enem
Mind Map: Nucleic Acids

*To download the mind map in PDF, Click here!
Nucleic acid structure
Nucleic acids are formed by nucleotides, molecules composed of three components:
- Phosphate group;
- Sugar five-carbon (pentose);
- Nitrogen base (base containing nitrogen).
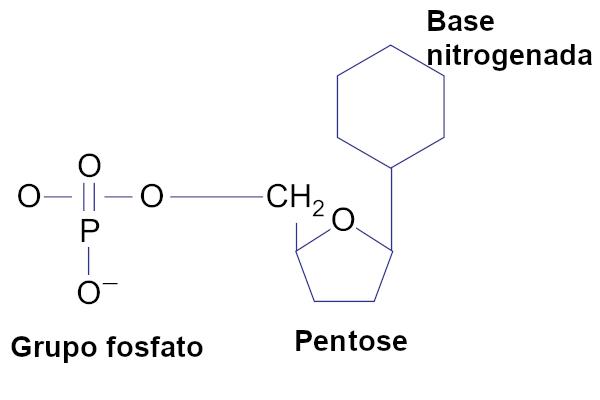
DNA and RNA, which are the two types of nucleic acids that exist, have differences in their nucleotides. The five-carbon sugar can be the ribose or deoxyribose. These sugars are differentiated in that deoxyribose has one less oxygen atom than ribose. Deoxyribose is present in DNA, whereas ribose is found only in RNA.
The nitrogenous bases of a nucleotide are also varied. They are nitrogen bases adenine, guanine, thymine, cytosine and uracil. They are grouped into two groups: pyrimidines and purines. Each nitrogenous base has one or two rings with nitrogen atoms.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
In the pyrimidines, the presence of a six-atom ring, including carbon and nitrogen, is observed. already in the purines, there is the presence of a six-atom ring fused to a five-atom ring. Cytosine, thymine and uracil are pyrimidines, while adenine and guanine are purines. In DNA, the nitrogenous bases cytosine, guanine, adenine and thymine are present. In RNA, in turn, thymine is absent and, in its place, we find uracil.

The nucleotides are linked through phosphodiester bonds, that is, a phosphate group connecting two sugars of two nucleotides. This bond is responsible for forming a pattern of sugar-phosphate units.
When the nucleotides bind together, the two free ends of the polymer are seen to be different from each other. At one end is the phosphate group, attached to carbon 5'; in the other, we have a hydroxyl group attached to the 3' carbon. These ends are called the 5' and 3' ends. throughout the sugar-phosphate chain, the nitrogenous bases are linked.
the DNA
O DNA is the nucleic acid responsible for store the hereditary information. The genetic information in this molecule is organized into units called the genes, which are inheritable.
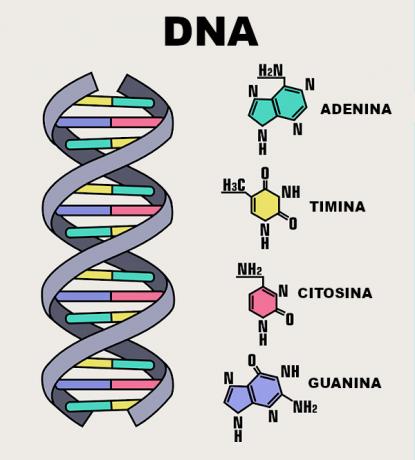
This nucleic acid is formed by two polynucleotides spirally arranged around an imaginary axis (double-helix). The sugar-phosphate chains are organized more externally and are joined through hydrogen bonds established between the more internally arranged nitrogenous base pairs. The sugar found in DNA nucleotides is the deoxyribose.
It is worth noting that the nitrogenous bases of the nucleotides are paired in a specific way. THE adenine only pairs with thymine, while the guanine always pairs with cytosine. With that, we have that the two chains in the DNA double helix they are complementary, so when we know the base sequence of one strand, we immediately know the bases of the other strand.
A curious fact is that molecules of DNA are too long, being formed by several nucleotides. DNA is the largest macromolecule in the cell.
Read too: Genes - the fundamental unit of heredity
the RNA
O RNA is a nucleic acid related to protein synthesis. in addition tosso, some RNA molecules have a catalytic function, being called ribozymes.
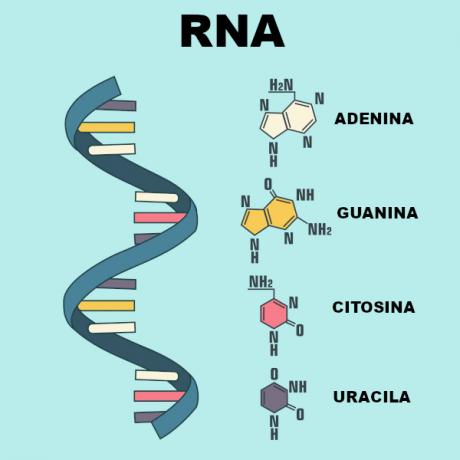
RNA molecules, unlike DNA molecules, present themselves as simple chains. In some situations, pairing occurs, but with bases present in the same chain. These combinations give the RNA the formation of three-dimensional structures. The RNA sugar is the ribose and its nitrogen bases are the cytosine, guanine, adenine and uracil. Aadenine only pairs with uracil, and guanine always pairs with cytosine. To learn more about this nucleic acid, read:RNA Types.
By Vanessa Sardinha dos Santos
Biology teacher
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
SANTOS, Vanessa Sardinha dos. "Nucleic acids"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/biologia/acidos-nucleicos.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.