Energythermal is a broad term, used to express different thermodynamic quantities, such as internal energy or an amount of heat exchanged between systems of many differenttemperatures. In this article, we will treat thermal energy as a synonym for energyinternal, which can be understood as the sum of the energieskinetics and potential From atoms and molecules that make up a thermodynamic system.
Lookalso:Before continuing, check out an amazing summary on thermology
Thermal energy
Energythermal is the result of sum gives energykinetics and potential of all the constituent particles of a body. thermal energy It dependsdirectly gives temperatureabsolute of the body, measured in kelvin (K), and also depends on the amount of degreesinfreedom of the system, that is: the number of directions in which molecules can move, vibrate, oscillate or even rotate.
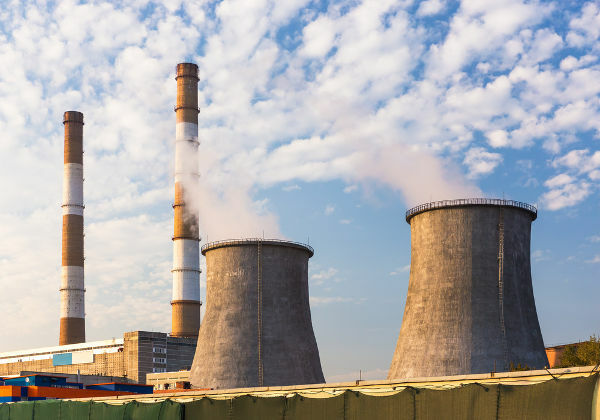

O theoremgivesequipartition of energy states that: at each degree of freedom of a system, its internal energy can be calculated from an integer multiple of the expression ½ k BT, where Kb is the constantinBoltzmann and T is the temperature measured in kelvin. The formula used to calculate the thermal energy of an ideal monoatomic gas is shown below, check it out:
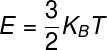
KB – Boltzmann constant (KB = 1,38.10-23 m².kg/s². K)
Since the thermal energy of ideal gases is expressed by the above formula and represents the energykineticsaverage of the system, we can write the following equality:
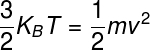
Lookalso:After all, what color is the water?
Using the formula above, it is possible estimatethe average translational speed of the atoms present in the atmospheric gas. Taking into account a temperature of 25 °C and taking atoms of oxygen (M = 16 g/mol), we found an average speed of 680 m/s or 1525 km/h — this is the speed at which atmospheric gas particles hit us all the time.
In the case of a diatomic gas, the factor ½k is added to the expression used for monoatomic gasesBT, due to the increase of one degree of freedom, resulting in the following expression:

According to the first law of thermodynamics, a energythermal of a system can be converted into other forms of energy, such as heat and work. The heat, for example, refers to the transferinenergythermal,exclusively due to temperature difference between a system and its surroundings; work, in turn, concerns the application of forces on the system or by the system.
In this sense, the work can be used to move a piston, as in steam-powered locomotives, and also in internal combustion engines, which power virtually all current motor vehicles. Below, we bring the first law of thermodynamics, note:
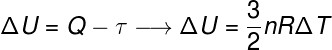
According to the 1st law of thermodynamics, the variation of internal energy is the difference between work and heat.
There are other ways to calculate the thermal energy modulus of a body, in the case of gasesideals, in which the potential energy between particles is considered null, for this we express the internal energy in terms of the number of moles (n) and also from the universal constant of perfect gases (R), check:
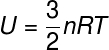
n - number of moles (mol)
R – universal constant of perfect gases (R = 0.082 atm. L/mol. K or 8.31 J/mol. K)
Still within the scope of perfect gases, combining the clapeyron equation (PV = nRT), with the energy definition exposed, it is possible to get a new expression, note:

P – pressure (Pa)
V – volume (m³)
See too:Warm air rises and cold air falls, but why?
Advantages and Disadvantages of Thermal Energy
Everyday, we make use of a large number of sourcesinenergythermal to produce energy. O Human Body, for example, consumes a lot of nutrients to generate the thermal energy necessary for the functioning of our vital processes. much of the electricity produced in the world it depends on our ability to transform thermal energy into electricity.
Check out the means that use thermal energy to produce electricity and its main advantages and disadvantages:
type of plant |
Benefits |
Disadvantages |
thermonuclear plant |
Low emission of polluting gases and high efficiency |
Radioactive waste production and radiation exposure |
Coal-fired thermoelectric power plant |
Large energy production and low cost |
Emission of polluting and greenhouse gases |
Thermoelectric power plant powered by natural gas |
Less pollution than coal burning |
Its cost varies a lot, since natural gas is a petroleum derivative |
Biomass-powered thermoelectric plant |
Low installation cost and low greenhouse gas emissions |
Deforestation and large monoculture plantations |
geothermal plant |
Does not polute |
High installation and maintenance cost |
See too: Learn hydrostatics once and for all!
Exercises on thermal energy
Question 1) Two moles of an ideal diatomic gas meet at a temperature of 127 °C. The thermal energy of this gas is approximately:
Data: R = 8.31 J/mol. K
a) 1.5.106 J
b) 1.7.104 J
c) 8.5.103 J
d) 5.3.104 J
e) 8.5.104 J
Template: Letter B
Resolution:
Let's calculate the energy of the gas using the following expression, since the gas is diatomic, however, before doing so, it is necessary to convert the temperature from degrees celsius to kelvin, note the calculation:
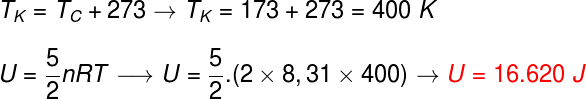
According to the calculations, this diatomic gas has an energy of 16,620 J, that is, approximately 1,7.104 J, if expressed in scientific notation and using the rounding rules.
Question 2) Three moles of an ideal monoatomic gas receive an amount of heat equal to 5.102 cal and performs a job of 2.102 lime during the process. Determine the temperature variation experienced by this gas, in degrees Celsius.
Data: R = 0.082 atm. L/mol. K
a) 214°C
b) 813°C
c) 1620 °C
d) 740°C
e) 370°C
Template: Letter B
Resolution:
To solve this exercise, it is necessary that we combine two distinct formulas, the first law of thermodynamics, which determines the energy variation, and the formula of the thermal energy of the ideal monoatomic gas, watch:
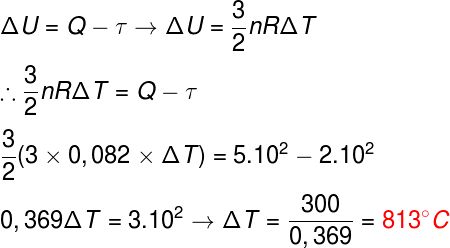
After we have replaced the data in the formulas, we find a variation of 813 °C, so the correct alternative is the letter B.
By Me. Rafael Helerbrock
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/fisica/energia-termica.htm
