THE asexual reproduction it is a type of reproduction in which only one individual is a parent, and this individual passes on his genes to his offspring. It does not involve the encounter of gametes and, therefore, there is no genetic variability, and the descendant, if there are no mutations, genetic copies equal to the individual who formed it.
The lack of genetic variability is unfavorable from an evolutionary point of view, as the presence of unfavorable characteristics in a population can lead to its decline. Some of the main types of asexual reproduction are the binary division, fragmentation, budding, parthenogenesis and vegetative propagation.
Read too: What is genetic variability?
What is asexual reproduction?
Asexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that happens without the encounter of gametes, thus not having the junction of genetic material. Thus, the individuals generated are, in almost all cases, genetically identical to those who formed them. For this reason, we can say that asexual reproduction is responsible for the formation of
clones. It is noteworthy, however, that differences may occasionally occur due to mutational processes.This type of reproduction can occur in different organisms, being observed in both unicellular and multicellular beings. As an example of unicellular beings that reproduce in this way, we can mention the bacteria. As an example of multicellular beings, we can mention bees, which give rise to drones through parthenogenesis processes.
Read too: General characteristics of living beings
Types of Asexual Reproduction
There are different types of asexual reproduction. Let's see below the main characteristics of some of them.
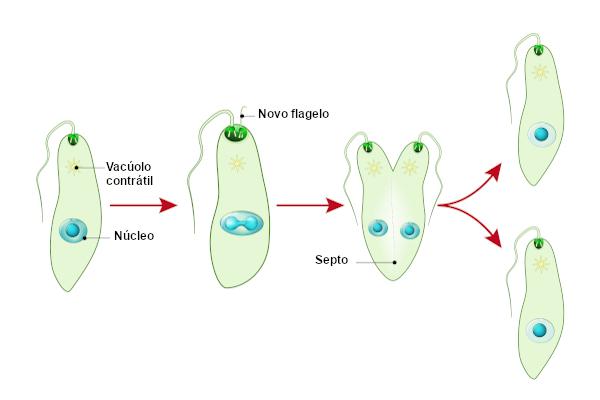
Binary division: also known as bipartition and cissiparity, individuals divide in half, giving rise to two individuals of approximately the same size. This process can be observed, for example, in protozoa and bacteria.
-
Multiple division: the cell divides and gives rise to three or more daughter cells. Initially the nucleus undergoes a series of divisions, which are followed by the division of the cytoplasm. This type of reproduction can be observed, for example, in the protozoan that causes the malaria (gender Plasmodium).
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
Sporulation: it is observed the formation of structures called spores, which consist of a cell surrounded by a resistant cell wall, which protects it from unfavorable conditions in the environment. When finding suitable conditions, the spore divides and gives rise to a new individual, without the need to join another cell. Sporulation is observed in plants, algae and fungi.
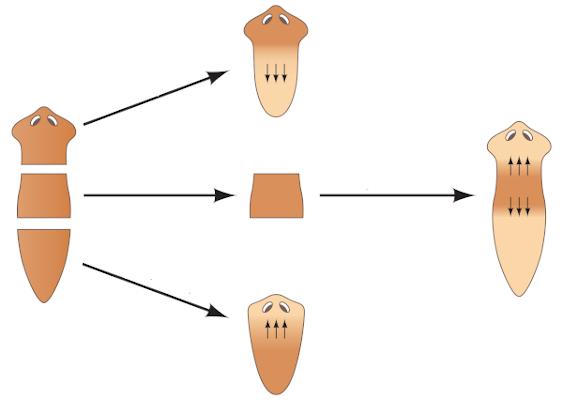
Fragmentation: also called regeneration, in it occurs the emergence of a new individual from a fragment. In this case, there are two steps: the fragmentation of an individual and the regeneration of that fragment, forming a new individual. This type of reproduction can be observed in different groups, such as sponges and cnidarians. It can also be seen when we cut a planarian into several parts. Each of these parts is capable of regenerating and giving rise to other planarians. It is worth noting that the planarian can spontaneously divide its body in a process called schizogenesis.
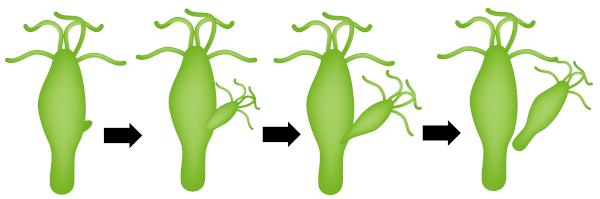
Budding: there is the emergence of a bud in the body of an already existing individual. This bud can detach itself from the individual that originated it or remain attached to it. This last case can be observed, for example, in the corals, in which the shoots remain attached, forming colonies.
Parthenogenesis: there is the development of the female gamete, which gives rise to a new being without it having been fertilized. One of the classic examples of parthenogenesis occurs in bees, a process in which the drone is formed. It is noteworthy that, in vertebrate animals, parthenogenesis in sharks, for example, has also been observed.
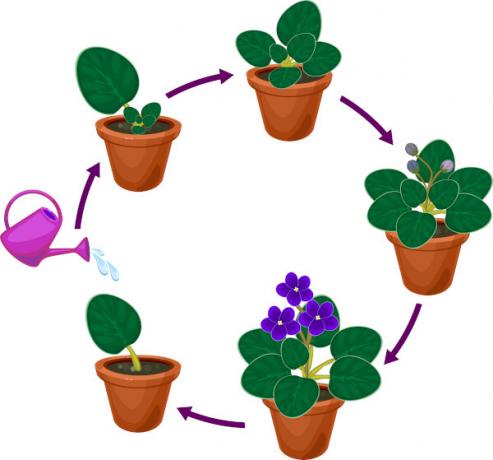
Vegetative Propagation: it is an asexual reproduction typical of vegetables. In this case, vegetative structures (root, stem and leaf) are capable of generating a new plant. Cassava and sugar cane, for example, can be propagated in this way.
Read too:Bees, invertebrate animals that can reproduce asexually
Difference between asexual and sexual reproduction
At sexual reproduction, there is the participation of gametes, so individuals are generated with unique combinations, which result from the genes inherited from the father and mother. Therefore, genetic variability is observed, which is absent in asexual reproduction. Sexual reproduction is also considered more complex than asexual reproduction, but it makes it possible to obtain fewer offspring and is slower.
By Vanessa Sardinha dos Santos
Biology teacher
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
SANTOS, Vanessa Sardinha dos. "Asexual reproduction"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/biologia/assexuada.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.