THE photosynthesis, a term that means “synthesis using light”, is generally defined as the process by which an organism manages to obtain its food. This process is carried out thanks to solar energy, which is captured and transformed into chemical energy, and occurs in tissues rich in chloroplasts, one of the most active tissues is the chlorophyllian parenchyma found in leaves.
Read too: plant nutrition
→ Photosynthesis steps
In plants, photosynthesis happens in chloroplasts and is characterized by the various chemical reactions observed. These reactions can be grouped into two main processes.
Light reactions: occur in the thylakoid membrane (inner chloroplast membrane systems).
carbon fixation reactions: occur in the chloroplast stroma (dense fluid inside the organelle).

In photosynthesis, carbon dioxide is used and oxygen is released. Gas exchanges with the medium happen thanks to the presence of stomata.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
→ Photosystems
Before understanding each reaction that takes place in photosynthesis, we must know where some of these reactions take place. Light reactions happen, for example, in the thylakoid membrane, more precisely in the so-called
photosystems.Photosystems are units in chloroplasts in which chlorophylls a and b and carotenoids are inserted. In these photosystems, it is possible to perceive two portions called the antenna complex and the reaction center. In the antenna complex, pigment molecules are found that capture light energy and take it to the reaction center, a place rich in proteins and chlorophyll.
In the photosynthesis process, it is possible to verify the presence of two photosystems linked by an electron transport chain: o photosystem I it's the photosystem II. Photosystem I absorbs light with wavelengths of 700 nm or more, while Photosystem II absorbs wavelengths of 680 nm or less. It is noteworthy that the designation of photosystems I and II was given in the order of their discoveries.
→ light reactions
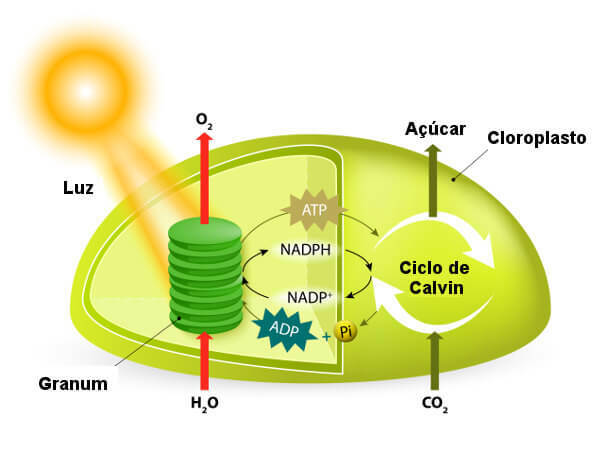
Note the diagram with the main points of the photosynthesis process.
In light reactions, initially the light energy enters the photosystem II, where it is trapped and carried to the chlorophyll P molecules680 of the reaction center. This chlorophyll molecule is excited, its electrons are energized and transported from the chlorophyll towards an electron acceptor. For each transferred electron, it is replaced by an electron from the water photolysis process.
Pairs of electrons leave the photosystem I by an electron transport chain, boosting the production of ATP (large source of chemical energy) by the process known as photophosphorylation. The energy absorbed by photosystem I is transferred to chlorophyll P molecules700 of the reaction center. Energized electrons are captured by the coenzyme NADP+ molecule and replaced in chlorophyll by electrons from photosystem II. The energy formed in these processes is stored in NADPH and ATP molecules.
Read too: What is ATP?
Mind Map: Photosynthesis

* To download the mind map in PDF, Click here!
→ carbon fixation
In carbon fixation reactions, NADPH and ATP produced earlier in light reactions are used to reduce carbon dioxide to organic carbon dioxide. At this stage, a series of reactions called Calvin cycle. In this cycle, three CO molecules2 they combine with a compound called ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP), forming an unstable intermediate compound that breaks down to produce six molecules of 3-phosphoglycerate (PGA).
The PGA molecules are then reduced to six molecules of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (PGAL). Five PGAL molecules rearrange themselves and form three RuBP molecules. The gain of the Calvin cycle is then of a PGAL molecule, which will be used for the production of sucrose and starch.
→ photosynthesis equation
The balanced equation for photosynthesis can be described as follows:
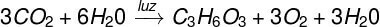
Look at the balanced equation of photosynthesis.
It is important to highlight that, generally, the formation of glucose as produced carbohydrate is observed in the photosynthesis equation. However, in the photosynthesis process, the first carbohydrates produced are sugars made up of just three carbons.
→ Importance of photosynthesis for the ecosystem
Photosynthesis is undoubtedly essential for ecosystems, being responsible, for example, for the oxygen supply, which is used by most living beings for processes of obtaining energy (cellular respiration). We must not forget that photosynthesizing organisms are part of the first trophic level of food chains and webs, and they are, therefore, the base in the trophic chain.
In photosynthesis, plants and other photosynthetic organisms are able to convert solar energy into chemical energy. When consumed, the energy accumulated by producers passes to the next trophic level. Thus, we can conclude that, for an ecosystem to function properly, it depends on the capture of solar energy and its conversion to the biomass of photosynthetic organisms.
Read too: food chain and web
→ Photosynthesis and Chemosynthesis
Photosynthesis and the chemosynthesis are two processes performed by autotrophic organisms. Chemosynthesis stands out for being a process in which solar energy is not needed. process performed by many organisms that live in extreme environments, such as hydrothermal vents in the abysses oceanic. In chemosynthesis, organic molecules are synthesized using chemical energy from inorganic compounds. In photosynthesis, in turn, there is a process in which organic compounds are formed using the light energy absorbed by special pigments.
→ Photosynthesis Summary
Photosynthesis is a process in which solar energy is captured and used to produce organic molecules.
Photosynthesis takes place in chloroplasts.
Chlorophyll and carotenoids are arranged in the thylakoids of chloroplasts, in units called photosystems.
Two steps can be observed in photosynthesis: light reactions and carbon fixation reactions.
At the end of photosynthesis, carbohydrates are produced.
Photosynthesis ensures that oxygen is made available to the environment.
Photosynthetic organisms are producers in the food chain.
By Ma. Vanessa dos Santos
