Seaquake is a phenomenon that occurs on the ocean floor due to intense movement on the borders of tectonic plates, through volcanic eruptions or because of landslides submerged in the ocean. This movement generates the earthquakes (earthquakes), which, in turn, cause agitation in ocean waters and originate gigantic waves, that propagate with great intensity and high destructive power.
Tsunami Formation
The tsunamis form from the displacement of large oceanic waters and give rise to waves that propagate towards the coast. When the shock is very strong, giant waves known as tsunamis they can form and cause great destruction on the coast.
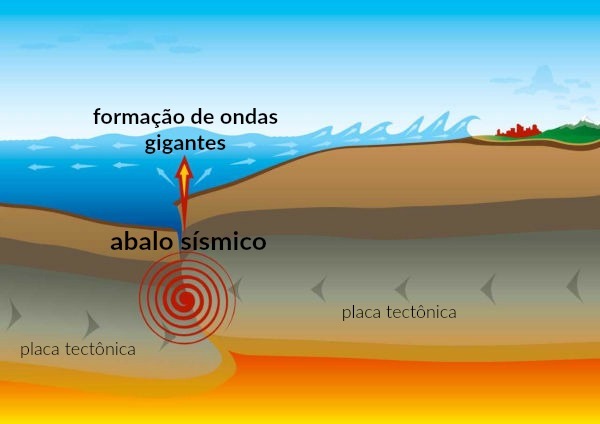
Seismic shock caused by the movement of tectonic plates.
The waves generated by tsunamis can reach more than 30 meters in height. Japan, Indonesia and the Pacific islands suffer most from the occurrence of tsunamis, the effect of the tsunami. Although they are rare, the tsunamis have already caused many deaths and material damage to the affected places. To quantify the damage caused by tsunamis, some scales were presented by scholars. One of them is the
Sieberg-Ambraseys scale, which has six degrees to represent damage, ranging from very small to disastrous.Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
Read too:Tsunami

Destruction caused by tsunami in Indonesia in 2004.
Are tsunami and tsunami synonymous?
It is common to see the use of tsunami and tsunami as synonyms, but making this association is a error. Tsunami is the phenomenon caused by seismic tremors on the ocean floor, by volcanic activity or submerged landslides and cause large displacement of water, generating waves of great magnitude. One of the effects of the tsunami is the tsunami, a giant wave that can reach more than 30 meters in height and cause great destruction. To be considered a tsunami, a wave must be gigantic in relation to its length. A normal wave has a wavelength close to 100 meters. The wavelength of a tsunami can reach 100 kilometers.
Read too: Are Tsunamis in Brazil Possible?
By Rafaela Sousa
Graduated in Geography
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
SOUSA, Rafaela. "Seaquake"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/geografia/maremoto.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.

