THE ulcerative colitis, also often called ulcerative colitis, is an inflammation of the lining of the skin. large intestine which affects the colon and rectum. When it affects only the rectal region, it is called proctitis. When the inflammation reaches the left colon, it is called left colitis, and when it reaches or surpasses the transverse colon, it is called extensive colitis or pancolitis.
Inflammation can eventually affect the portion of the terminal ileum. Generally, ulcerative colitis affects adolescents and young adults more frequently, triggering symptoms such as diarrhea and bloody stools. The treatment of the disease is not curative, but it prevents crises. In some patients, however, surgery may be recommended.
Read too: Digestive system - responsible for processing the food we eat
What is ulcerative colitis?
ulcerative colitis it's a chronic diseasethat reaches the colon and rectum region and is characterized by being a inflammation of the intestinal mucosa without specific cause.
Despite this, hereditary and immunological components are an important basis for the development of the disease.Experts believe that an individual inherits genes that make it susceptible to disease, and environmental factors (until then unknown) cause the Imune system respond to trigger inflammation. Inflammation in ulcerative colitis starts in the rectum and can extend to the colon continuously.
Differences between ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease
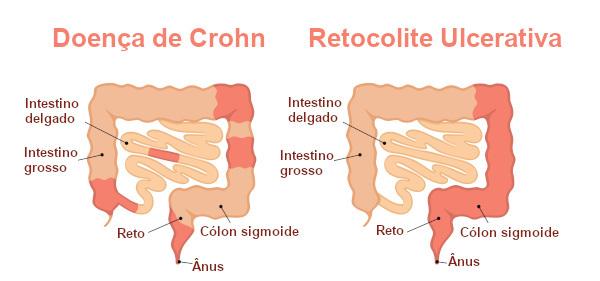
THE Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis are known as inflammatory bowel diseases.. Although sometimes the symptoms are similar, some differences can be observed between them. Ulcerative colitis, for example, presents an inflammation that starts in the rectum and continues for the entire colon in a continuous manner, unlike Crohn's disease, where you may have regions saved.
In addition, rectocolitis is restricted to the large intestine, whereas Crohn's disease can affect other portions of the gastrointestinal tract, predominantly occurring in the lower part of the gastrointestinal tract. small intestine and in the large intestine. Another observed difference between these two inflammatory diseases is the site of inflammation. While Crohn's disease affects the entire intestinal wall, ulcerative colitis causes inflammation only in the mucosa.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
Signs and symptoms of ulcerative colitis
Ulcerative colitis triggers symptoms such as diarrhea with blood alive in the stool, evacuation urgency, abdominal pain and cramps. Diarrhea is caused because inflammation of the wall of the large intestine causes one of its primary functions not to be performed: the absorption of Water. Bleeding occurs due to ulcerations that occur in the intestinal wall. It is noteworthy that blood loss may be responsible for triggering anemia in the individual.
The disease can occur with manifestations in other parts of the body, like joints, biliary tract and the skin. Ulcerative colitis may, in some patients, be associated with ankylosing spondylitis, a problem that affects the spinal joints, promoting stiffness with immobility and pain in the region.
Diagnosis of ulcerative colitis
To diagnose the problem, the doctor must evaluate the patient's symptoms and family history. The doctor may request stool tests, blood tests, rectosigmoidoscopy, and colonoscopy.
The differential diagnosis of ulcerative colitis is made through biopsy. This is due to the fact that bacteria, virus and parasites they may also be responsible for triggering inflammation of the intestinal mucosa, and it is essential to exclude these causes.
After confirming the diagnosis of the disease, the physician will analyze the extension and severity of the case, so that, in this way, he is able to indicate an efficient treatment for the patient.
Read too: Appendicitis - inflammation of the appendix that triggers abdominal pain
Treatment of ulcerative colitis
Ulcerative colitis is a disease that no cure, but the treatments available today can ensure that the inflammation is under control. Treatment varies from one patient to another, being fully individualized. In some patients, it can guarantee long periods of remission. It is noteworthy that crises can occur and can be an indication of the need to change the medication or the way it is being administered.
In some cases, the surgery may be indicated for treatment. It can be recommended, for example, when the patient does not respond well to medications, when the patient develops colon cancer, when it presents massive hemorrhage or perforation, and in patients with biliary cirrhosis triggered by sclerosing cholangitis and who will submit to transplant. It is worth noting, however, that only a doctor will be able to ascertain whether or not it is a case of surgery.
Surgery in these cases consists of removing the entire colon and rectum, a procedure known as total proctocolectomy. After removal, an artificial opening of the ileum is made in the abdominal wall, and the stool is emptied into a synthetic bag that adheres to the skin. There is also a technique in which the external bag is not placed, creating an internal bag called ileoanal anastomosis, which allows the patient to eliminate their feces through the anus.
By Vanessa Sardinha dos Santos
Biology teacher
