O International System of Units, abbreviated by the acronym SI, is a set of measurement units corresponding to the physical greatness fundamentals and their derivations. The SI represented an evolution of the metric system when established in 1960, during the General Conference on Weights and Measures (CGPM) in France.
See more: Frequency and period - scalar physical quantities
Introduction to the International System of Units
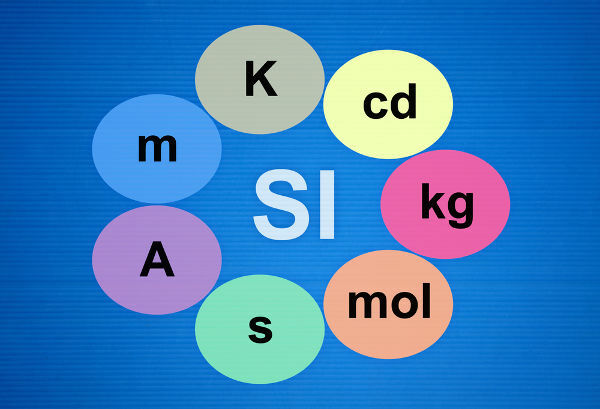
The International System of Units is completely written about seven basic measurement units, based on fundamental physical quantities: length, time, pasta, electric current, temperaturethermodynamics, amount of matter, and luminous intensity.
The SI units referred to such quantities and their symbols are, respectively: subway (m), second (s), kilogram (kg), ampere (THE), kelvin (K), mol (soft candela (CD). In the table you can see all the basic SI units, as well as their symbols and definitions:
Greatness |
Unit |
Symbol |
modern definition |
Length |
subway |
m |
The meter is defined as the space covered by the light (in vacuum) in a fraction of 1/299,792,458 s. |
Time |
second |
s |
The second is equivalent to 9,192,631,770 hyperfine energy transitions of one cesium atom. |
Pasta |
kilogram |
kg |
Currently the kilogram is now based on Planck's constant, equal to 6.62607015.10-34 J.s. |
Electric current |
ampere |
THE |
The amp is equal to the passage of 1.602176634.1019 elementary charges per second, corresponds to the current that produces a force of 2.10-7 N between two parallel lead wires, spaced 1 m apart. |
thermodynamic temperature |
kelvin |
K |
Recently, thermodynamic temperature has been measured in terms of the Boltzmann constant, with a modulus equal to 1.380649.1023 J.s. In the past, it was related to the triple point of water. |
Quantity of matter |
mol |
mol |
O mol is defined in terms of the Avogadro's number, which defines as 6.02214076.1023 the number of particles contained in a mole. |
Light intensity |
candela |
CD |
The luminous intensity is based on a monochromatic light frequency equal to 540.1012 Hz. |
In addition to these basic units, there are others 22 derived units, such as newton (N = kg.m/s²), joule (kg.m²/s2) and the coulomb (A.s). For each SI unit, basic or derivative, you can apply unit prefixes. Altogether there are 20 unit prefixes, shown in this table:
Prefix |
Symbol |
Base power 10 |
Yotta |
Y |
1024 |
Zeta |
Z |
1021 |
Exa |
AND |
1016 |
peta |
P |
1015 |
Will have |
T |
1012 |
gigantic |
G |
109 |
Mega |
M |
106 |
kilo |
k |
103 |
Hecto |
H |
102 |
deca |
gives |
101 |
I decided |
d |
10-1 |
centi |
ç |
10-2 |
mili |
m |
10-3 |
Micro |
μ |
10-6 |
nano |
no |
10-9 |
Peak |
P |
10-12 |
femtus |
f |
10-15 |
act |
The |
10-18 |
Zepto |
z |
10-21 |
Yocto |
y |
10-24 |
Also access: Thermodynamics - first and second laws
SI derived quantities
are those expressed as theproductin betweenthe seven fundamental magnitudes of the SI, raised to different powers. Let's analyze the case of one of these quantities, the acceleration, whose formula and dimensionality are as follows:
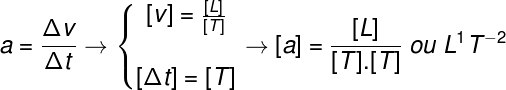

Dimensionality
Sometimes some quantities have their units expressed in terms of their dimensionality, for example, the greatness velocity, which relates displacement and time interval, can be expressed in any system of units according to equationdimensional Next:

L - distance or length
T - time or duration
after that dimensional analysis, it is possible to determine the correct unit for speed on any system used, some possible examples are the m/s (meter per second), the km/h (kilometers per hour) and the mi/h (mile per hour).
Exercises about the SI
Question 1) Check the alternative that presents only written units of measure according to the SI:
a) m, cm, l
b) kg, m, m/s
c) s, m², cal
d) in, cm, K
e) °C, kg, N
Template: Letter B
Resolution:
Of the units shown in the alternatives, several are not derived from the fundamental SI units, such as l (liter), lime (calorie), in (inch) and °C (degrees celsius), so the correct alternative is the letter B.
Question 2) The dimensionality of the force quantity, which can be calculated by the product of mass and acceleration, is correctly expressed as:
a) [M]-¹.[L]¹.[T]-2
b) [M]¹.[L]².[T]-2
c) [M]¹.[L]¹.[T]-2
d) [L]¹.[T]-2
e) [L]¹.[T]-1
Template: Letter C
Resolution:
The force quantity relates the mass (M) with the acceleration, which has a space dimension per time squared (L/T²), so the correct alternative is the letter c.
Question 3) Regarding the IS, check the correct alternative:
a) The g is one of the basic units of the SI.
b) C is the fundamental quantity of electrical charge.
c) The second is the basic unit of time.
d) The centimeter is the basic unit of distance.
e) The celsius is the basic unit of temperature.
By Rafael Hellerbrock
Physics teacher
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/fisica/sistema-internacional-unidades-si.htm