Waves are disturbances that move in space carrying, exclusively, energy from one point to another, without carrying matter. there are waves of nature mechanics, electromagnetic and gravitational. As for its propagation, we can classify three types of waves: waves one-dimensional, two-dimensional and three-dimensional. As for the direction of disturbance, they are divided into wavestransversals and longitudinal.
check out: nature of a wave
Wave properties
Regardless of the nature, form of propagation or disturbance, all waves have the same properties: frequency, lengthinwave, amplitude, velocity and time course. The figure below shows a wave and its elements. Watch:
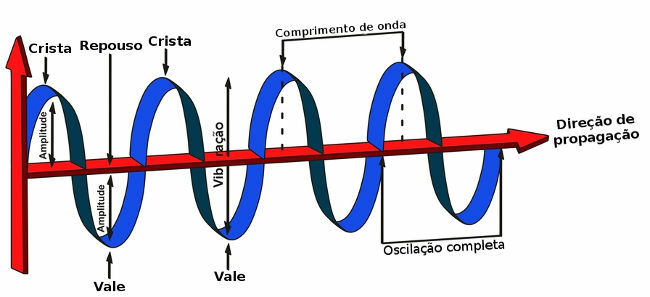
In this figure, it is possible to observe some important elements of the waves.
Wave-length
The wavelength is represented by the symbol λ and is equivalent to the space the waves travel until they realize a complete wobble. The wavelength is also defined as the distance between two consecutive valleys, two consecutive crests or three consecutive nodes.
Nodes are positions in the middle that remain at rest during wave propagation. In the International System of Units (SI), the wavelength is a quantity defined in meters (m).Frequency
The wave frequency is given by the number of oscillations that she performs every second. In the International System, this magnitude is measured in s-1 (inverse of a second), which is equivalent to hertz (Hz). For example: a wave of 20 Hz performs twenty full swings every second.
Time course
The period of a wave is the time interval that she takes to perform oneoscillationcomplete. In the SI, this magnitude is measured in seconds (s). In addition, the properties time course and frequency can be related by the following expression:
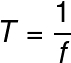
Subtitle:
T = period(s)
f = frequency (Hz or s-1)
propagation speed
THE wave speedIt depends of quite where it spreads. In the International System of Units, it is measured in meters per second (m/s). In addition, this quantity has a mathematical relationship with the frequency (or period) and wavelength quantities:

Subtitle:
v = wave propagation velocity (m/s)
λ = wavelength (m)
f = frequency (Hz or s-1)
Amplitude
The amplitude of the wave is related to its intensity. For example, when the sound volume is turned up, sound waves are being produced with high amplitudes. Amplitude is measured as the distance from the equilibrium position to the height of a ridge or valley. Perexample: when a drop of water falls on the surface of a lake, a small wave forms. The points of this wave that are at the same height as the rest of the lake are positionsinbalance, also called we.
Lookalso: periodic waves
Wave propagation
Waves can propagate in the three directions from space, however, some waves can travel in a smaller number of dimensions, such as one-dimensional waves and two-dimensional waves. The number of directions in which a wave propagates can be determined by the geometry of the medium it is in and by the polarization of the wave (in cases where it is polarizable).
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
One-dimensional waves: they are disturbances that propagate only in one direction in space. Example: waves formed by a spring pressed forwards or backwards.
two-dimensional waves: waves that propagate on surfaces, therefore, travel in two directions of space simultaneously. Example: a wave that forms on the surface of the lake as a result of the disturbance generated by a rock falling on it.
three-dimensional waves: they are waves that move in three directions of space at the same time, in spherical shapes and concentric to their source, that is, when both originate from the same position. Example: Sound waves leaving a speaker, light propagating from a lit lamp.
See too: Wave classification
Disturbance
According to the relationship between the direction of the disturbance that originates a wave and the direction that this wave will propagate, it is possible to classify the waves as longitudinal or transversals.
longitudinal waves: waves that propagate in the same direction as the disturbance that generated them. Example: the sound is a wave longitudinal generated by the compression and rarefaction of molecules in a medium such as air, regions where the density from the air stays bigger and smaller, respectively. Look at the figure below:
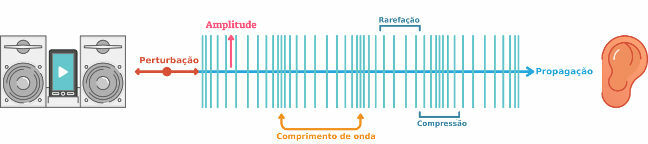
Transverse waves: waves that propagate in directions perpendicular to the direction of the disturbance that generated them. Example: a wave that is produced on a string being swung or light being produced by oscillating electric and magnetic fields. Look at the picture:
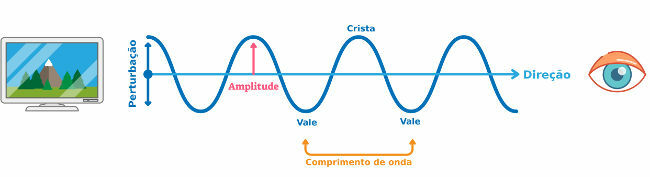
wave nature
waves can have nature mechanics, electromagnetic or gravitational.
Mechanical waves: These waves do not propagate in a vacuum, they are disturbances that can only propagate in some medium filled with matter, such as water, air, metals and so on. Examples: sounds and earthquakes.
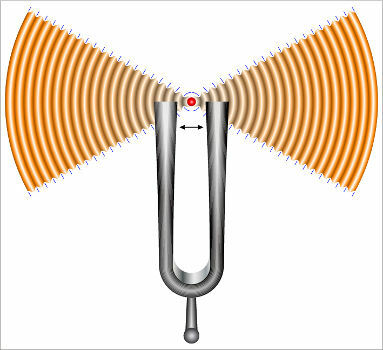
Sound waves propagating through the air through the vibration of a tuning fork.
Lookalso: Sound waves
waveselectromagnetic: are waves that do not need a medium to propagate. They are formed by the oscillation of electric and magnetic fields. Example: light, infrared, ultraviolet.
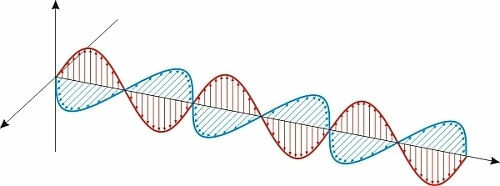
Electromagnetic waves are produced by oscillating electric and magnetic fields.
wavesgravitational: its existence was proposed a long time ago by Albert Einstein, however, it was only confirmed in 2016, with the collision of two black holes distant. This type of wave causes deformations in space-time.

Binary systems, like the one in the figure, can oscillate around their center of mass at high speeds, producing gravitational waves.
Lookalso: gravitational waves
By Rafael Hellerbrock
Graduated in Physics
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
HELERBROCK, Rafael. "What is a wave?"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/o-que-e/fisica/o-que-e-onda.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.
Physics

Do you know how to classify a wave? For a wave to be correctly classified, we must consider its nature, propagation direction and vibration direction. There are waves of a mechanical, electromagnetic and gravitational nature, and they can propagate in up to three directions in space.
