The calculation of some measurements of regular polygons, such as side and apothema, can be performed with the help of a circle. For possible calculations, the polygon must be inscribed on the circumference, where we will determine the measure of the side and the apothema as a function of the measure of the radius.
Square inscribed on the circle
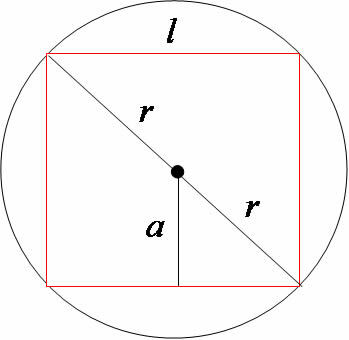
Applying the Pythagorean Theorem we have the following relationships:
Side
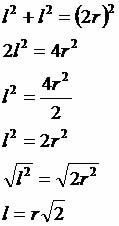
Apothem
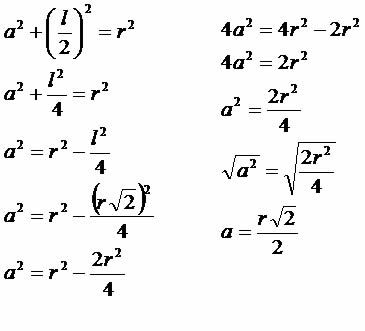
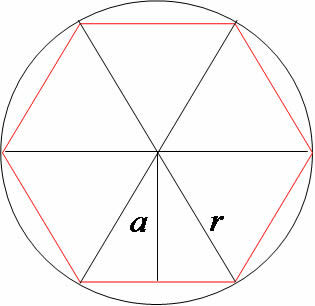
Hexagon inscribed on the circle
Side
Note from the figure that 6 triangles were formed, all equilateral. To verify this statement, just remember that the complete turn on the circumference has 360º, dividing this value between the six triangles we create equal vertex angles at the center of the circle. to 60º. Thus, the angles at the base of each triangle also measure 60°, so we conclude that they are equilateral. In this case we have that the measure of the radius of the circle is equal to the measure of the side of the hexagon.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
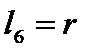
Apothem
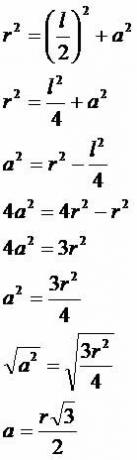
To calculate the measure of the apothema and the side in relation to other polygons, we must use as reference to the demonstrations carried out, establishing dependence on the measure of the radius of the circumference.
by Mark Noah
Graduated in Mathematics
Brazil School Team
Trigonometry - Math - Brazil School
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
SILVA, Marcos Noé Pedro da. "Regular Polygons and Circumference"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/matematica/poligonos-regulares-circunferencia.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.

