Weight is strengthinattraction exercised between bodies that present pasta. Every mass generates its own gravitational field, and this field is responsible for attracting other masses through the strengthWeight.
Weight in Physics
In physics, it is understood Weight as the strength of gravitational attraction exercised among the masses. The weight, also called strengthWeight or strengthgravitational, is one of fundamental forces of nature, together with the forceselectromagnetic,strengthnuclearstrong and strengthnuclearweak. In addition, weight strength is the most weak of all interactions: are necessary pastasgigantic so that the strength weight can be perceived. However, over long distances, as in the case of the interplanetary distances, the weight force shows itself to moresignificant, setting the course of stars,planets,systemssolar and even from galaxies.
See too: What has weight in space?
The unit assigned to the weight in the International System of Units it's Newton (N), an abbreviation for the unit
kg.m/s² (kilogram per meter per second squared). It is a physical greatness vector for presenting module, direction and sense. The weight of any body, for example, is simply the strength with which the Earth draws it towards its own ray, the direction of which points to the center from the earth.Also, the weight depends on the gravitylocal and of the pasta of the bodies submitted to it. O Weight of any body on the Earth's surface, for example, depends only on its pasta, in kilograms (kg), and of terrestrial gravity, in m/s².
This way, if a body with mass is left in a location of gravitynull,yourweight shouldto beequallynull.
weight and mass
It's common confuse the concepts of Weight and pasta. While the weight is a strength,pasta and the amount of matter contained in a body. In addition, mass is a scalar quantity, as it only has module. In the International System of Units, the mass of a body is given in kilograms (kg).

Despite being confused, weight and mass are very different concepts from each other.
to know what is the weight of a body, enough multiplyTheyourmass and themodulegivesgravity where the body is.
Lookalso:What is the weight of a cloud?
It is important to say that when we step on a scale, we are not measuring weight or mass, but the modulus of strengthincompression made on the scale, also called normal force. You can show this through a simple test: just step on a scale and ask someone to push you down. You will see that the mass indication on the scale increases à measure that the force applied to you too increases. Similarly, if you were being pulled up, your weight and mass would not be changing at all, but the reading displayed by the scale would be affected.
Weight formula
It's easy to calculate the weight of a body. Just use the formula presented below:
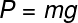
Subtitle:
P – Weight (N – Newton);
m – body mass (kg – kilogram);
g - local gravity (m/s² – meters per second squared).
With the Laws of Universal gravitation, we can calculate the modulegivesgravity produced by a point body or spherical symmetry (as in the case of planets) through the following equation:
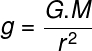
Subtitle:
g – local gravity (m/s² – meters per second squared);
G – universal gravitation constant (6.67408.10-11N.m²/kg²);
M – gravity generating mass (kg – kilogram);
r – radius of the gravity generating mass (m – subway).
Lookalso: gravitational waves
How to calculate your weight
At sea level, Earth's gravity is approximately 9.8 m/s² (This value may vary slightly depending on your distance from the center of the Earth). If we consider a human being with a mass of 70.0 kg, its weight would be calculated as follows:

If this same human being were in the surfacegivesMoon, its mass would remain the same, however, its weight would have a completely different modulus, considering that the Moon's gravity is about 1.62 m/s²:

Summary on weight and mass
If an object has a mass of 70.0 kg, its mass will have the same modulus anywhere in the universe. Your Weight, however, it will depend on the value of the accelerationgivesgravity local.
O Weight of a body is a uniquely attractive force, being defined by the product of the body's mass and the value of gravity at that position.
Weight is greatnessvector, because it presents module, direction and sense; the mass is a greatnessclimb, presenting only module.
The unit of weight in the International System of Units is the Newton.
Gravity is a vector quantity, with acceleration dimension, given in m/s² in the International System of Units.
By Me. Rafael Helerbrock
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/o-que-e/fisica/o-que-e-peso.htm

