flat mirrors they are surfaces that reflect light in a regular way. When some light source illuminates them, it is possible to observe the formation of imagesvirtual, “behind” the surface of the mirror. Such images, in turn, are formed when two extensions of light rays cross, giving rise to images that are virtual, straight and that present the same size as the object.
See too: Light - what it is, propagation and characteristics
Image formation on plane mirrors
The formation of images in plane mirrors occurs when two or more rays of light intersect, giving rise to virtual imagess. Virtual images are always rights, that is, they have the sameguidancevertical of your objects, and cannot be projected, as in the case of real images.
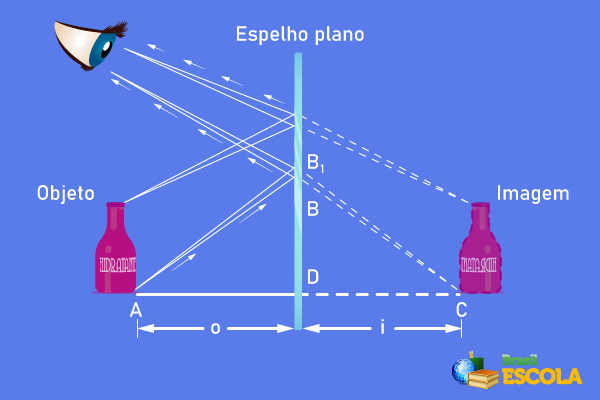
The images formed on the plane mirrors are at the same distance from the mirror that the object of the image, so if you see your image reflected in a mirror 2 m away, your image is formed at a distance of 4 m in relation to you.
Despite being straight, the images formed by the plane mirrors have the sidesinverted, that is why cannot be superimposed one over the other. It is the same as with the left and right hands: one is a reflection of the other and, for this reason and because they are asymmetric, they cannot be overlapped.

This property of laterally inverting images is known as enantiomorphism and it is because of this that, in fire engines and ambulances, it is common to find reversed writing, for that drivers can make way for these vehicles when they see their reflections in mirrors rear view mirrors.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
Plane Mirror Translation
The translation of images in plane mirrors works as follows: when we approach or move away from the mirror at a certain distance, our image travels the same distance. For example, if we approach 2 m towards the mirror, our image will have approached 2 m with respect to the mirror, so we will have approached 4 m with respect to the image.
THE same logic applies to speed of approach or departure between the object and its image. We just double the speed at which the object approaches or moves away and then we get the relative speed between them.
See too: Auroras, mirages, solar halo, iridescence – the most incredible optical phenomena
association of plane mirrors
The association of plane mirrors is done aligning two mirrors with a certain angle α, measured in relation to the direction normal to the surface of the mirrors, as shown in the following figure:
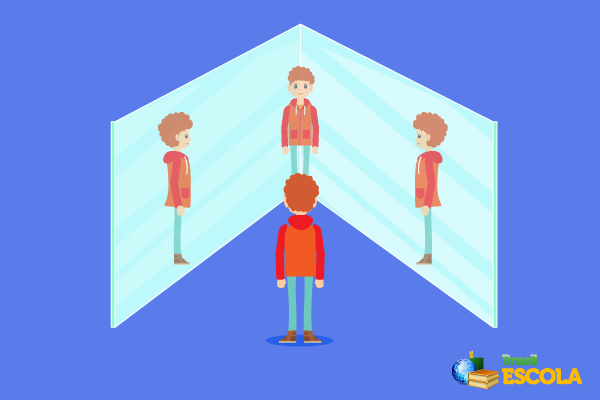
In this case, the formation of a numberprogressiveinimages, as the angle α decreases. The formula that allows us to calculate the number of images formed by the association of two plane mirrors is as follows:

N – number of images
α – angle between normal directions to each mirror
See too: ANDsconcave and convex spherical hairs - formulas, definitions and exercises
Solved exercises on plane mirrors
Question 1 — Regarding the formation of images by plane mirrors, the following statements are made:
I – The images formed by the plane mirrors are always inverted.
II – The formation of images in plane mirrors occurs when there is an intersection between two reflected light rays.
III – In flat mirrors, diffuse reflection of light occurs.
IV – The distance between an object and its image reflected by a plane mirror is equal to the distance between the object and the mirror.
They are true:
a) I and II.
b) II and III.
c) I, II and III.
d) None of the statements.
Resolution:
Let's look at the alternatives:
I - FALSETHE. The images formed by the plane mirrors are always straight.
II - FALSETHE. The rays of light reflected by the plane mirrors do not intersect, but their extensions do.
III - FALSETHE. Flat mirrors promote regular reflection of light, so we see our reflection when we look in their direction.
IV - FALSETHE. The distance between an object and its image, when it is produced by a plane mirror, is equal to twice the distance between the object and the mirror.
Based on the analysis made above, it is clear that the correct answer is the letter D.
Question 2 — When approaching a plane mirror, with a speed of 1 m/s, a person perceives his image approaching. Considering that the initial distance between this person and the mirror is 20 m, determine how long it takes for the distance between him and his image to be 2 m.
a) 39 s
b) 19 s
c) 20 s
d) 40 s
Resolution:
Initially the distance between the observer and the mirror is 20 m. In order for the observer to be 2 m away from his image, he needs to be 1 m away from the mirror, having therefore walked 19 m. Since the observer's speed is 1 m/s, the time required for the distance between the observer and his image to be 2 m is 19 s, so the correct alternative is letter B.
question 3 — Two flat mirrors are aligned so that the directions normal to the surfaces of these mirrors form a 30° angle to each other. Determine the number of images formed by these mirrors.
a) 11
b) 12
c) 10
d) 6
Resolution:
To calculate the number of images formed between the two mirrors, we must do the following calculation, please note:
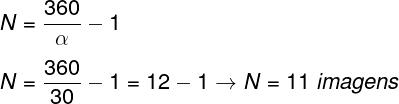
Based on the calculation made above, the correct alternative is the letter a.
By Rafael Hellerbrock
Physics teacher