THE Newton's third law, known as law of action and reaction, states that for every action force that is applied to a body, a reaction force arises in a different body. This reaction force has the same intensity as the action force and acts in the same direction, but in the opposite direction.
Through Newton's third law, you can see that all forces they form and cancel each other in pairs, that is, when body A exerts force on body B, body B resists the application of this force through the reaction, which acts on body A. The action and reaction forces have equal intensities,sensesopposites and act in different bodies. Furthermore, these forces produce accelerations in bodies A and B, however, if we look at bodies A and B as a single system of bodies, we will see that the action and reaction forces cancel each other out. That's why we say that the forces of action and reaction are internal.
Read too: Newton's Laws - Newton's 1st, 2nd and 3rd Law and Applications
Action and reaction forces and their effects
Consider two ice skaters, A and B, positioned on flat ground, with no friction forces. If skater A pushes skater B, they both move away as the action and reaction forces act on different bodies and in opposite directions. Although the action and reaction forces are equal, the acceleration acquired by each of the skaters is different as it depends on their masses (inertia).
The idea that the forces of action and reaction have the same intensity can be littleintuitive. To try to understand this better, imagine a situation where a moving truck hits a small feather. The force that the truck exerts on the plume is equal to the force that the plume exerts on the truck, however, the acceleration produced on the truck is very small, due to its great inertia. This is why the effect of reaction forces is much more expressive in smaller bodies. pasta.
Similarly, the Earth pulls us down and we pull the Earth up with the same intensity, however, the acceleration that is produced on us is much greater than that which is produced on the Earth.
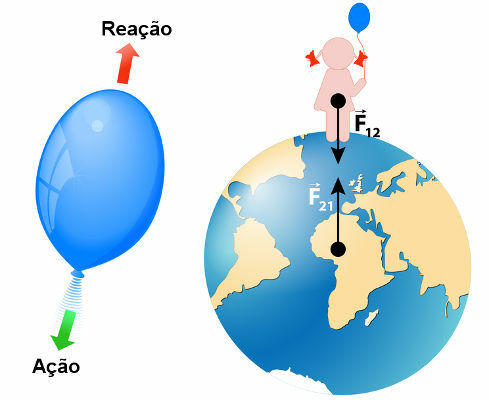
Internal and External Forces
Imagine the following situation: a person is left inside a parked vehicle, free to move, on a flat street. The person can apply forces against any of the internal parts of the vehicle that it will not move. This is because the force made by the person on the vehicle is equal to the force the vehicle makes on the person.
This analysis can be applied to all matter that is in solid state, for example. In a metal bar, the forces of attraction between atoms cancel out in pairs, so that their shape always remains the same. There is no reason for these forces to stop canceling each other at some point, so only external forces are capable of making some change in the state of motion of this metal bar or deforming it, for example.
Newton's Third Law Formula
To express mathematically the Newton's third law, we say that the force that a body A makes on a body B (FA, B) is equal in intensity to the force that body B exerts on body A (FB, A), however, as the two forces act in the same direction, but in opposite directions, their signs are different:

FA, B – force that body A does on B;
FB, A – force that body B does in A.
The following figure shows a situation in which one body applies a force on another body. Realize that the forces of action and reaction act in different bodies and in opposite directions.

Examples of Newton's Third Law
- When we walk, we push the ground back and the ground pushes us forward. This only happens because of the existence of a frictional force between the surfaces of our feet and the ground.
- The propeller of a helicopter produces its sustaining force to the push the air down, which consequently pushes it up.
- When firing a projectile, it is possible to feel that the firearm recoils, since the force applied to the bullet is returned to the weapon in equal intensity, but in the opposite direction.
- when they go up, rockets spew large amounts of heated gases downward, thus, these gases push the rocket upwards.
strength weight and normal strength
It is common to think that the forces Weight and normal form a action and reaction pair, however, this is not true. The weight force is the force that the stars exert on all bodies that are subject to their gravitational field. When the Earth pulls us down, for example, we pull the Earth up, however, if there is any surface that can prevent us from continuing to fall towards the center of the Earth, we will make a contact force on that surface. Consequently, that surface will react to the application of that force with a reaction, called a normal force.
When we find ourselves perfectly aligned with the horizontal, the strengthnormal and the strengthWeight they act in the same direction and in opposite directions, canceling each other out. However, as they act in the same body, they cannot be considered pairs of action and reaction.
When we find ourselves on an inclined surface, the normal and weight forces do not act in the same direction, so they do not completely cancel each other out. In this way, one of the components of the weight force acts in the direction of the plane, making us slide if there is no friction force.
Lookalso: Tips for Solving Newton's Law Exercises
Exercises on Newton's Third Law
Question 1 -(Enem - 2018) During a cleaning, the mother asked her son to help her, moving a piece of furniture to move it. To escape the task, the son said he learned at school that he could not pull the furniture, as Newton's Third Law defines that if you pull the mobile, the mobile will also pull it back, and so it will not be able to exert a force that can put it in movement.
What argument will the mother use to point out the boy's misinterpretation?
a) The force of action is that exerted by the boy.
b) The net force on the mobile is always nil.
c) The forces that the ground exerts on the boy cancel each other out.
d) The action force is slightly greater than the reaction force.
e) The pair of action and reaction forces do not act on the same body.
Template: Letter e
Resolution:
The forces of action and reaction always form in the same direction, but in opposite directions. Furthermore, these forces do not cancel each other out, since they do not act on the same bodies.
Question 2) (IFSC) A bird is standing on one of a boy's hands. It is CORRECT to state that the reaction to the force that the bird exerts on the boy's hand is the force:
a) of the Earth on the boy's hand.
b) of the bird on the boy's hand.
c) of the Earth over the bird.
d) of the bird on Earth.
e) of the boy's hand on the bird.
Template: Letter e
Resolution:
Let's analyze the statements:
Letter a: FALSE. The force that the Earth exerts on the boy is the force of weight.
Letter B: FALSE. The force that the bird exerts on the boy's hand is the force of action.
Letter C: FALSE. That force is the bird's weight.
Letter D: FALSE. This is the force of reaction to the bird's weight.
Letter e: TRUE. The force exerted by the boy's hand is a normal reaction force.
Question 3) (UERN) Two identical metallic spheres are charged with electrical charges of equal signs and different modules and are situated in a vacuum, separated from each other by a distance x. About the electric force, which acts in each of these spheres, it is understood that they are:
a) equal in module and have opposite directions.
b) equal in module and have the same direction.
c) different in module and have opposite directions.
d) different in module and have the same meaning.
Template: Letter a
Resolution:
As we know, according to Newton's third law, the forces that the spheres exert on themselves must be equal, as they are an action and reaction pair. Furthermore, these forces must necessarily have equal modules, in addition to being arranged in opposite directions.
By Rafael Hellerbrock
Physics teacher
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/fisica/terceira-lei-newton.htm
