THE atomic bomb, or nuclear bomb, is a weaponinexplosion with a great destructive power, due to the great amount of energy it releases. This bomb works through the nuclear reaction process of fission of atoms, which enables a large release of energy from a small amount of matter.
Read too: Einstein and the Atomic Bomb
History
With the advance of Second World War, it was necessary to develop more powerful weapons that could cause greater impacts on opponents. With this intention, the north-americans started a race against the GermanyNazi to create the first nuclear weapon. This project was named “ProjectManhattan”, which lasted from 1942 until 1945, when the first test of a nuclear fission device was carried out.
World War II ended with the use of the first atomic bombs used in human history. The bombs were dropped on the cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, on August 6 and 9, 1945, respectively. These bombs became known as little boy and fat man, because of their formats and the explosive capacity of each one.
Also access: Find out five facts about WWII
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
How does an atomic bomb work?
The operation of nuclear bombs is similar, differing only by the element used in the composition. The main elements that make up the bombs are uranium-235 and plutonium-239. The nuclear bomb works on the principle of fissionnuclear, which is the splitting of an unstable atom by the bombardment of particles, like a neutron. This generates a chain reaction that causes the nuclear fission of the other atoms present.
uranium bomb
One of the elements used in the construction of atomic bombs is uranium, but not just any uranium isotope can be used – only U-235 is considered unstable enough for this purpose. The fission reaction of a uranium-235 atom is shown below:
n+ 235U92 → 91Kr36 + 142Ba56 + 3n + energy
Note that each uranium atom that undergoes disintegration releases another three neutrons, which, in the atomic bomb, are used to break another three nuclei, generating the chain reaction and releasing a large amount of energy, as shown in image a follow:
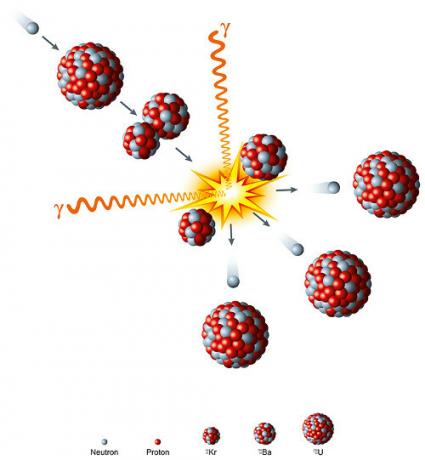
The chain reaction caused by the nuclear fission of uranium is used as the principle of atomic bombs.
Atomic bomb destruction power
The destructive power of nuclear bombs is measured in kiloton or in megaton, units related to the destruction power of dynamite (TNT). The kiloton is equivalent to the explosion of 1000 tons of dynamite, and the megaton corresponds to 1,000,000 (1 million) tons of TNT.
For comparison, the atomic bomb dropped on Hiroshima (known as little boy) had a destructive power equivalent to 16 thousand tons of TNT, that is, 16 kilotons, and the bomb dropped on Nagasaki (the fat man), around 20 thousand kilotons. Despite the damage caused, the nuclear bombs used in World War II are not among the most powerful already made in the world.
To give you an idea, the bomb with the greatest destructive capacity that has been reported in history, the Tsar Bomb, had a destructive power of 50 megatons.
Read too: Tsar Bomb – The most powerful bomb in history
Brazilian nuclear weapons
Although the amount of nuclear weapons is enormous, Brazil is considered a country free of weapons of mass destruction, which encompass nuclear weapons. To declare this feat, in 1998, the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons (NPT) was signed. aims to prevent the creation of new weapons and the development of production-related technologies from them.
It is known that Brazil uses technology for peaceful purposes (as the Brazilian Constitution allows), which includes nuclear power plants for the production of electric energy, the use for medical purposes, in agriculture, among others. All these actions are regulated and inspected by international bodies such as the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) and the Brazilian-Argentine Agency for Accounting and Control of Nuclear Materials (ABACC).
Little boy, the first atomic bomb used in history
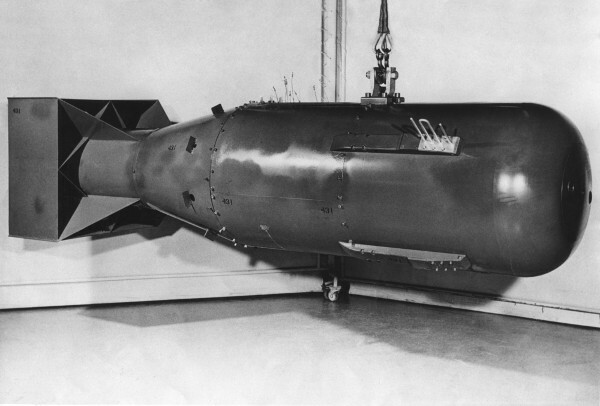
little boy this is how the atomic bomb dropped on Hiroshima in 1945 by the United States during World War II became known.
The bomb dropped on the city of Hiroshima was a nuclear bomb from uranium-235 with an estimated power of 16 kilotons (1 kiloton = 1000 tons of TNT). It exploded at a height of approximately 570 meters from the ground and caused a cloud of smoke that reached 18 km in height.
Its explosion generated a fireball with a temperature of approximately 300 °C, which reached a radius of 2 km of destruction, in addition to spreading a a cloudradioactive. This resulted in the death of over 80,000 immediate victims and a total of over 140,000 deaths in as a result of burns and injuries caused by the explosion and damage caused by exposure to radiation.
By Victor Ricardo Ferreira
Chemistry teacher
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
FERREIRA, Victor Ricardo. "Atomic bomb"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/bomba-atomica.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.