In some events of our daily lives, we come across physical phenomena, but we don't even realize that they are inserted in our daily lives. We often think that we will only know them and use them in the classroom. But, contrary to that, as already said, they are in different events around us. One of these phenomena is the one in the photo above, which is due to the refraction of light in ice crystals.
Refraction is the name given to the phenomenon that occurs when light, when crossing the boundary between two media, undergoes a variation in its propagation speed. In the study of refraction, taking into account the variation in the speed of light propagation, it is defined, for homogeneous and transparent media, a number called refractive index.
We can define the refractive index (n) of a medium as the quotient between the speed of propagation of light in a vacuum (c) and its speed of propagation in the considered medium (v).
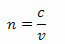
Second Law of Refraction
The Snell-Descartes Law is also commonly known in the media as the second law of refraction. She states that:
Analytically, we can write the following:
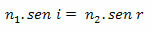
In the equality above, if we consider that no2 > no1(or, what is equivalent, v2 < v1), then sin r < sin i and r < i. We can then conclude that when light passes from a less refracting medium to a more refracting medium, the speed of light decreases and the light ray approaches the normal line, that is, the angle that the light ray forms with the normal line decreases. See the figure below.
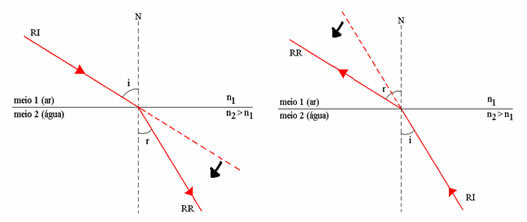
When going from a more refracting medium to a less refracting medium, the speed of light decreases.
By Domitiano Marques
Graduated in Physics
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/fisica/lei-snell-descartes.htm
