Some metals are not found free in nature and must be obtained through laboratory procedures. One of the effective and economical methods of purifying metals is through Electrolysis. Electrolysis takes place in electrolytic cells, with two electrodes connected to the terminals of a direct current generator.
It is known that in an electrolytic cell there is a cathode and an anode, see the definition for each:
Cathode: It is the negative electrode that attracts cations, and this is where the cation reduction occurs.
anode: The positive electrode that attracts anions and, therefore, this is where the anion oxidizes.
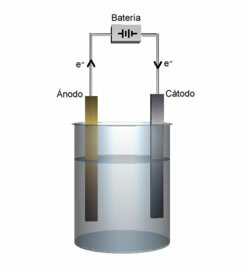
Anode and cathode demonstration.
Copper Purification
Copper as found in nature has impurities such as silver, iron, gold, zinc. Through electrolysis it is possible to isolate this metal obtaining it in pure form, follow the process:
- Impure copper works as an anode and an aqueous solution of copper sulfate works as an electrolyte, which is inside the electrolytic cell. The cell's cathode is Copper itself in a high degree of purity.
- Copper is transferred from the anode to the cathode while the impurities remain in solution. Copper in its pure state accumulates at the cathode and thus can be used.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
By Líria Alves
Graduated in Chemistry
Brazil School Team
See more!
Electrolysis Reactions
Electrolysis Products
Electrolysis - Physicochemical - Chemistry - Brazil School
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
SOUZA, Líria Alves de. "Metal Purification through Electrolysis"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/purificacao-metais-atraves-eletrolise.htm. Accessed on June 28, 2021.


