Reforestation is the environmental activity or action of planting trees and vegetation in areas that have been deforested, whether by nature (fires and storms) or human influence (fires, dam construction, mineral or logging and etc).
The term reforestation can only be used when the action is to replant, that is, to plant again in a place where vegetation previously existed.
It can happen spontaneously or planned, that is, naturally or through an action created to reforest a region or a species of vegetation.
Reforestation can have different objectives, such as: recovering a native species, preserving an ecosystem or reducing the harmful effects of pollution and global warming.
Importance of reforestation
Reforestation brings several benefits to the environment. See some of them:
- It is important for the photosynthesis process,
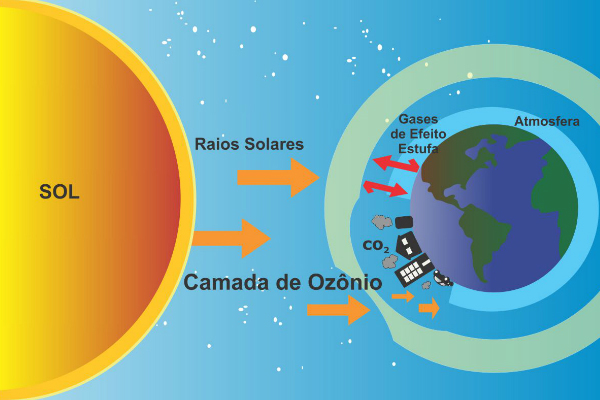
- Improves air quality and balances CO2 levels in the environment (carbon dioxide),
- Helps to lower the temperature of the environment,
- Restores and preserves regional biodiversity,
- Assist in maintaining the balance of ecosystems.
 Reforestation area with eucalyptus.
Reforestation area with eucalyptus.
Reforestation and afforestation
One of the most common actions of reforestation is the afforestation, a technique that consists of planting trees in areas that did not have vegetation for a long time. Usually, this practice takes place in large urban centers, where there are no more "green areas".
Afforestation, as an alternative to reforestation, improves air quality, helping the well-being of the local population, who suffer from constant pollution in large cities.
Reforestation is essential for this "air purification" process. A large number of trees and vegetation, through photosynthesis, help to remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. This process releases more oxygen and avoids the intensification of the greenhouse effect on the planet.
Learn more about photosynthesis.
Reforestation of native species
The reforestation of native species is especially important for the environment, as the action helps in the recovery and preservation of ecosystems. The objective is to preserve endangered species.
For the reforestation of native species to be successful, it is necessary to know the region and identify which species belong to the biome. Brazil has six biomes: Amazon, Caatinga, Cerrado, Atlantic Forest, Pampa and Pantanal.
Read more about the Brazilian biomes and meet: Caatinga, thick, Atlantic forest, pampa and wetland.
Reforestation in Brazil
In Brazil, the Forest Code created from Law Decree No. 4.771/65, determines the legislation responsible for afforestation and reforestation in Brazilian territory, also determining punitive measures for non-compliance with laws.
The Amazon region, in particular, is one of those that suffer most from deforestation and criminal fires.
Also read about Legal Amazon and Amazon International.
Reforestation actions are encouraged by government policies and by NGOs (Non-Governmental Organizations). The objective is to raise awareness among businessmen, loggers and the population about the importance of reforestation for the preservation of the environment.
See also the meanings of logging and extractivism.