The epithelial tissue is characterized by presenting cells united and with little extracellular matrix between them. In this tissue, cells responsible for coating surfaces and for secreting substances are found. These cells have a varied shape, which is usually accompanied by the nucleus. In cubic-shaped cells, for example, the nucleus tends to be spherical. On the other hand, in flat cells, the nucleus also has a flat shape.
Read too: human tissue
Another important feature of epithelial tissue is the fact that it has two distinct sides, that is, it is polarized. The side facing the outside of the organ (cavity) is called the apical surface. The portion facing the opposite side is called basal surface.
Generally, the basal surface is supported by connective tissue, which is related to the supply of nutrients to the epithelial tissue. Since most epithelia lack blood vessels, their nutrients arrive through capillaries in the underlying connective tissue.
Another point that deserves to be highlighted is the fact that the epithelial tissue has some specializations (intercellular junctions), which allow the
adhesion and communication between cells.In addition, the surface of epithelial cells may contain specializations such as microvilli (small cytoplasmic projections), cilia and flagella. what they increase the contact surface and facilitate the movement of particles.→ Functions of epithelial tissue

The epidermis, one of the layers that make up the skin, is made up of epithelial tissue.
Because it has very united cells, the epithelial tissue acts mainly as a barrier, ensuring protection against microorganisms, against excessive water loss, in addition to mechanical protection. The epithelial tissue still acts in the gland formation, which perform various functions in the body. THE sweat gland, for example, produces sweat, which allows control of body temperature.
Read too: Importance of organ and tissue transplantation
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
→ lining epithelial tissue
The lining epithelial tissue is responsible for lining the body and organ surfaces. For this reason, it is related to protection, absorption of substances and even the perception of certain stimuli.
→ Classification of lining epithelial tissue
The lining epithelial tissue can be classified in different ways, according to the number of cell layers and cell shape. With regard to cell layers, the epithelial tissue can be divided into:
Simple: it has only one layer of cells.
Stratified: it has multiple cell layers.
Pseudostratified: it has only one layer of cells, however, it has an appearance that gives the false impression of having several cell layers. This is because cells vary in size, and the location of the nucleus is different in each cell.
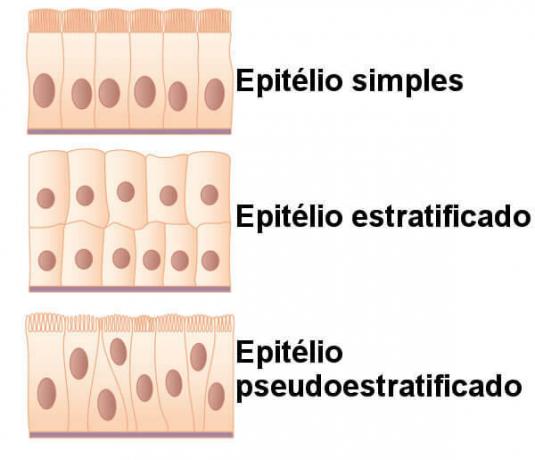
Note the difference between simple, stratified, and pseudostratified epithelial tissue.
The lining epithelial tissue can be further classified according to the shape of the cells. According to this classification, we have:
Cubic epithelium: tissue with cubic-shaped cells.
Columnar epithelium: tissue with elongated cells.
Squamous epithelium: tissue with flat cells, which resemble tiles.
Transitional epithelium: cell-shaped tissue that varies according to the distension of the organ in which it is found. In urinary bladder tissue, for example, cells become more flat when this organ is full. When the bladder is empty, the cells take on a more globose shape.
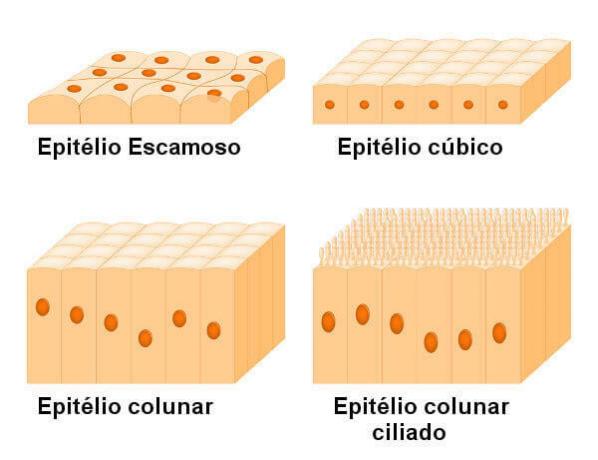
Note the different shapes of epithelial cells.
Read more about:Classification of epithelial tissues
→ glandular epithelial tissue
The glandular epithelial tissue forms the glands, being responsible for secreting substances. It is noteworthy that the cells of this tissue are not always aggregated to form complex glands. The goblet cell, for example, is a glandular epithelial cell and is called by some authors unicellular gland cells.
Multicellular glands, which are the glands themselves, can be classified into three types:
Endocrine gland: They are ductless glands that produce secretions released directly into the blood. As an example, we can mention the thyroid.
Exocrine gland: They are glands that have ducts and release their secretion into cavities or on the surface of the body. As an example, we can mention the sebaceous gland.
- Mixed gland: This gland has an endocrine portion and an exocrine portion. As an example, we can mention the pancreas.
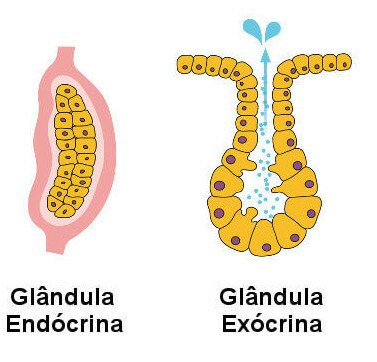
Note the structures of an endocrine and an exocrine gland.
Read too:Major endocrine glands and their hormones
→ Exercises
Epithelial tissue is found in our body lining and forming glands. This tissue, as well as other tissues in the body, is of great importance for the proper functioning of the body. Due to its importance, it is frequently addressed in entrance exams. Note below two questions that address the topic:
QUESTION 1- (UDESC) Epithelial tissues, also called epithelia, play many roles in our body. In relation to these tissues, analyze the propositions:
I. Epithelial tissues are multi-stratified due to their protective role.
II. Some epithelia have specializations that increase their absorption capacity.
III. Epithelial specializations like desmosomes and adhesive junctions increase its absorption capacity.
IV. The skin is an example of epithelial lining tissue.
V. The mammary glands, as well as the sweat glands, are examples of epithelial secretion tissue.
Check the correct alternative.
a) Only statements II and V are true.
b) Only statements I, III and IV are true.
c) Only statements II, III and V are true.
d) Only statements III, IV and V are true.
e) Only statements I, II and V are true.
RESOLUTION: Letter a
Statement I is incorrect, as there are simple and pseudostratified epithelia.
Statement III is incorrect as desmosomes and junctions are related to cell adhesion.
Statement IV is wrong, as the skin is an organ.
QUESTION 2- (UNICENTRO) Tissues are groups of cells specialized in carrying out certain functions. In the vertebrate organism, there are a great number of tissues, whose cells present a great diversity of structure and functions. Based on knowledge about the different tissues existing in vertebrates, it is correct to state that:
a) The glands originate from connective tissue cells present in the ground substance.
b) The epithelial tissue is characterized by having little intercellular substance and juxtaposed cells.
c) Adipose tissue is a type of muscle tissue in which large, rounded cells that store lipid drops predominate.
d) Nervous tissue has spindle cells made up of numerous actin and myosin microfilaments in its cytoplasm, which allows the conduction of the nerve impulse from cell to cell.
RESOLUTION: Letter B
The epithelial tissue has cells very close together and little extracellular matrix between them.
By Ma. Vanessa Sardinha dos Santos



