Phylogeny or phylogenesis is the study of the relationships between different groups of organisms and their evolutionary development. Phylogeny attempts to trace the evolutionary history of all life on the planet.
It's based on phylogenetic hypothesisthat all living organisms share a common ancestry.
The relationships between organisms are described in what is known as a phylogenetic tree.
However, evidence for such relationships is almost always incomplete, as the vast majority of species who once lived is extinct and relatively few of his remains have been preserved in the record. fossil.
Most phylogenies are therefore hypotheses based on indirect evidence.
How does the phylogenetic tree work?
In a phylogenetic tree, or cladogram, the species or groups of interest, are found at the ends of the lines referred to as tree branches.
For example, the phylogenetic tree below represents relationships between five species, A, B, C, D and E, positioned at the ends of the branches.
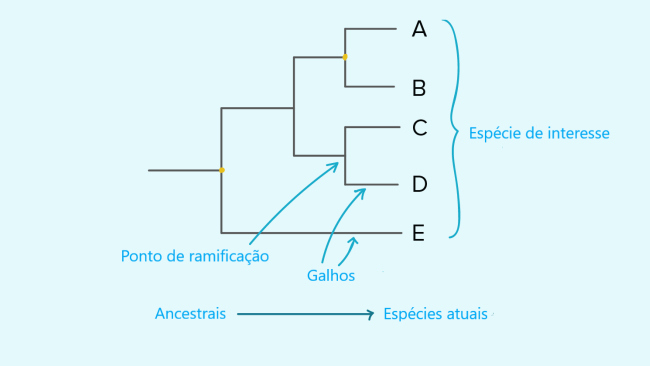
How the branches connect represents our understanding of how the species on the tree evolved from a series of common ancestors.
At each branch point, it's the most recent common ancestor of all descendant groups from that branch point.

For example, at the branch point that gave rise to species A and B, we would find the most recent common ancestor of these two species.
At the farthest point on the left branch, we would find the most recent common ancestor of all species on the tree. Not all phylogenetic trees look the same.
Some are irregular, like the tree on the left below. Others use diagonal lines, or of any type, oriented vertically or facing sideways, such as the tree in blocks.
The orientation of the phylogenetic tree does not change the information in the tree.
 Examples of different types of phylogenetic trees
Examples of different types of phylogenetic trees
Important facts about the phylogenetic tree
- Phylogenetic trees are relatedness hypotheses: although it is understood that modern organisms evolved from ancient organisms, the path of this evolution is sometimes the best guess, based on the amount of evidence available in the time. The more that is discovered about the lineage of a set of organisms, the more accurate the phylogenetic trees become;
- Phylogenetic trees are not just based on physical characteristics: to create a phylogenetic tree, scientists often compare and analyze many characteristics of the species or other groups involved. While this can include internal and external physical traits, it can also include other factors such as behavior or DNA sequences.
The applications of phylogeny in the modern world
An exciting development in phylogenetics is the application of phylogenies to various modern problems. In medicine, phylogenies have been used to track the origins and transmission rates of infectious diseases such as AIDS, influenza and dengue.
Phylogenies developed from molecular genetics have been particularly useful in conservation biology to identify the distinction. evolution of endangered species, paternity in captive breeding programs and the levels of hybridization and inbreeding between species.
Phylogenetic analyzes have also been used as admissible evidence in criminal court cases involving the determination of intentional viral transmission.
See too:
- Heredity;
- Gene;
- Mutation;
- DNA;
- Evolutionism.



