For you to understand the phenomenon of ionization it is first necessary to know what ions are. Note the explanation below:
Every atom has the same number of protons and electrons; therefore, every atom is electrically neutral. Furthermore, substances formed by groups of atoms also have an electrical charge balance, being electrically neutral.
However, an atom or a group of atoms can lose or gain electrons; when that happens, they lose neutrality and become ions.
If the atom or group of atoms loses electrons, it will be positively charged and will be an ion called cation. However, if you gain electrons, the charge will be negative and the ion will be a anion.
Inorganic substances are ionic or have the ability to form ions.
One of the ways to form ions is by placing molecular substances in water, that is, formed by covalent bonds, in which electrons are shared.
For example, if we test the electrical conduction of hydrochloric acid (HCl) in aqueous solution (hydrogen chloride dissolved in water), we will see that the solution is electrolytic, that is, it conducts an electric current, because there are ions in this solution.

This means that water acted as a reactant, forming ions from hydrochloric acid. This occurs according to the reaction below:
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
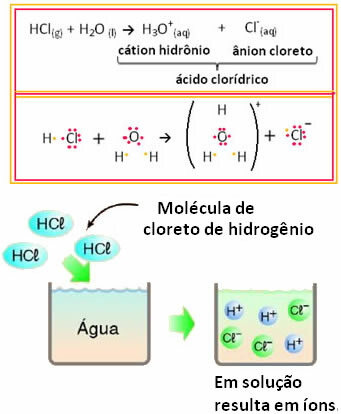
Note that before putting hydrogen chloride in water, there were no ions. However, its molecules reacted with water and formed positive H ions3O+ (cations) and negatives Cl- (anions). Since chlorine is more electronegative than hydrogen, it attracts the pair of electrons from the covalent bond close to it and forms the anion. Hydrogen, on the other hand, is attracted by oxygen in water, which is more electronegative than chlorine; and between hydrogen and oxygen a covalent bond is formed, giving rise to the hydronium cation. This phenomenon of ion formation is calledionization.
Based on the above explanation, we can define ionization as follows:

Note that the ions did not exist before, because if they did exist, as in the case of the dissolution of ionic compounds, we would have an ionic dissociation and not an ionization.
All acids placed in contact with water undergo ionization. However, not every molecular compound undergoes ionization.For example, sugar (C12H22O11) is molecular, however, when placed in water, no ions are formed, it just dissolves, originating a non-electrolytic molecular solution, which does not conduct electricity.
By Jennifer Fogaça
Graduated in Chemistry
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
FOGAÇA, Jennifer Rocha Vargas. "Ionization"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/ionizacao.htm. Accessed on June 28, 2021.


