Fieldelectric is defined as the electric force per unit of charge. THE direction of the electric field define The direction gives strengthelectric that arises between two charges. Also, the electric field is radial and can point so much to inside how much for outside load, for signal loads negative and positive, respectively. We usually call positive electric charges sources of electric field and the negative electric charges of sinks.
See too: Electric field
All chargeelectric is able to influence the surrounding environment through its fieldelectric. when a chargeelectric is placed in a region close to another charge, their electric fields add vectorally. You can check the rules of sumvector accessing the link: Vector operations. If you want to know more about the calculation of the electric field generated by more than one charge, go to: Electric field generated by multiple charges.
Read too: The Coulomb Torsion Balance
Electric Field Formulas
We can calculate the electric field produced in a vacuum by a point charge with the following equation:
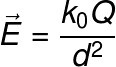
In the equation above, k0 and the constantelectrostatic of the vacuum (k0 = 8,99.109 N.m²/C²), Q is the electric field generating charge, in Coulomb, and d and the distance from the point where the electric field is observed even the electric charge.
The electric field can also be written in terms of the electrical force on the proof load module:

Also check: Coulomb's Law
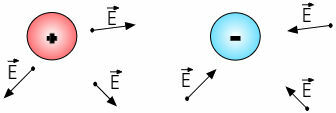
In each point of space around you, the charges produce different modules, directions and senses in fieldelectric. Note the following figure, which illustrates the electric field at some points around electrical charges positive and negative:
Electric field measurement units
In the International System of Units, the electric field can be measured in both Newton per Coulomb (N/C) as in Volt per subway (V/m), which are compatible units.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
Relationship between electric field and electric voltage (or potential difference)
The closer we are to a source of electric field (positive charge), the greater the electric potential in the region. Similarly, the closer we are to the loadsnegative (electric field sinks), lower will be the electrical potential.
The parallel projection of the electric field on the line connecting two points gives us the potential difference between these two points. Watch:

In this figure, we have an electric field AND and two points spaced at a distance d. the potential difference U, in Volts, between these two points is given by:
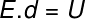
See too: Electric potential
In the equation above, AND is the module of the electric field, U is the potential difference between the points in the figure and d is the distance between them.
If an electrical charge moves in the direction of the lines blue and red, she will always be in the samepotentialelectric, because the electric field has the sameintensity at all points located above these lines, receiving the name of equipotential surfacethere.
Read too: Electric tension
lines of force
To view the fieldelectric, a device called linesinstrength. The lines of force are a geometric construction that allows us to understand the direction it's the sense of the electric field more easily. They are constructed so that the electric field is always tangent the lines.

The lines of force of the electric field of two charges of equal sign are shown in the diagram below:

The lines of electric field force produced by two charges with different signals are outlined below:

See too: Electric field exercises
By Rafael Hellerbrock
Graduated in Physics
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
HELERBROCK, Rafael. "What is an electric field?"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/o-que-e/fisica/o-que-e-campo-eletrico.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.
Physics

Do you know what an electric field is? The electric field is vector, that is, at each point in space it has a specific module, direction and direction. The electric field is responsible for the emergence of forces of attraction and repulsion between electrical charges. Its units are Volts per meter or Newtons per coulomb.