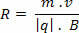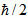You raysgamma, also called gamma radiation, are a type of electromagnetic radiation of high frequency, which has high penetration power into matter and is harmful to health. THE radiation gamma is produced, in most cases, by the radioactive decay of unstable atomic nuclei.
Gamma rays are extremely energetic and are the waves with the highest frequencies of the entire electromagnetic spectrum (over 1018 Hz). This type of radiation is used in the sterilization of surgical tools, food irradiation, complex surgeries and astronomical observations.
Because of their enormous energy, gamma rays can rip electrons from many materials, as well as cause damage to DNA molecules in living things, that's why we say that this type of radiation is ionizing. The processes by which gamma rays are able to ionize matter are:
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
It is madephotoelectric: In this process, the gamma-ray photons collide with the surface of the materials, ejecting their electrons with energies lower than the energy of the incident gamma photons;
Compton scattering: In this process, gamma radiation photons are absorbed by atoms that emit new photons of lower energy and frequency than the incident photons;
Production of pairs: When high-energy gamma photons collide with the atomic nucleus, their energy results in the generation of an electron-positron pair that annihilate each other, producing two other lower-energy gamma-ray photons.
Lookalso:Everyday radiation sources
Gamma ray properties

Gamma rays can be measured by devices like the one shown in the photo.
Because it is electromagnetic radiation, gamma rays do not have electric charge nor mass. Because they are not electrically charged, gamma rays cannot be deflected by electric and magnetic fields.
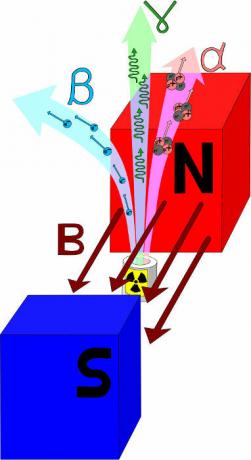
Because they do not have an electrical charge, gamma rays are not deflected by the magnetic field.
Gamma rays propagate in a vacuum with the speed of light, about 3.0.108 m/s. Furthermore, because they are waves, theoretically, gamma rays are subject to all wave phenomena that other light frequencies exhibit, such as reflection,refraction,diffraction and polarization.
Among all the known forms of radiation, it has the greatest penetration power, being able to propagate in practically anyquite. To get an idea, if we wanted to reduce the intensity of gamma radiation by a factor of 1 billion, it would have to pass through approximately 40 cm of lead.
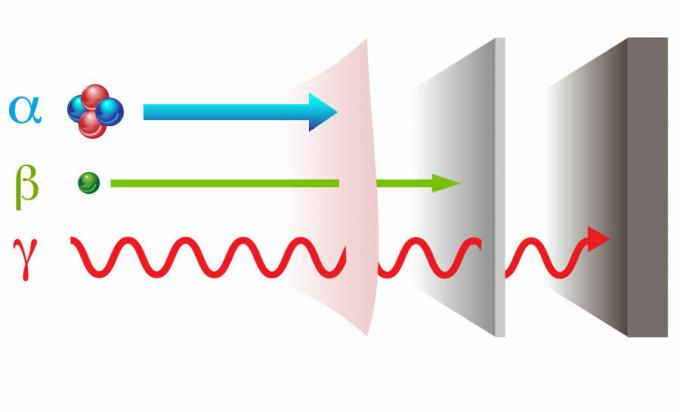
Among ionizing radiation, gamma rays have the greatest penetration power.
Lookalso: Nuclear physics
Gamma ray sources
The main sources of gamma rays are:
reactions nuclear:Gamma radiation is produced by a nuclear decay of the same name, gamma decay, which can occur along with alpha and beta decays. The photons of this radiation carry energies of the order of megaelectron-volts (MeV – 106 eV). Check out an example of nuclear decay that results in the emission of photons from gamma radiation:
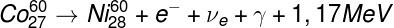
Example of gamma decay together with the emission of an electron and an electronic neutrino.
Peer Annihilation: When particles and antiparticles meet, like electrons and antielectrons, they annihilate each other producing high-energy gamma photons;
Cosmic Rays: Gamma rays coming from all directions of space, coming from other galaxies or produced by explosions of stars collide with atoms in the atmosphere, resulting in the production of pairs that annihilate immediately afterwards;
Rays: Atmospheric discharges are capable of heating atoms to the point of making them emit brief pulses of gamma radiation;
Magnetars and pulsars: Pulsars and magnetars are extremely dense, hot types of neutron stars that rotate at enormous speeds, emitting X-rays and gamma radiation through their poles;
Solar Eruptions: The activity of the solar surface and atmosphere causes the Sun to produce a large amount of gamma rays.
See too: Meet modern physics
Gamma Ray Effects
Gamma radiation is capable of producing several biological effects. However, these effects are determined by some factors, such as the type of tissue that is irradiated, the exposure time and the intensity of the radiation.
When gamma radiation interacts with molecules present in tissues, it strips electrons from them, forming ions. In some cases, chemical bonds can be broken, giving rise to free radicals: molecules capable of degrading cells and causing damage to the body, affecting the process of cell division. The consequences of these mutations are the appearance of tumors, anemia, genetic mutations, among others.
→ Is gamma radiation ionizing?
Radiation is considered ionizing when it is capable of ripping electrons from atoms and molecules. However, different atoms and molecules have different values for their ionization energies and, therefore, the definition of ionizing radiation is somewhat imprecise.
However, we know that radio waves, microwaves, visible light and infrared rays do not have enough energy to ionize molecules. Furthermore, the types of waves that are beyond the frequency of visible light - the ultraviolet, x-rays and gamma rays are capable of ionizing molecules if the energy of their photons have energies greater than 10 eV. Therefore, gamma radiation is, in fact, ionizing radiation.
Benefits and harms of gamma rays
Check out some benefits and harms of using gamma radiation:
→ Benefits
Gamma radiation can be used to sterilize different types of equipment, killing microorganisms;
Gamma rays can destroy complex-to-remove tumors, reducing surgical risks;
We can use gamma radiation to irradiate foods such as vegetables, killing microorganisms that reduce shelf life;
It can be used for determining various physical characteristics of solid materials.
→ harm
The use of gamma radiation must be done with caution and safety, due to its great penetration capacity;
Gamma radiation is ionizing and can cause serious damage to living organisms, such as the appearance of tumors.
Alpha, beta and gamma radiation
At alpha, beta and gamma radiation they are mostly produced by nuclear decays. While alpha and beta radiation are corpuscular (they are made of particles), gamma radiation is electromagnetic in nature.
-
Alpha radiation: formed by helium atom nuclei (He), that is, two protons and two neutrons. This form of radiation has low penetration power, however, it can be ionizing if the kinetic energy of alpha particles is sufficiently high.
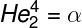
-
Beta radiation: is formed by electrons. This type of radiation is ionizing and has a moderate penetration power.
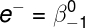
Gamma radiation: is formed by photons of high energy and frequencies. It is an ionizing radiation with high penetration power.
By Me. Rafael Helerbrock