active isomer is a molecule, belonging to a certain substance, which has the characteristic of polarize, that is, make the beam of light propagate in a single direction, deflecting it to the right or to the left. This means that this molecule has optical activity.
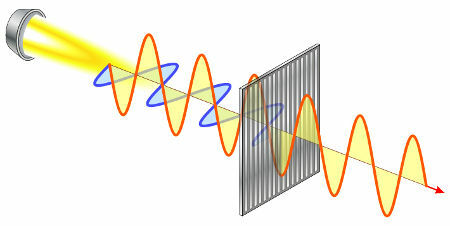
Representation of the polarization of light
When the active isomer shifts the plane of light to the left, it is called the levogiro. In the case of shifting the plane of light to the right, the active isomer is called right-handed. These isomers exist in any compound that exhibits optical activity.
To determine whether an organic compound has optical activity, simply check for the presence of one or more atoms of chiral carbon, which is carbon that has four different ligands in its structure.

General representation of a chiral carbon
If we analyze the following structural formula for butan-2-ol:

Structural formula of butan-2-ol
We verified that carbon 2 (marked by the black arrow) has hydroxyl (OH), hydrogen (H), methyl (CH) as ligands
3) and ethyl (CH2-CH3), that is, it has four different ligands and, therefore, it is considered a chiral carbon. If in butan-2-ol there is a chiral carbon, it presents, for this reason, optical activity performed by the active isomers right-handed and right-handed.Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
Note: In summary, if there is chiral carbon in the structure, there is optical activity, so there are active isomers, which can be right-handed or left-handed.
How to know the number of right-hand and left-hand molecules that a substance with optical activity has?
To determine the number of active isomers (IOA) that a molecule has, just raise, in number 2, the number of chiral carbons present in its structure:
IOA = 2no
Also, half the amount of active isomers The other half is made up of right-handed turns (which deflect light to the right) and the other half is made up of right-handed turns (which deflect light to the left).
Example: 2,3,4,5-tetrahydroxy-pentanal
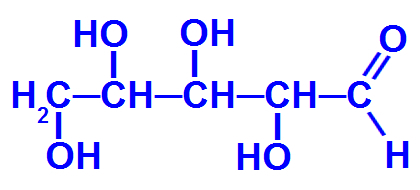
Structural formula of 2,3,4,5-tetrahydroxy-pentanal
In this 2,3,4,5-tetrahydroxy-pentanal structure, there is the presence of three chiral carbons, which are marked in the chain below:

Chiral carbons in 2,3,4,5-tetrahydroxy-pentanal
In this way, your number of active isomers will be from:
IOA = 23
IOA = 8
of these active isomers, four will be right-handed and four will be right-handed.
By Me Diogo Lopes
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
DAYS, Diogo Lopes. "What is an active isomer?"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/o-que-e/quimica/o-que-isomero-ativo.htm. Accessed on June 28, 2021.