We can define a Uniformly Varied Motion (MUV) as one in which the scalar acceleration is constant and non-zero. It is also worth remembering that in MUV, the variation in scalar velocity is directly proportional to the time interval and that, for equal time intervals, we will have equal scalar velocity variations. The hourly equation of the MUV spaces is represented in the image below.
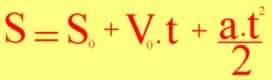
This equation shows us how space s may vary over time. For this reason it is called hourly space equation. Below we will analyze the uniformly varied movement across the chart.
Hourly diagram of positions: s x t
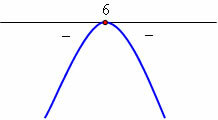
As we can see in the equation in the image above, the hourly equation of the spaces of a MUV is of the 2nd degree in t, therefore its graphical representation in a Cartesian system (s x t) is a parable arc. at the moment t0 = 0 the abscissa of the mobile is s0 and at that moment the parabola cuts the s axis. The parabola will have concavity facing upwards or downwards, because it is the coefficient of the 2nd degree term, depending on the value of acceleration (a), whether positive or negative. Let's see the graphics below:
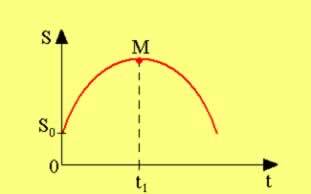

In the graphs above we can see point M. This point is where the reversal of the direction of movement occurs. it occurs in the instant ti, just when you have V = 0.
By Domitiano Marques
Graduated in Physics
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/fisica/representacao-grafica-espaco-funcao-tempo.htm