Drop shipping (or stock at source) is a method of organizing logistics in which the stocking and shipping of products is the responsibility of the supplier, not the reseller.
Drop shipping works as follows: the customer orders the product in any form (internet, telephone, physical store, etc). The store receives payment and forwards the order to the supplier or manufacturer, who maintains the stock and is responsible for sending the product to the customer.
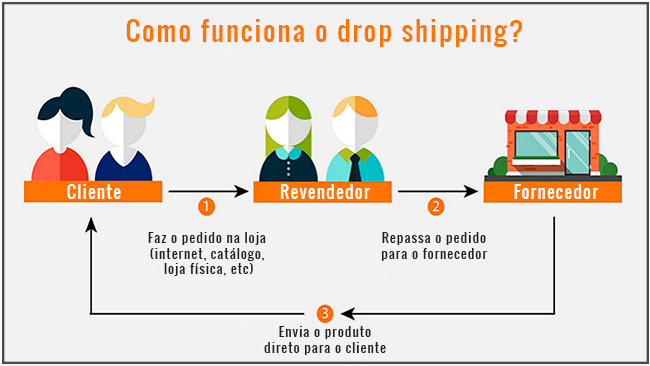
Example:
Josué orders a bouquet of flowers from the website “Portal das Flores”, paying a total of R$50.00. The site forwards the order to the florist “Esquina das Rosas”, paying the supplier the amount of R$30.00.
The florist then removes the product from stock and sends it directly to Joshua. At the end of the transaction, the website “Portal das Flores” earned R$20.00.
Most resellers who adopt drop shipping take their profit from the difference between the amount paid by the customer and the amount paid to the supplier. However, there are also resellers who profit from commissions paid by the supplier.
Drop shipping can be used occasionally (when the reseller has not adopted it as a fixed model). This is usually the case when a small business receives a very large order or when it comes to expensive products that would be costly to keep in stock for the dealer.
The drop shipping business model was invented in 2006 in the United States and although it is mainly aimed at virtual stores, nothing prevents physical stores from using the technique.
Some examples of companies that use drop shipping are Deal Extreme, GearBest and DHGate.
What are the advantages of drop shipping?
The main advantage of drop shipping is that the system enables the emergence of small businesses that do not have the structure to maintain stocks or arrange for the shipment of products.
The model offers much lower costs for the reseller as the maintenance of stock and shipping is the responsibility of the supplier. In this way, the reseller is responsible for concentrating only on marketing the product.
Another form of savings brought about by drop shipping is the cutting of duplicate expenses with maintenance, packaging and shipping. In other businesses, products go through this process twice: from supplier to dealer and from dealer to customer.
Drop shipping offers a greater level of security to the reseller, since it has no expenses with obtaining stock. In this way, all resources are used to promote the product.
Drop shipping also allows the reseller to have a much larger product catalog and therefore a wider target audience.
Disadvantages and risks of drop shipping
In addition to strong competition, the main disadvantages and risks of drop shipping arise from communication failures between the reseller and the supplier.
Often the stock data that the dealer has is not fully up to date and when the customer closes the deal, the product is not available. This leads to an extension of the delivery period and eventual cancellation of the order, reflecting negatively on the reseller.
See also the meaning of E-Commerce.
