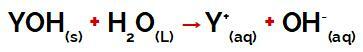When we talk about metamorphosis (from the Greek metabole = change), we refer to the changes that occur in the structure, shape of the body, and even the way of life of some organisms during their development. Some authors define the process as a transition from the larval to the adult form during development.
When an organism undergoes metamorphosis, we say that it has indirect development. Those who do not undergo these transformations present what we call direct development, as is the case with human beings.
→ Main cases of metamorphosis
There are several groups of animals that undergo metamorphosis, such as molluscs, echinoderms, fish, amphibians and insects. Without a doubt, the best known metamorphoses are those that occur in amphibians and insects. Let's see more about the metamorphosis of these groups:
-
Metamorphosis in anuran amphibians
US amphibians frogs, like frogs, occur very intense changes from larva to adult form. There is, for example, the variation in the mouth, which, in the tadpole, is adapted to the ingestion of algae and filtration; but in the adult it is large and adapted for ingesting insects. Breathing is also a big change since, in young people, it is branchial and, in adults, it is pulmonary.
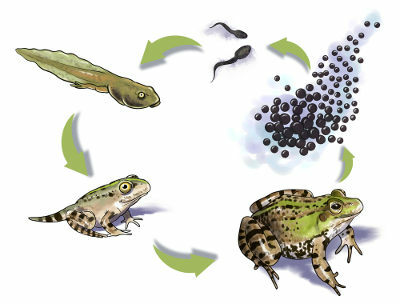
Observe the changes that occur in the body of this amphibian during its development.
First, small larvae are born from the eggs, which are called tadpoles. These larvae have gills, a tail and no legs. The changes in the tadpole are initially few, basically, its growth. Then there is the appearance of the legs – the posterior ones appear before the anterior ones – and the disappearance of the gills. The tail regresses and the animal starts to look like an adult.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
-
insect metamorphosis
Insect metamorphosis can be of two types: complete or incomplete. In complete metamorphosis, clearly visible changes occur, as the immature stage is completely different from the adult. In incomplete metamorphosis, changes are gradual. When an insect has complete metamorphosis, it is called a holometabole; when it presents incomplete metamorphosis, it is called hemimetabolus.
As an example of complete metamorphosis, we can mention the butterfly metamorphosis. This animal hatches from the egg as a larva, which feeds intensely. Later, after some molts, the caterpillar enters the pupa stage, that is, it is trapped inside the chrysalis (cocoon). At this stage, there is no food and the animal survives only on its accumulated reserves. After some time, hatching occurs and the winged adult is formed.
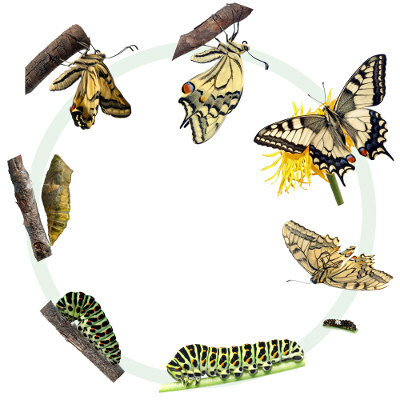

The butterfly is an organism that undergoes complete metamorphosis
At incomplete metamorphosis, the modification is gradual and less noticeable. This type of modification can be seen in grasshoppers, for example. In these animals, there is an immature stage called the nymph, in which the insect does not have wings and its reproductive organs are poorly developed. Over time, after successive molts, these characteristics appear until we have an adult with wings and ready for reproduction.
By Ma. Vanessa dos Santos
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
SANTOS, Vanessa Sardinha dos. "What is metamorphosis?"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/o-que-e/biologia/o-que-e-metamorfose.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.