O kingdom monera encompassed unicellular organisms and prokaryotes, i.e, bacteria, arches and cyanobacteria. Currently the realm is no longer considered valid, since the classification of living beings in three Domains caused the prokaryotic organisms to be divided into two groups. Although the Monera kingdom was dismembered, we still find references to it in many textbooks, so we'll learn a little more about this kingdom below.
Read more: Diseases caused by bacteria - list, symptoms and treatment
Characteristics of Monera kingdom organisms
The organisms belonging to the Monera kingdom are prokaryoteyou and single-celled that can form colonies or not. By prokaryotic organisms, it is understood those that have cells no hascore defined, with the genetic material dispersed throughout the cytoplasm. In addition to not having a nucleus, prokaryotic cells no haveorganelles membranous, which means they don't have structures like mitochondria, golgi complex and endoplasmic reticulum, typical of eukaryotic cells.
The genetic material in prokaryotic cells is located in a region called nucleoiin. In general, prokaryotes have a chromosome Circular. In addition to the single chromosome, small molecules of DNA calls from plasmids.
In Monera kingdom are included organisms autotrophic and heterotrophic. Autotrophic organisms are capable of synthesizing their own food. Cyanobacteria, for example, are able to carry out photosynthesis, a process in which solar energy is used to form organic molecules.
There are also organisms chemosynthetics, capable of synthesizing organic compounds using the energy obtained by the oxidation of inorganic compounds. In addition to autotrophic organisms, in the Monera kingdom, heterotrophic organisms are present, which need to obtain organic matter from external sources. This is the case with decomposing bacteria.
Analyzing the role of oxygen in metabolism, prokaryotes can be classified into mandatory aerobics, mandatory anaerobes and facultative anaerobes. Mandatory aerobics require oxygen to perform cellular respiration, its growth not being possible in the absence of oxygen.
Obligatory anaerobes are those that only grow anaerobic, being killed or inhibited in the presence of oxygen. Finally, facultative anaerobes utilize oxygen when it is present, and perform anaerobic respiration or fermentation when it is absent.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
Reproduction of Monera kingdom organisms
The representatives of the Monera kingdom reproduce themselves in a way asexual through binary division.In this process, the duplication of the prokaryote's genetic material and the subsequent division of the cell into two genetically identical cells is observed. THE genetic variability among prokaryotes arises due to events of mutation and also through genetic recombination. In genetic recombination, organisms unite and exchange genetic information. Genetic recombination can occur by conjugation, transformation and transduction.
In conjugation, two cells temporarily unite and there is a transfer of DNA. In transformation, a prokaryotic organism incorporates DNA fragments that are free in the medium. Finally, in transduction, virus that infect bacteria ensure that genes are carried from one cell to another.
Read more: Asexual reproduction of fungi
Examples of organisms from the kingdom Monera
The kingdom Monera includes all prokaryotic organisms, such as bacteria, archaea and cyanobacteria. Next, we'll talk a little more about bacteria, the best-known organisms in this kingdom.
Bacteria
At bacteria are unicellular organisms well known for causing disease, however, bacteria do not only cause damage, they are important, for example, in decomposition organic matter and food production such as yoghurts. the bacteriahave prokaryote-type cell, that is, it does not have a nucleus and cell organelles.
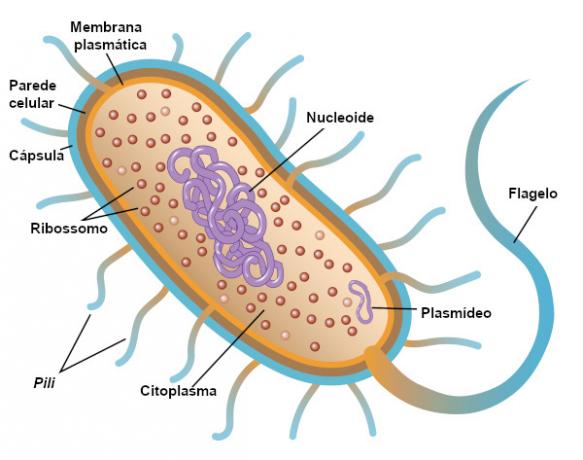
Bacteria present cell wall, a structure that surrounds the cell, ensuring its protection. The cell wall is located outside the plasma membrane and has peptidoglycan in its composition, a polymer consisting of sugars and polypeptides. The composition of the cell wall varies from one bacterium to another.
A technique known as Gram stain allows you to classify bacteria into gram negatives and gram positives. Gram-positive bacteria are characterized by having simpler cell walls, with a large amount of peptidoglycan. Gram-negative bacteria, in turn, have less peptidoglycan and a more complex structure.
Bacteria can present different formats, as they are a way of classifying them. Format bacteria spherical, for example, are called coconuts. Those that have the format of bat are called bacilli. There are also bacteria spirals. In this group are the vibrios, spirochetes and spirochetes.
Some bacteria have scourges as locomotion structures. Another structure that can be found in these organisms are the fimbriae, similar to hairs, which help the bacteria to attach to the substrate. There are also the pili, also called sexual pili — appendages that hold bacteria together during the transfer of genetic material.
Read more: Main ways of classification of bacteria
Importance of Monera kingdom organisms
Despite being highly disease-related, organisms from the Monera kingdom are of ecological as well as economic importance. See below for examples:

Many bacteria decompose, being fundamental in nutrient cycling;
Some bacteria establish interactions mutualistic, this being the case of bacteria that live in our intestines and that act, for example, facilitating the absorption of some substances and synthesizing vitamins;
Some bacteria participate in the nitrogen cycle, ensuring the fixation of atmospheric nitrogen;
Cyanobacteria and other autotrophic prokaryotes produce organic matter that is used in food chain;
Cyanobacteria produce oxygen that is released into the atmosphere;
the bacteria Clostridium botulinum produces botulinum toxin, used to smooth expression lines and wrinkles;
Some bacteria are used in food manufacturing, such as yogurt.
In which group are the organisms of the extinct Monera kingdom classified?
With the adoption of the classification of living beings into three domains (taxonomic category above kingdom), the Monera kingdom became obsolete. According to the classification into domains, living beings are grouped into the Bacteria, Archaea and Eukarya domains. US Bacteria and Archaea domains, are the prokaryotic organisms, which were part of the Monera kingdom.
In the Bacteria domain are most of the known prokaryotes. In the Archaea domain, there are organisms that live in extreme environments, known as extremophiles. Currently, most authors recognize at least six realms: Archaea, Bacteria, protist, fungi, Plante and animalia.
By Vanessa Sardinha dos Santos
Biology teacher
The Monera kingdom is composed of the most abundant beings on the planet, also known as microorganisms, as they are all unicellular and microscopic. They also present the absence of the caryotheca, being, therefore, classified as prokaryotes. The groups that make up the Monera kingdom are:
Bacteria present, as a mechanism for promoting the mixing of genes between different individuals, the process of genetic recombination. This process can occur in three ways, one of which is through the formation of a bridge (pili) between the two cells, with the migration of genes from one bacterium to another. This form of recombination is known as:



