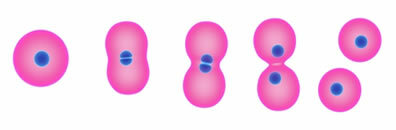
At bacteria are microscopic organisms belonging to the Kingdom Monera. are organisms prokaryotes, that is, devoid of caryotheca (membrane that covers the cell nucleus) and for this reason their genetic material is found scattered in the cell cytoplasm. At bacteria reproduce asexually by a process called binary division, also known as splitting or bipartition.
THE binary division occurs when a bacterium it duplicates its genetic material and then divides, giving rise to two identical bacteria. A bacterium, when under ideal conditions of temperature and nutrients, takes approximately twenty minutes to complete the entire division process. Now, imagine, if every twenty minutes two new bacteria appear, how many will appear in a 24-hour period?
Some bacteria (mainly those of the genus Clostridium and Bacillus), when under unfavorable conditions, they dehydrate, forming very resistant structures called endospores. These structures are able to withstand high temperatures, lack of water and even the action of substances that, in most cases, kill microorganisms. When they find favorable environmental conditions, the
endospores they rehydrate and the bacterium reconstitutes itself, returning to reproduce by binary division. The fight against bacterial endospores is a great challenge for the food industry and for medicine, as, as we have seen, they are extremely difficult to be exterminated.Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
At bacteria do not show any type of sexual reproduction, it is yes genetic recombination which can occur by transformation, transduction or conjugation.
THE transformation it occurs with some bacteria that can absorb DNA fragments that are dispersed in the medium. These fragments are incorporated into the genetic material of bacteria, transforming them.
At bacterial transduction exchange of genetic material between bacteria occurs with the participation of a bacteriophage.
THE bacterial conjugation, as it happens in the transformation and on transduction, it is the passage of DNA from a donor to a recipient cell. In the case of conjugation, the contact between the bacterial cells is necessary, and the donor has a conjugative plasmid, which has genes that code, for example, for the pili F (F = fertility). This binds to the recipient bacterial cell and receives a strand of Plasmid (remember that plasmids are extrachromosomal DNA molecules). As the strands are complementary, the one that remained serves as a template for another strand and the one that went to another cell as well. Conjugation is a form of genetic recombination between bacteria. As there is no increase in the number of bacterial cells, it cannot be considered a form of reproduction.
By Paula Louredo
Graduated in Biology
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
MORAES, Paula Louredo. "Reproduction of bacteria"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/biologia/reproducao-das-bacterias.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.
