Let's consider the figure above, where two blocks A and B are moving in the same horizontal direction, but they have opposite directions. We can see in the figure the possible situations before the collision and after the collision between blocks. As we know that blocks have a certain amount of movement, if the system, during the interaction period between the blocks, do not suffer any external resultant force action, we say that they (the blocks) do not have impulse. Thus, through the impulse theorem we can write:
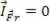

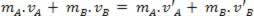
The final result above tells us that the total movement amount of the system before the collision is equal to the total movement amount of the system after the collision. With that, we can say that the amount of movement of the system is conserved. we say system mechanically isolated for a system that is free from the action of resultant external force. The result obtained in the equation above can be stated as the Law of conservation of momentum:
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
The amount of movement of a mechanically isolated system is constant.
The law of conservation of momentum is a non-fundamental law in nature that is sometimes also called the principle of conservation of momentum.
We cannot forget that a system is said to be isolated if the resultant of the external forces at work can be neglected. And that the amount of motion of a system can remain constant even if the mechanical energy does not remain, because the conservation principles are independent.
Also don't forget that the momentum of a system consisting of n elements is the vector sum of the momentum of all the elements.

By Domitiano Marques
Graduated in Physics
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
SILVA, Domitiano Correa Marques da. "The law of conservation of momentum"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/fisica/lei-conservacao-quantidade-movimento.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.