Hubble's Law was obtained experimentally and establishes a direct relationship between the distance of a galaxy any until the Earth and the speed with which this galaxy is moving away from us. According to this law, the further away from Earth, the faster the galaxies move away, a fact that suggests the possibility of living in a universe in constant expansion.
See more:Astrophysics - is dedicated to the study of the Universe by applying the laws of chemistry and physics
What does Hubble's law say?
Hubble's law says that the greater the distance between a galaxy and Earth, the faster that galaxy moves away from us. Hubble's law was discovered and formulated by the American physicist and astronomer Edwin P. Hubble (1889-1953). The figure below shows it:
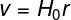
v -retraction speed (km/s)
H0 – Hubble constant (70 (km/s)/Mpc)
r – distance between Earth and galaxy (Mpc)
In this law, the constant H0, known as Hubble constant, represents how big is the increase in the speed of the galaxies at each Mpc (megaparsec). O
Mpc is a measure of astronomical distances worth approximately 3.26 million light years.Hubble was able to arrive at the above expression using data on the distance speeds of 24 nearby galaxies, previously collected by the astronomer. I wear M. slipper. Slipher was able to precisely measure the take-off speeds thanks to the spectroscopy, that is, analyzing the color frequencies emitted by galaxies. As these galaxies moved away from Earth, the frequencies of the electromagnetic waves issued by them should undergo changes due to the Doppler effect.
![Taken by the Hubble telescope, the image shows billions of galaxies in a tiny fraction of the night sky. [1]](/f/7cf0d759f3fc9e79890e3416c860d6f6.jpg)
O Doppler effect explains why we hear small frequency changes in sounds that are emitted by sources that move with respect to the observer. For example: when an ambulance approaches or departs from us, we may notice, respectively, that the sound emitted by it becomes higher and then lower.
This apparent change in the frequency of sound waves also happens for electromagnetic waves — once galaxies move away, the light that is emitted by them tends to move to lower frequencies, so we say that, in these galaxies, it is possible to observe a redshift (in English, red-shift).
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
Hubble constant
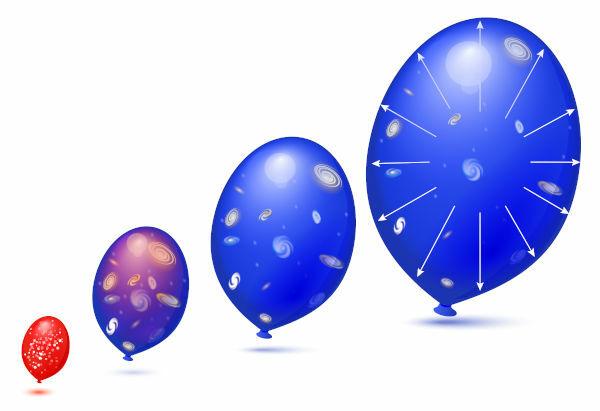
Over the years, the Hubble constant has had its value updated several times. These changes were due to the precision with which we are able to measure the distances between Earth and galaxies. According to astronomical measurements, the Hubble constant it's the same for all directions we look — there is no preferred departure direction. In practice, it's as if we were a small dot in a bladder being constantlyinflated.
In Hubble's time, the method used to measure astronomical distances was rudimentary, so he developed a much more intelligent way of inferring them: comparing the brightness between them, since the farther away they are, the lower the brightness emitted by them. It was through the shinerelative among the galaxies that Edwin Hubble was able to determine, with even greater precision, the value of its constant.
See too: Black holes - what they are, what they are made of, discoveries and curiosities
Universe expansion
The first indications of a possible expansion of the Universe were only possible thanks to the discoveries of Edwin Hubble. However, we still know very little about how the Universe expands, in this sense, the discovery of Hubble's law produced, in the same measure, new answers and new questions.
It is still not really known what causes the expansion of the Universe, when, from the point of view of classical physics, supported by the law of universal gravitation, the tendency of the Cosmos would be to shrink rather than expand. There are a large number of theories that try to explain the phenomenon of expansion, however, none of them could be proven until the present day.
In an attempt to explain the accelerated expansion of the Universe, physicists proposed the existence of dark matter. According to modern theories, dark matter should be able to explain what is observed in Hubble's law, however, this type of matter must have “exotic” properties that, until then, have never been observed in matter. ordinary.
Hubble's Law in Enem
Hubble's law has already been enforced in the And either, in the 2019 test. The question directly addressed the use of Hubble's law, shall we analyze it?
(And either) Astronomers measure the speed of distance from distant galaxies by detecting the light emitted by these systems. Hubble's law states that a galaxy's speed of departure (in km/s) is proportional to its distance to Earth, measured in megaparsec. In this law, the proportionality constant is the hubble constant (H0) and its most accepted value is 72 (km/s)/Mpc. The parsec (pc) is an astronomical unit of distance, worth approximately 3.1016 m. Astronomical observations have determined that the speed away from a given galaxy is 1440 km/s.
Using Hubble's law, it can be concluded that the distance to this galaxy, measured in km, is equal to:
a) 20.100
b) 20.106
c) 6.1020
d) 6.1023
e) 6.1026
Template: Letter C
Resolution:
To resolve this issue, it is necessary to interpret the statement. Through it, it is possible to solve it even if you do not know the expression of Hubble's law, however, before starting the calculations, we need to adjust the measurement units, remembering that 1 pc is equivalent to 3.1016 m or 3.1013 km, note:

After we have correctly adapted the measurement unit of the Hubble constant, we can do the calculation to determine the distance:

Know more:Radio telescopes - what they are and what they are for
Hubble's Law Exercises
Question 1) The Andromeda Galaxy is the closest spiral galaxy to the Milky Way and lies at a distance of approximately 0.77 Mpc. Based on Hubble's law, the speed at which the Andromeda galaxy moves away from the Milky Way is approximately:
Data: H0 = 72 (km/s)/Mpc
a) 96.5 km/s
b) 55.4 km/s
c) 108.4 km/s
d) 15.7 km/s
Template: Letter B
Resolution:
The measurement units provided by the statement are already compatible with each other, so we just use Hubble's law and replace the data:
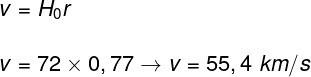
The result indicates that the Andromeda galaxy moves away with a speed of approximately 54 km/s, so the correct answer is letter B.
Question 2) A galaxy A is at a distance d from Earth and away with speed v. Knowing that galaxy B is twice as far from Earth than galaxy A, it can be said that its speed of departure:
a) will be half the speed of departure from galaxy A.
b) will be equal to the speed of departure from galaxy A.
c) will be four times smaller than the speed of departure from galaxy A.
d) will be twice as fast as galaxy A's speed away.
Template: Letter D
Resolution:
Hubble's law establishes a directly proportional relationship between the speed of departure and the distance, so being twice as far away, galaxy B moves twice as fast:
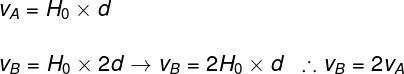
Image credits
[1] NASA | commons
By Rafael Hellerbrock
Physics teacher