At intermolecular forces are a topic in Chemistry that, for sure, can appear in the National High School Exam (And either). Therefore, it is worth checking out the main contents of this subject in this article.
Definition
intermolecular forces they are forces – of varying intensities (weak, medium or strong) – of electrostatic attraction or bonds established between the molecules of a substance that maintain the union between them.
Types of intermolecular forces
The) Induced dipole
And the intermolecular force that occurs between molecules of a substance with a nonpolar characteristic. It happens, for example, between molecules of substances such as O2, H2, no2, CO2, CH4.
The union between these molecules occurs when a dipole is created between them. This happens when the electrons of one molecule displace the electrons of another, thus creating a negative and a positive pole, which is transferred from one molecule to another.
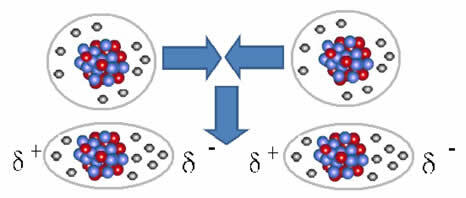
Representation of dipole formation in nonpolar molecules
Between these molecules, two poles were formed, and the negative pole of one interacts with the positive pole of the other. Because these poles were created, it is a low-intensity intermolecular force.
B) permanent dipole
And the intermolecular force that occurs between molecules of a substance with a polar characteristic. Examples are molecules of substances such as HCN, H2O, NH3, CO, CH3Cl.
The union between these molecules happens when the negative pole of one interacts with the positive pole of the other.
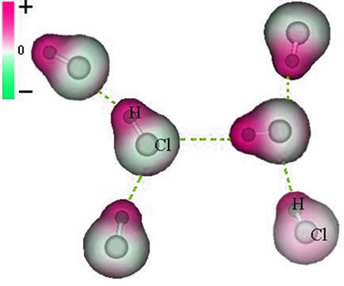
Representation of the permanent dipole force between HCl molecules
As the poles already exist, the permanent dipole intermolecular force is of greater intensity than the induced dipole.
ç) hydrogen bonds
That intermolecular force it occurs between polar molecules that have a hydrogen atom bonded directly to an oxygen, nitrogen or fluorine atom.
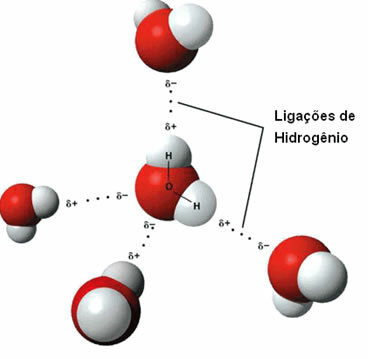
Representation of hydrogen bonds between water molecules
A hydrogen bond is formed when the hydrogen in one molecule interacts with the oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine of the other molecule.
d) dipole ion
This intermolecular force occurs between a polar molecule, which has a pair of non-bonding electrons, and an ion (cation or anion) in the solution.
The water molecule, for example, has two pairs of non-binding electrons in oxygen. If there are ions in the aqueous medium, they get closer to the water molecule, as there are poles in it.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
Importance
The importance of knowing the intermolecular forces for Enem it is the understanding they bring regarding the physical states, melting point, boiling point and solubility of substances.
The) Relationship with the melting and boiling point of the substance
The melting point indicates the temperature of the transition from a solid to a liquid state, and the boiling point indicates the temperature of the transition from a liquid to a gaseous state.
This passage is directly related to the interaction between the molecules of the substance, as what differentiates one physical state from another is the level of aggregation between its molecules.
Thus, the more intense the intermolecular force, the higher the melting and boiling points. The less intense the intermolecular force, the lower the melting and boiling points. Thus, we can define the descending order of melting and boiling point:
Hydrogen bond > permanent dipole > induced dipole
B) Relation to solubility
In general, we must know that like dissolves like, that is, polar substance dissolves polar substance and non-polar substance dissolves non-polar substance.
However, there is still the possibility of interaction between the solute molecules and the solvent molecules. This happens only if this new interaction is greater than what already exists between the molecules of the substance itself.
Example of application of intermolecular force in Enem
1st Example: (Enem-2011) Human skin, when well hydrated, acquires good elasticity and a soft and smooth appearance. On the other hand, when it is dry, it loses its elasticity and appears opaque and rough. To prevent skin dryness, it is necessary, whenever possible, to use moisturizing moisturizers, generally made with glycerin and polyethylene glycol:

The water retention on the skin surface promoted by moisturizers is a consequence of the interaction of the hydroxyl groups of the wetting agents with the moisture contained in the environment through:
a) ionic bonds
b) London forces
c) covalent bonds
d) dipole-dipole forces
e) hydrogen bonds
The answer to this question is hydrogen bonding, as the water molecule has hydrogen bonded to an oxygen atom. The same happens with the molecules of propylene glycol and polyethylene glycol, a favorable condition for the occurrence of this type of intermolecular force.
By Me. Diogo Lopes Dias
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
DAYS, Diogo Lopes. "Intermolecular Forces in Enem"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/forca-intermoleculares-no-enem.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.


