THE ozone layer (O3) it is formed by atmospheric gases, which are found between 20 km and 35 km in altitude, in the stratosphere. Its primary function in the Earth's atmosphere is filter and prevent the passage of ultraviolet rays (UV-A, UV-B and UV-C) to the surface of the Earth.
The central importance of the ozone layer is to keep out ultraviolet rays. When performing this primary function, the results are positive, as the UV filter prevents the Earth from warming, which, in turn, does not develop the greenhouse effect, global warming, diseases triggered by this process, such as skin cancer, the decrease in biodiversity, between others. Its destruction is taking place through the unrestrained emission of gases such as CFC, which causes an increase in the harmful effect on human and planet health.
Read too: Four new gases that deplete the ozone layer
Formation of the ozone layer
The ozone layer (O3) é formed by atmospheric gases, which lie between 20 km and 35 km of altitude, in the stratosphere. Approximately 90% of the ozone layer is formed by this gas.
In the atmosphere, this gas is created when the ultraviolet (UV) solar radiation comes in contact with oxygen (O) and interacts with the molecule of oxygen, causing it to be broken into two oxygen atoms (O2). When they come into contact with another oxygen molecule, the Ozon. Note the following equation:
(O2 + O = O3)
Thus, the importance of this interaction of UV rays with oxygen is observed, in the formation of more oxygen gas and in promoting the natural maintenance of the ozone layer.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
Ozone layer function
The primary function of the existence of the ozone layer in the Earth's atmosphere is filter and prevent the passage of ultraviolet rays (UV-A, UV-B and UV-C) to the Earth's surface. Thus, any change in the ozone layer directly affects this function, causing an environmental imbalance.
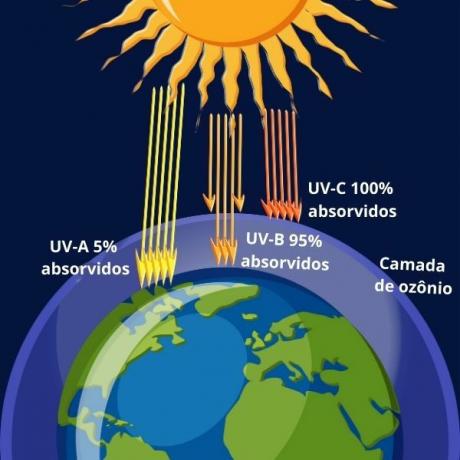
It is understood that this layer protects living beings at various times and various factors that are caused by the inexistence or destruction of the ozone layer. These are problems related to health and environmental balance that can lead to the destruction of life on Earth. Highlights:
- Skin cancer and diseases related to Sun and to UV rays
- Skin diseases
- Problems related to eyesight
- Global warming
- Greenhouse effect
- Change of water cycle
- Melting of polar ice caps
- Increased level of oceans
- loss of biodiversity
See too: Seven man-made ecological disasters
Importance of the ozone layer
It is understood that the importance of the ozone layer is related to balance of planet earth, in general, its natural maintenance avoids these environmental problems faced today.
The central importance of the ozone layer is keep out ultraviolet rays. When performing this primary function, the results are positive, as the UV filter prevents the Earth from warming, which does not develop the greenhouse effect or global warming, without the melting of the ice caps and, consequently, the rise in the level of the oceans. Finally, no type of biodiversity is affected by this phenomenon of rising waters, the water cycle is maintained, and the environmental and natural balance remains.
Thinking about the functioning of the ozone layer and its importance is the same as thinking about the health and maintenance of life on planet Earth, and keeping the layer working will reflect that same result.
What harms the ozone layer?
The ozone layer is being harmed by the existence of gases that come into contact with UV rays and end up reacting with them, reducing the amount of ozone gases in the Earth's atmosphere. There are several substances, such as:
- Nitric Oxide (NO)
- Carbon dioxide (CO2)
- Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)
- Nitrous oxide (N2O)
These gases are produced by various activities, like the burning of fossil fuels, the burning of fuels in vehicles and the chemical industries, even household appliances and products used in everyday life are responsible for damaging the layer of ozone.
When coming into contact with the layer, the molecules of these substances promote the decomposition of the ozone molecule (O3), thus creating oxygen gas (O). The absence of ozone in the layer disrupts its central function of filtering out ultraviolet rays. This action causes problems in the ozone layer.
Depletion of the ozone layer
Ozone can be destroyed in the atmosphere naturally or as a result of human activities. It is naturally destroyed by the Sun's ultraviolet radiation., for each ozone molecule destroyed, one oxygen atom and one oxygen molecule are formed, being able to recombine to produce ozone again, and thus maintain the layer. of ozone.
Despite its natural reconstitution, the ozone layer is being chemically altered and it is not returning to normal, being altered by intense human activities, with the burning of fossil fuels and industrial development. Some gases are among the most harmful emitted into the atmosphere, capable of altering the ozone layer, they are:
- Halom (CBrCtF2)
- Carbon tetrachloride (CTC)
- Hydrochlorofluorocarbon (HCFC)
- Chlorofluorocarbon (CFC)
- Methyl bromide (CH3BR)
When released, these gases reach the ozone layer and move above it, promoting its alteration and consequent destruction. Another relevant aspect is the fact that some chemical elements are active for 80, 90, 100 years.
Hole in the ozone layer
O Buraco in çbeloved of Ozon consists of a phenomenon that occurs in the polar regions, especially in Antarctica, where the ozone concentration decreases. It is a natural phenomenon at certain times of the year and then disappears. Its existence in Antarctica is easier due to the region's cold, which allows for greater interaction between chemical elements.

In the last decades the hole started not disappearing, due to the increase of gases in the atmosphere, resulting from the activities of human beings. The most common example of pollutant gas is chlorofluorocarbon gas, which easily reacts with ozone and is widely used in industry, in refrigerators, freezers and spray aerosol.
There is currently a worldwide attempt to reduce the use and production of these gases, in order to stabilize the ozone layer and prevent the growth of the hole, considering that its destruction will bring harmful results to human health and environmental balance planetary.
See more: Acid rain - atmospheric phenomenon consisting of precipitation with high acidity
Consequences of the destruction of the ozone layer
As already mentioned, planet Earth needs the functioning and existence of the ozone layer as a way to protect against radiation coming from the Sun and the arrival of ultraviolet rays in the lithosphere. Its destruction would cause some problems.
Without the protection of the ozone layer, various impacts to the environment and health would be registered more frequently. Among them we highlight:
- Risks and damage to eyesight
- Premature aging
- Increased cases of skin cancer
- Cell degeneration of the skin
- Weakening of the immune system
Such health-related factors plus those of environmental imbalance (such as an increase in the Earth's temperature, or reduction of polar ice caps and consequent increase in ocean levels) can only be remedied as what governmental actions and practices are carried out, thus reversing the actual increase in the ozone layer.
By Gustavo Henrique Mendonça
Geography teacher


