Impulse and amount of movement they are vector physical quantities used in the study of dynamics. The unit of measurement for both is the same (kg.m/s), and they are related by the impulse theorem and also by the Newton's second law.
What is momentum?
Quantity of movement is the product between the pasta of a body and its speed. It is a vector quantity whose unit of measurement, according to sInternational System of Units (SI), it can be either the kg.m/s or the N.s.
THE formula used to calculate the amount of movement is as follows:
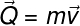
Q - amount of movement (kg.m/s)
m – mass (kg)
v – speed (m/s)
The amount of movement is a particularly useful quantity for studying the collisions, since, in elastic collisions, the total amount of movement must be kept constant.
What is impulse?
Impulse is the measure of variationgivesthe amountinmovement. Like momentum, it is a vector quantity. When you apply a boost to a body, its amount of movement changes. The simplest definition of impulse is shown in the formula below.
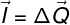
I – impulse (kg.m/s or N.s)
∆Q – variation in the amount of movement (kg.m/s or N.s)
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
impulse and strength
When applying a strength to a body, the impulse that is applied to that body depends on the time of contact between the bodies. The longer this time, the greater the thrust provided and the greater the amount of movement variation.
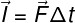
F – force (N)
t – time interval(s)
From the above formula, you can see that for a given impulse measure, force and time interval are inversely proportional. This fact explains the usefulness of car bumpers, since, since the collision lasts longer due to the deformation of the bumper, the force exerted on the vehicle and the passenger is smaller, although the impulse suffered is the same as that of a collision that would occur without this protection.
See too: Acceleration - what is it, solved formulas and exercises

Newton's second law, impulse and quantity and motion
Originally, the Newton's second law, known as Fundamental Principle of Dynamics, was written in terms of quantities such as momentum, momentum, and time. According to this law, the net force on a body is equal to the product of its mass and its acceleration, but this definition can also be written so that the resulting force is equal to the change in the amount of movement during a certain interval of time.
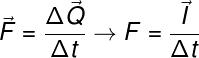
Finally, the two expressions shown above can be combined so that the variation of the amount of movement is equal to the product of the resulting force and the application time interval of strength. This identity is called the impulse theorem.
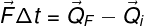
Read too: Summary with all the most important things about Newton's three laws
Solved exercises on impulse and amount of movement
Question 1 – (Udesc) O air bag and seat belts are safety items present in all new cars manufactured in Brazil. Using the concepts of Newton's First Law, of thrust of a force and variation of momentum, analyze the propositions.
I. O air bag increases the thrust of the average force acting on the car occupant when colliding with the dashboard, increasing the amount of movement of the occupant.
II. O air bag it increases the collision time between the car occupant and the dashboard, thus decreasing the average force acting on the car occupant in the collision.
III. The seat belt prevents the car occupant, in a collision, from continuing to move with a uniform rectilinear movement.
IV. The seat belt slows the car occupant in a collision, increasing the occupant's amount of movement.
tick the alternative correct:
a) Only statements I and IV are true.
b) Only statements II and III are true.
c) Only statements I and III are true.
d) Only statements II and IV are true.
e) All statements are true.
Template: letter B.
Resolution:
Let's analyze each of the alternatives:
[I] - False. O air bag reduces the force applied to the body, increasing the time of force application.
[II] - True.
[III] - True.
[IV] - False. The amount of movement of the occupant is reduced.
Question 2 - (PUC-RJ) A tennis player, during the service, throws the ball vertically upwards. Upon reaching its maximum height, the ball is hit by the tennis racket and leaves with a speed of 108 km/h in the horizontal direction.
Calculate, in kg.m/s, the modulus of the ball's linear momentum variation between the instants just after and just before being hit by the racket.
Given: Consider the mass of the tennis ball equal to 50 g.
a) 1.5
b) 5.4
c) 54
d) 1500
e) 5400
Template: letter a.
Resolution:
To solve the exercise, it is necessary to write the mass, which is in grams, in kilograms (m = 50.10-3 kg). Furthermore, the speed, which is in km/h, must be expressed in m/s. Note the calculation:

Question 3 - (UECE) Consider a very small sphere with a mass equal to 1 kg traveling at a speed of 2 m/s without rotating for 3 s. In this time interval, the linear momentum of this particle is:
a) 2 kg.m/s
b) 3 s
c) 6 kg.m/s
d) 6 m
Template: letter a.
Resolution:
To solve the exercise, it is enough to multiply the mass and speed of the body, but it is also necessary to remember the unit of measure of the amount of movement, the kg.m/s.
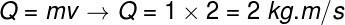
By Rafael Hellerbrock
Physics teacher
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
HELERBROCK, Rafael. "Impulse and amount of movement"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/fisica/impulso-e-quantidade-de-movimento.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.