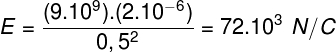Magnetic Flux
Suppose a flat surface of area A that is placed in the presence of a uniform magnetic field and magnetic induction B. Let n be normal to the surface and α the angle that n makes with the direction of magnetic induction, see:

Thus, we can define magnetic flux by the letter Φ(fi), as being the product of the magnetic induction, the area of the flat surface and the cosine of the angle formed, that is:
Φ = BA cos θ
Remembering that magnetic induction is a vector quantity, so it has a magnitude, direction and sense. In the International System of Units (SI), the unit of magnetic flux is the weber, in honor of the German physicist who lived in the 19th century and, together with Gauss, studied terrestrial magnetism. The unit of magnetic induction (B) is the tesla (T).
Magnetic flux can be understood as the number of lines of induction that cross the surface, so therefore, we can conclude that the greater the number of lines that cross the surface, the greater the flux value magnetic.
Faraday's Law
Faraday performed numerous experiments and in all of them he noticed a very common fact that occurred whenever an induced electromotive force appeared. By analyzing all his works, he found that when the electromotive force appeared in the circuit, there was a variation in the magnetic flux in that same circuit. Faraday observed that the intensity of the f.e.m is increasing the faster the variation of the magnetic flux occurs. More precisely, he found that during a time interval Δt the magnetic flux varies ΔΦ, and that way he concluded that f.e.m is given by the ratio between variation of magnetic flux and variation of time, Look:
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
ε = ΔΦ/Δt
The appearance of the electromotive force was called electromagnetic induction and the expression described above became known as the Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction.
By Marco Aurélio da Silva
Brazil School Team
Electromagnetism - Physics - Brazil School
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
SANTOS, Marco Aurélio da Silva. "Magnetic Flux and Faraday's Law"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/fisica/fluxo-magnetico-lei-faraday.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.