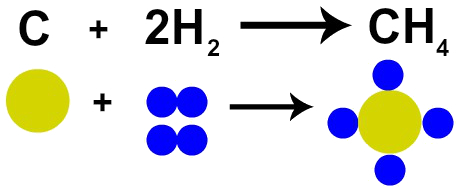
What evidences a reaction is the transformation that occurs in substances in relation to their initial state, these modifications depend on the type of reaction that the reactants will go through.
There are several criteria to classify chemical reactions, one of them relates the number of substances that react (reactants) and the number of substances produced (products). To better illustrate, we will use the letters: THE, B, Ç, X, Y.
Synthesis or addition reaction: are those in which two or more substances originate a single product.
A + B → Ç
Example of this reaction: when magnesium reacts with oxygen in the air:
2Mg(s) + 1 O2(g) → 2MgO(s)
This reaction is present in disposable photographic flashes and signal rockets.
Analysis or decomposition reaction: in this reaction a single substance generates two or more products.
THE → B + C
Some reactions are given special names:
Electrolysis: substances decompose by the passage of electrical current.
Photolysis: chemical decomposition by light.
Pyrolysis: decomposition by the action of heat and fire.
Example: Airbags are safety devices present in many cars. When we trigger this device, the rapid decomposition of the NaN sodium compound3(s) originates N2(g) which inflates the airbags. See the reaction:
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
2 NaN3(s) → 3 N2(g) + 2 Na(s)
Simple exchange or displacement reaction: occurs when a simple substance reacts with a compound, originating new substances: one simple and one compound.
A + XY → Y+X
Example: When a sheet of zinc is introduced into an aqueous solution of hydrochloric acid, zinc chloride will form and hydrogen gas will be released.
Zn (s) + 2 HCl (aq) → ZnCl2(aq) + H2 (g)
Note that Zinc displaced Hydrogen, hence the name “displacement reaction”.
double exchange reaction: two reagents react forming two products, that is, if two compound substances react giving rise to new compound substances, they receive this name.
AB + XY → Y+XB
Example: The reaction between sulfuric acid with barium hydroxide produces water and barium sulfate.
H2ONLY4 (aq) + Ba (OH)2(aq) → 2 H2O(1) + BaSO4(s)
The barium sulfate product: BaSO4(s) is an insoluble white salt.
By Líria Alves
Graduated in Chemistry
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
SOUZA, Líria Alves de. "Types of Chemical Reactions"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/tipos-reacoes-quimicas.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.