THE acceleration it is the quantity that determines the rate of change of speed as a function of time. In other words, it indicates the increase or decrease in speed over time. Acceleration is a Vector greatness, therefore, has module, direction and meaning.
The equation below determines the magnitude of the acceleration:
a = ov
t
a = acceleration (m/s2);
Δv = speed variation (J);
Δt = time variation (s).
Direction and direction of acceleration
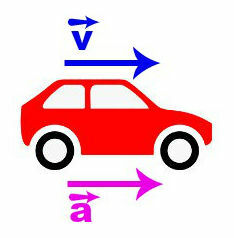
When the acceleration value is positive, it means that an increase in velocity occurred over time. In this case, the movement is called accelerated movement, and the acceleration vector has the same direction and direction as the velocity vector.
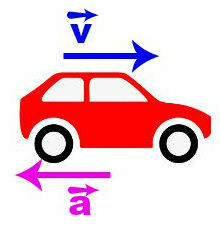
When the speed value is negative, it means that the speed has decreased over time. In this case, the move is called delayed movement, and the acceleration vector has the same direction and opposite direction as the velocity.
Unit of measure for acceleration
According to International System of Units (SI), the unit of measure for speed is the meter per second (m/s). As acceleration is the ratio between velocity variation and time variation, its unit is the result of the ratio between velocity and time units, therefore:
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
(m/s) / s = m/s2
Acceleration is given in meters per second squared, that is, a body that has an acceleration equal to 8 m/s2 has its speed increased by 8 m/s for every second of movement.
gravity acceleration
every body that runs free fall near the earth's surface it always falls with the same acceleration value. This acceleration is known as gravity acceleration and it is related to the mass of the planet and the square of the distance between the body and the surface of the planet.
For Earth, the acceleration of gravity corresponds to 9.8 m/s2. This means that, near the earth's surface, any body that is in free fall will have a speed increase of 9.8 m/s at every second of movement. On the Moon, for example, this increase corresponds to 1.6 m/s every second, so the gravity of our natural satellite is 1.6 m/s2.
By Joab Silas
Graduated in Physics
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
JUNIOR, Joab Silas da Silva. "What is acceleration?"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/o-que-e/fisica/o-que-e-aceleracao.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.
