Dissociation of bases it is a physical process that occurs with this important group of inorganic substances when they are dissolved in water, or when they go through the fusion process (passage from the solid state to the liquid state through heating).
In general, the phenomenon of base dissociation it is the release of the cations and anions that form the ionic compound, which, in this case, is the base. So, during the base dissociation, the release of ions that already exist in the compound, that is, no new ions are formed.
The base is formed by any metal (X), which is the cation of the compound, or by the ammonium cation (NH group4+), bonded to the hydroxide anion (represented by the OH group), as in the representations below:
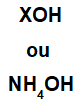
General representations of a base formula
the form of represent the base dissociation it is done through an equation in which, in the reactant, we have the base and, in the products, we have the ions (cations and anions). What makes the difference is how the dissociation takes place:
Dissolution of the base in water:
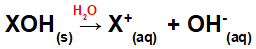
Equation representing the dissociation of a base in an aqueous medium
Dissociation by base merger:
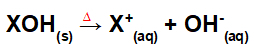
Equation representing the dissociation of a base by the fusion process
Analyzing the general equations above, we verify that in all of them we will always have the base, the cation (which is the metal or NH group4+) and the anion (OH-). But are they all like that? Is there no difference between them? For the first question the answer is no and for the second question the answer is yes.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
When we carry out the dissociation from a base, it is fundamental first to analyze the base formula, because, from it, we can determine the load of the cation and the mol amount of hydroxide anions, since the mol amount of cation is standard (always 1 mol).
It is worth remembering that the amount of OH groups present in the base formula determines the charge of the cation and the amount in mol of the hydroxide anion in the dissociation of the base.
Let's look at the examples of aluminum hydroxide [Al(OH)3] and gold hydroxide (AuOH). In the aluminum base formula, there are three OH groups, and in the gold base formula, only one OH group. Thus, in the dissociation of these bases, we have:
Al(OH) dissociation3:
As this base has three OH groups in the formula, the charge on the cation will be +3 and the amount in mol of anions is equal to 3 mol, as we can see in the following equation:
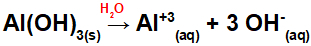
Aluminum base dissociation equation in aqueous medium
Dissociation from AuOH:
As this base has an OH group in the formula, the charge on the cation will be +1 and the amount in mol of anions is equal to 1 mol, as we can see in the following equation:
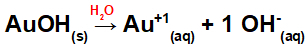
Equation of base dissociation with gold in aqueous medium
By Me. Diogo Lopes Dias
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
DAYS, Diogo Lopes. "What is base dissociation?"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/o-que-e/quimica/o-que-e-dissociacao-das-bases.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.
Chemistry

Dissociation and Ionization, Italian Scientist Volta, Electric Current, Swedish Physical Chemist Svant August Arrhenius, Theory of Arrhenius, positive ions, cations, negative ions, anions, caustic soda, table salt, polar molecules, dissociation ionic,

