Urbanization it's the growth of cities, so much in population how much in extension territorial. It is the process in which the rural space is transformed into urban space, with the consequent population migration of the countryside-city type, which, when it occurs in an intense and accelerated way, is called rural exodus.
urban space and rural space
In terms of territorial area, in the current world, the countryside is much broader than the urban space. This is because the first requires greater space for the practices developed in it, such as farming, O extractivismmineral and vegetal, in addition to the delimitation of areas of environmental preservation and forests in general.
However, in terms of population and in productive activities in the economic and capitalist context, the city, currently, is overlapping the countryside. If you are more interested in this topic, read our text: urban space and rural space.
urbanization process
The process of formation of cities occurs since the times of the period
neolithic. However, from a structural point of view, they were always linked to the field, as they depended on it to survive.What changes in the current urbanization process capitalist, which intensified from the 18th century onwards, is that now it is the countryside that becomes dependent on the city, as it is in it that the economic-social logics that structure the rural environment are defined.
The urbanization process in the context of the industrial period is based on two types of causes: attractive factors and the factors repulsive.
→ Attractive factors: As the name suggests, they are those in which urbanization occurs due to the structural conditions offered by the space of cities, the biggest one being industrialization.
This process is characteristic of developed countries, where the urbanization process first took place. Cities like London and New York became predominantly urban from the 1900s onwards, early 20th century, due to the amount of jobs and of the housing conditions offered (although, at first, most of these housing were precarious compared to the current development patterns of these cities).
→ Repulsive factors: are those in which urbanization occurs not because of the productive advantages of cities, but thanks to this kind of expulsion from the population from the countryside to urban centers. This process occurs, in general, through the modernization of the field, which provided the replacement of man by machine, and by the process of land concentration, which left most of the amounts of land in the hands of a few large landowners.
This phenomenon is characteristic ofunderdeveloped countriesand is marked by high speed in which the rural exodus took place, as well as the concentration of the population in the metropolises (metropolization). Such cities are unable to absorb this amount of population, providing the forganization of slums and irregular housing, generally precarious and without infrastructure.
Briefly, the urbanization process takes place in four main stages, with a few variations in different parts of the planet:
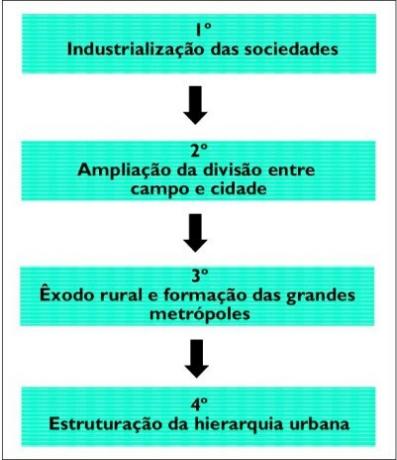
In general, what is observed is industrialization functioning as a motor for the urbanization of societies (1st point of the previous scheme). Then, the economic divisionsand productive, with the field producing raw material and cities producing industrialized goods and carrying out activities characteristic of the tertiary sector (2nd point).
This process is accompanied by a high rural exodus, with the formation of large metropolises and, in some cases, even megacities, with populations exceeding 10 million inhabitants (3rd point). Finally, the call is structured urban hierarchy, which ranges from small and medium-sized cities to large metropolises.
Remember that this scheme is just illustrative, Because the sequence of these events is not linear. Often the aforementioned phenomena happen at the same time. Another important caveat is that such a sequence does not happen equally across the world. In pioneer countries in the urbanization process, it occurs more slowly and gradually, while in countries of late industrialization, this process manifests itself more rapidly, which creates greater problems structural.
See too:Industrialization and urbanization
Mental Map: Urbanization
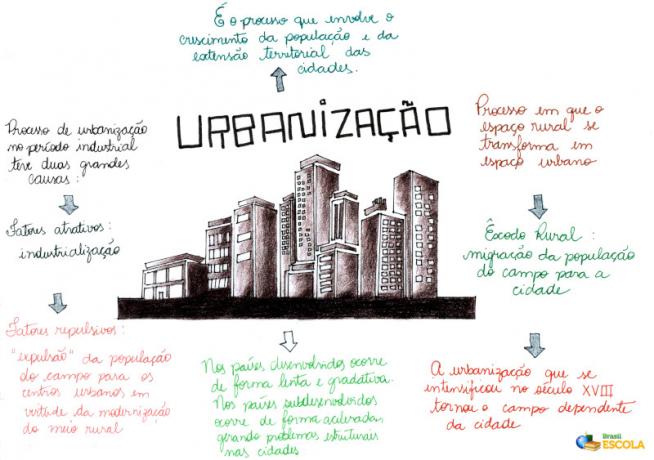
* To download the mind map in PDF, Click here!
world urbanization
Over the years, society has undergone several changes, especially with regard to the appropriation of geographic space. in mid- 1800, the world population was practically rural, only about 3% lived in urban areas. However, one fact marked a whole social transformation, completely changing the population structure around the world.
O increase in industries, linked to an expressive technological development, made people migrate for cities looking for work. Therefore, the Employment Opportunities during this period they are considered attractive factors, while the intense field mechanization it was considered a repulsive factor.
By 1950, the urban population was approximately 746 million people. In 1950 there was a very significant increase, going to 3 billion and 900 million inhabitants in the urban area.
at the moment, according to United Nations Organization, about 54% of the world's population lives in urban areas, and there are projections by the organization that this percentage will increase, by 2050, to 66%, corresponding to almost 2.5 million people moving to these areas. Expected growth is especially concentrated on the continents African and Asian.
Thus, according to the UN, the growth of the world urban population, being high, especially in developing or underdeveloped countries, did not occur sustainably, causing several social, environmental and even climatic problems.
Approximately 900 million people who moved to cities now live in slums around the world, inserted in a misery context, hunger and various health problems. To learn more, read our text: urbanization in the world.
Brazilian urbanization

São Paulo is the city with the highest urban concentration in Brazil.
The industrialization process, provided by theIndustrial Revolutionstarted in Europe, was the driving factor of urbanization in Brazil, which began in the 20th century. The modernization of the field lived in the period of industrialization provoked an expressive rural exodus. It is noteworthy that, until around 1950, the Brazilian population mostly lived in rural areas.
According to the Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics (IBGE), there was a big increase of the Brazilian urban population between the years of 1940 and 2010, note the urbanization rate in this period:
Time course |
urbanization rate |
1940 |
31,24 |
1950 |
36,16 |
1960 |
44,67 |
1970 |
55,92 |
1980 |
67,59 |
1991 |
75,59 |
2000 |
81,23 |
2007 |
83,48 |
2010 |
84,36 |
Thus, according to the agency, currently more than 80% of the population in the country live in urban areas. And of this total population, 28% is concentrated in the region Southeast, more specifically in Sao Paulo (13%), Rio de Janeiro (10%) and Belo Horizonte (5%). Thus, it is possible to affirm that the urbanization process occurs unevenly in the country.
THE Southeast region is,therefore, the one that concentrates the most population, about 92% of these live in urban areas. And this is due to countless attractive factors, such as the presence of industries and the consequent job offer. The region Midwest comes in second, with about 88.8% of the population living in urban areas. The South region concentrates approximately 92% of the inhabitants in cities. the regions North and North Eastpresent the lower rates of urbanization, 73.53% and 73.13%, respectively.
UN projections indicate that, in the year 2050, the Brazilian urban population can reach 93.6%, which corresponds to approximately 237 million inhabitants living in cities across the country.
Read too:How urbanization happened in Brazil
Consequences
The urbanization process, in addition to occurring unequally, not only in Brazil but in different parts of the world, takes place in an uneven way. messy, then pointing to Lack of planning. This entails several urban problems of a social and environmental order. Some of them are:

The Rocinha favela, located in Rio de Janeiro, is the largest favela in Brazil.
slums: The lack of planning and public policies makes many people (when going to cities and not finding places to shelter) occupy terrestrial areas, often in risky areas. Favelização is a consequence of urban swelling and disorderly occupation of cities.
Excess garbage: Visibly, where there is a greater concentration of people, there is also greater waste production. The increase in the number of inhabitants in large cities meant that there was greater production of garbage, which, by sometimes it is discarded incorrectly, causing other urban problems as well as environmental problems. According to the IBGE, in Brazil, around 50% of the waste generated is deposited in incorrect places, in the open air.
Pollution: The issue of pollution can have different natures. Large cities concentrate, in addition to a large number of inhabitants, also a large number of industries and automobiles, which daily emit various polluting gases into the atmosphere, causing air pollution. THE noise and visual pollution it is also a major problem experienced in urban centers, compromising the population's well-being.
Violence: Processes such as the marginalization of the population through slums or disorderly occupation contribute to the increase in violence. The swelling of cities associated with the inability to house the entire population, unhealthy housing conditions and the lack of public policies that serve this portion of the population has the direct consequence of increasing the crime.
Floods: The urbanization process is linked to several issues, such as the increase in waste production associated with soil sealing. The paving of cities and poor planning affect the flow of water, causing floods.
Read too:Environmental problems in large urban centers
Most Populated Cities in the World
The most populous cities in the world today are:
- Tokyo(aproapproximately 36 million inhabitants)
- Mexico City (with a little over 20 million inhabitants)
- Mumbai (with about 20 million inhabitants)
- Beijing (with 19.6 million inhabitants)
- Sao Paulo (approximately 19.5 million inhabitants)
However, a study by Canadian researchers, Daniel Hoornweg and Kevin Pope, point out that these cities will no longer configure themselves at the top of the ranking in 2100, giving way to cities located on the African continent.
THE new projected list, based on the researchers' studies, points out that lakes, in Nigeria, will reach the first place with approximately 88 million inhabitants; kinshasa, in Congo, with 83 million inhabitants, in second place; Dar es Salaam, in Tanzania, with 73 million inhabitants, in third place; in fourth place, Mumbai, in India, with 67 million inhabitants; and, in fifth, another Indian city, New Delhi, with 57 million inhabitants. The forecast indicates that São Paulo will drop to 44th position.|1|
Summary
- The urbanization process refers to the growth of cities due to population increase.
- The increase in population in large cities is associated with rural exodus, that is, with the fact that the population leaves the countryside to head for urban centers.
- The urbanization process takes place according to attractive factors, such as industrialization, and repulsive factors, such as the modernization of the countryside.
- Currently, more than half of the world's population lives in urban areas.
- According to the Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics, approximately 80% of the Brazilian population lives in urban centers.
solved exercises
(Ufac) The intense and accelerated Brazilian urbanization has resulted in serious urban social problems,
like:
a) Lack of infrastructure, limitations on individual freedoms and high living conditions in urban centers.
b) Increased number of slums and tenements, lack of infrastructure and all forms of violence.
c) Conflicts and urban violence, struggle for land tenure and accentuated rural exodus.
d) Sharp rural exodus, changes in the fate of migratory flows and an increase in the number of slums and tenements.
e) Struggle for land tenure, lack of infrastructure and high living conditions in urban centers.
Answer: B
The main urban problems facing the social sphere in relation to Brazilian urbanization are: a housing issue, as many people are marginalized in cities, increasing the process of slums; the lack of infrastructure, given that public policies are not able to meet the demands; and the increase in violence.
(Unifal) Read the following statements.
I - The rural exodus is one of the causes of accelerated urbanization, which causes, among other problems, the increase in unemployment and the growth of the informal sector of cities in industrializing countries late.
II - The growth in the urbanization rate implies a marked improvement in the living conditions of the population of underdeveloped countries.
III - The increase in slums, clandestine subdivisions and the homeless population can be seen as a consequence of the rural exodus and growing urbanization.
Based on these statements about urbanization, mark the correct alternative.
a) Only I and II are correct.
b) Only I and III are correct.
c) All alternatives are correct.
d) Only III is correct.
Answer: B
I. correct
II. Incorrect: The increase in the urbanization rate is not related to the improvement in the living conditions of the population in underdeveloped countries, but rather to the increase in urban social problems. In these countries, the urbanization process, in most cases, is associated with issues such as increased violence, slums, increased pollution, among others.
III. correct
|1| The seven most populous cities in the world in 2100. To access, Click here.
by Rafaela Sousa
Graduated in Geography



