O heat it is the thermal energy that passes from a body with a higher temperature to another with a lower temperature. When there is no difference in temperature between two bodies, there is no heat.
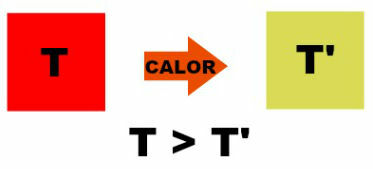
The image above shows the passage of heat from a body with temperature T to another body with a lower temperature corresponding to T'. When body temperatures equalize, we say that the thermal balance has been reached and at that moment, as there will be no temperature difference, the heat will stop flowing.
Here are some important points about heat:
1) CALORIC: Until the beginning of the 19th century, it was believed that heat was related to the presence of an invisible and weightless fluid called caloric. The higher the temperature of a body, the greater the amount of this substance in its interior. Based on observations made by Benjamin Thompson, known as Earl of Rumford (1753-1814), experiments were carried out to prove the idea that heat is energy. The experiment with the greatest prominence in this proof belongs to Prescott Joule (1818-1889).
Mind Map: Heat
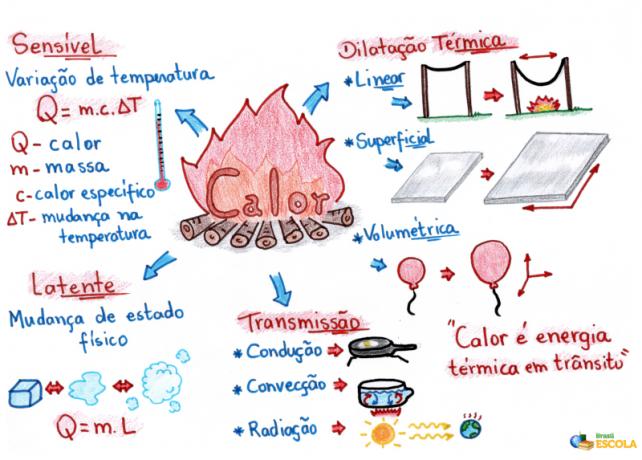
*To download the mind map in PDF, Click here!
2) Unit of measure: According to International System of Units (SI), the unit of measure for heat is the joule, but the unit of calorie (cal) is used a lot.
1 cal = 4.18 J
A calorie is the amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of 1 g of water by 1°C.
3) Heat sources:Any element capable of producing an increase in temperature in another body is a source of heat. As an example, we can mention the flame of a stove, oven, fireplace, etc.
4) Heat transmission: There are three possible ways for the heat transmission:
- Driving: When heat passes from molecule to molecule of material;
- Convection: Heat transfer in a fluid that occurs due to a mass displacement of the fluid itself;
-
Radiation: Heat transmission through electromagnetic waves.
5) Types of heat: When you supply an amount of heat capable only of generating temperature variation in a body, that amount of energy is called sensible heat. When the amount of heat transmitted generates a change in physical state, it is called latent heat.
By Joab Silas
Graduated in Physics
*Mental Map by Me. Rafael Helerbrock
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/o-que-e/fisica/o-que-e-calor.htm