Isomerism in cyclic chain compounds occurs when they have different linking groups on at least two carbons of the cycle, as shown in the scheme: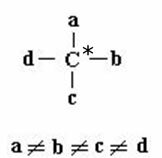
a B C D they are binding groups that are distinct from each other. Example of cis-trans isomers:
Cis isomer: Trans isomer: 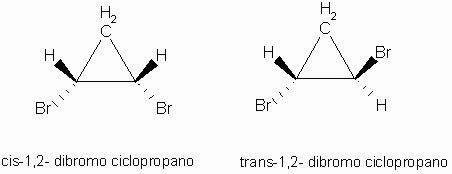
In this case there are three distinct ligands: CH2, H, Br.
Cyclic chain geometric isomers 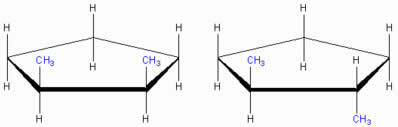
cis-1,2-dimethyl cyclopentane trans-1,2-dimethyl cyclopentane
Note that both structures have identical molecular formula, the difference is only in the position of the CH linking groups3. We say that this difference can only be perceived through the spatial (three-dimensional) structural formula, therefore, this is a cyclic chain geometric Isomer.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
By Líria Alves
Graduated in Chemistry
Brazil School Team
See more! flat isomer
space isomer
Isomerism - Organic chemistry - Chemistry - Brazil School
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
SOUZA, Líria Alves de. "Cyclic Chain Isomerism";
Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/isomeria-cadeia-ciclica.htm. Accessed on June 28, 2021.