Alkaloids are a group of compounds belonging to the group of cyclic amines, which have heterocyclic rings containing nitrogen.
The name "alkaloids" means "similar to alkalis" and this name was given to these compounds because alkalimeans "base" and amines have this basic or alkaline character.
Alkaloids can be synthesized in the laboratory, but their origin is vegetable. Today, it is known that the bitter taste of the leaves and flowers of some plants is due to the presence of these amines. They were even called formerly vegetable alkalis. In plants, alkaloids have a defense function against predatory insects and animals.
Alkaloids have complex structures that allow their use in medicines. They normally act as stimulants of the central nervous system, however, they can cause physical and psychological dependence, being allowed their use only with the presentation of a medical prescription.
See below the main examples of alkaloids, their plant origins and their chemical formulas:
- Nicotine: this alkaloid is found in tobacco plants, used to produce tobacco, and is therefore also produced in cigarette burning. It is mainly responsible for the dependence that smokers feel and for the feeling of abstinence when they stop smoking.
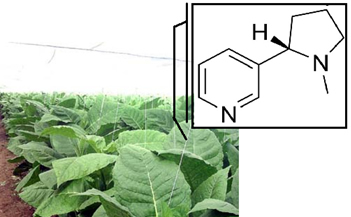
- Caffeine: this alkaloid is well known as it is present in coffee, mate tea and many other beverages.
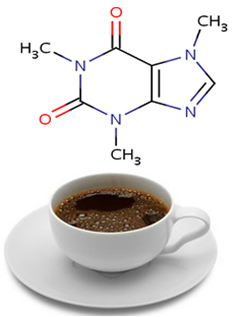
- Morphine: its natural source is the poppy flower. Its name is derived from Morpheus, the Greek god of sleep, because it is used as a medicine to induce sleep and as an analgesic to relieve severe pain.
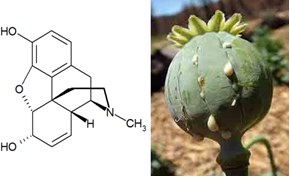
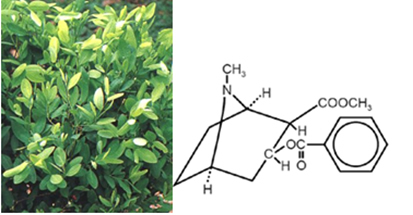
- Cocaine: extracted from the leaves of Erythroxylon coca, plant found exclusively in South America. Fights hunger and fatigue. Unfortunately, it has become a drug that has degraded the health and taken the lives of countless people around the world. And this situation got much worse with the introduction of crack (obtained by adding sodium bicarbonate to coca paste) and merla (mixture of coca paste, with various chemical agents, such as sulfuric acid, kerosene and quicklime).
By Jennifer Fogaça
Graduated in Chemistry
