The circular movement can be transmitted by wheels through contact or connection between them using a belt.
After the "contact" and established the circular movement, we will do some analysis.
Two wheels are connected through a belt and the radius (r1 is smaller than r2) in which the transmission occurs from the wheel with the smallest radius to the one with the largest.
The speed between them is the same (for the endpoints), so:

V = scalar velocity (m/s)
W = angular velocity (rad/s)
r = wheel radius (m)
From the expression above we take the following relationship:
As W = 2.pi.f we have that:
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)

f = frequency (Hz)
r = radius (m)
As an example, we can mention two pulleys connected by a belt with radii of 20 cm and 50 cm each. The smaller radius pulley rotates with a frequency equivalent to 50 Hz. How often will the larger pulley be rotating?
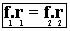
50.0.2 = f.0.5
10 = 0.5.f
f = 10/0.5
f = 20Hz
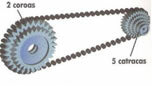
The crowns and ratchets of a bicycle make a circular motion transmission
by Frederico Borges
Graduated in Physics
Brazil School Team
mechanics - Physics - Brazil School
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
ALMEIDA, Frederico Borges de. "Circular Movement Transmission"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/fisica/transmissao-movimento-circular.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.