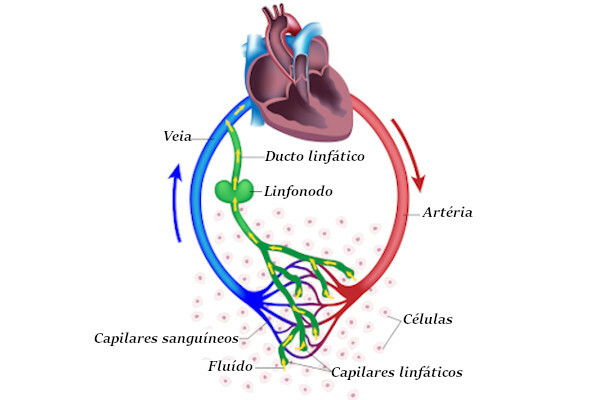
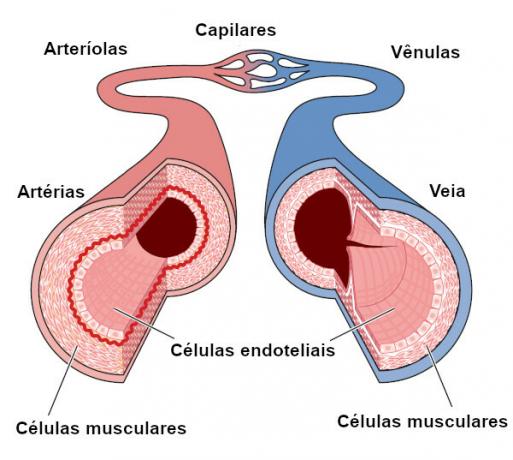
Who has never found themselves in need of medical care or the use of medication to regain health? Even those who are most reluctant cannot deny that a medical consultation helps to clear up countless doubts about the situation of our body. We cannot imagine what our lives would be like without the performance of this professional.
Can you imagine a couple wanting to wait for 9 months of pregnancy to find out if the child is a boy or a girl? Currently, this situation is almost impossible.
Medicine, in the sense of the formation of its word, basically refers to the art of healing, and it has always been developed by agents who proposed to cure the ills of others.
Thus, we have primitive forms, such as the shaman, who, as a healer of the indigenous tribe, prescribes and performs procedures that go beyond the person's physical body. Some rituals are dated approximately 10 000 years ago, where operations were already carried out to remove from people what was causing them harm, these interventions were called trepanation and caused small holes in the skulls of individuals for the exit of the spirits that could possibly be the cause of their illnesses.
Medicine became a science in Greece, with the first reports and experiments of Hippocrates, more than 2,500 years ago. At that time it was believed that the body's ailments were the result of an imbalance of fluids present in the body. With the growth of Rome, many doctors from around the world moved there to further their studies. However, one deserves to be highlighted, the Greek Galen who, through the dissection of animals, built an anatomical model that was used from then on to study the human organism by comparison.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
In Egypt, the practice of medicine was improved with a close connection with religion, after all, doctors attended to the Pharaohs, who were considered the incarnation of gods. In this way, the Egyptians developed various techniques for treating illnesses and even plasters made from the guts of lions or elephants. Thanks to the techniques and works developed by these practitioners and scholars, we have the preservation of the mummified bodies of ancient Egyptian pharaohs.
During the Middle Ages the great challenge was to overcome the impositions and prohibitions of religion that, by proposing that the human body was sacred, it prevented desiccations and the very study of the internal parts of the body. Only in the 15th century (1401-1500) was the authorization to carry out the first dissections, the bodies chosen were those of criminals sentenced to death. But it was not enough, some doctors carried out adventures such as waiting for the execution of a person and then stealing their bodies. The story goes that Versalius, a Belgian doctor, stole a skeleton left on a gallows.
Medicine, with the end of impositions, developed and, together with the discovery of other sciences such as biology, physics, chemistry, in addition to society itself, we have the science we know at the moment.
Fabricio Alves Ferreira
Graduated in Biology
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
FERREIRA, Fabricio Alves. "The History of Medicine"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/biologia/a-historia-medicina.htm. Accessed on June 28, 2021.