THE guinea is an African country located in the West Africa region. É also called Guiné-Conakry to differentiate it from one of its neighboring countries, Guinea-Bissau. Its climate is predominantly Tropical, characterized by high temperatures and high humidity, one of the highest on the continent. The country is home to the source of the main rivers in the region, and is rich in iron ore and bauxite. Despite this, the country has a low HDI and high poverty rates.
Read too: What are the countries in Africa?
Guinea General Data
Nameofficial: Republic of Guinea
Gentile: Guinean, Guinean, Guinean
Extensionterritorial: 245,857 km²
Location: Western Africa
capital: Conakry
Climate: tropical
Government: presidential republic
Divisionadministrative: seven administrative regions and the capital, Conakry
Language: French (official)
-
religions:
Islam: 77,6%
Traditional religions: 12.4%
Christianity: 9.3%
Non-religious and atheists: 0.2%
Unknown: 0.4%
Population: 13,133,000 inhabitants (UN, 2020)
Densitydemographic: 53.4 inhab/km² (UN, 2020)
Human Development Index (HDI): 0,477
Coin: Guinea Franc (GNF)
Gross Domestic Product (GDP): US$ 12.297 billion
GDP per capita: US$ 962.84
Gini: 0.337 (World Bank, 2012)
Timezone: Greenwich Mean Time (GMT)
-
foreign relations:
African Union (AU)
world Bank
IMF
UN
WTO
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
history of guinea
The occupation of the territory of Guinea began 30,000 years ago. As time went by, several peoples settled in that region. Upper Guinea, which covers part of the north, northeast and a portion of the east of the country, was incorporated into the Mali Empire, which extended from the 13th to the 17th century.
French interest in the country began in the mid-19th century, and Guinea became a colony of France at the end of that period. French rule over Guinean territory lasted until 1958, when a constitutional referendum was held to consult on the country's inclusion in the French community. Ahmed Sékou Touré, who was leading the independence of Guinea, became the first president of the country.
Touré's government lasted until 1984 and was marked by increasing repression and the exile of large numbers of Guineans. A military junta then took power in the country.. Lansana Conté ruled Guinea until his death in 2008.
A new coup d'état happened in the country, and only in 2010 free and democratic presidential elections took place|1|.
Read too: Government regimes - how the ruler behaves in power
Guinea map
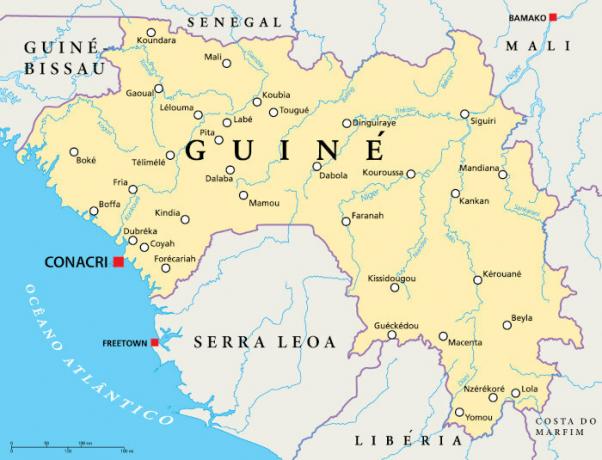
Guinea Geography
Guinea is an African country located in the West Africa region.It has a coastline of 320 km, where, in its southern portion, is the country's capital, Conakry. The country borders, to the northwest, with Guinea Bissau; to the north, with Senegal; and to the east, with the mali. It also borders the Costa do Marfim, Liberia and Sierra Leone, respectively to the southeast, south and southwest.
Climate
O Guinea's climate is of the type Ttropical, with high temperatures and high levels of relative air humidity for most of the year. Between June and November, the rainy season predominates, when rainfall can reach 2500 mm per year in some parts of the country. In the capital, this index reaches 4300 mm.
Under the influence of dry and dust-laden northeast winds, originating from the Sahara and known as harmatán, there is a dry season that can last from December to May. During this period, the thermometers reach 38 ºC in certain regions, and rainfall reaches the lowest annual values.
Relief
Orelief of Guinea is composed of a narrow flat land coastal, which extends over the entire coastline of the country, through plain areas, predominant to the north, and fromHighland, which dominate thes portionionscentral and south from the country. The main mountainous region of Guinea is called Fouta Djallon, an area from which some of the main rivers in West Africa originate.
The average altitude of the Guinean terrain is 472 meters. Mount Nimba, on the border between Guinea, Côte d'Ivoire and Liberia, is the highest point in the country, with an altitude of 1752 meters.
Vegetation
The vegetation cover of Guinea is formed by:
Swamps and small vegetation, typical of coastal wetlands on the coast;
Savannas and Open Forests, in the western and central portions of the territory; and
Tropical Forest, predominant in the southeast of the country.
Hydrography
The Niger River, the third largest in the Africa, is born in guinea and crosses the entire country in a northeasterly direction, towards Mali. The Bafing and Bakoye rivers also originate in Guinea, the second being shared with Mali, and the confluence of the two courses gives rise to the Senegal River. Another important river in West Africa that originates in Guinean territory is the Gambia.
![Mount Nimba is the highest elevation in Guinea. [1]](/f/137154a0e7f772585f900e71b7ad7c4e.jpg)
Guinea Demographics
Guinea has a population of 13,133,000 inhabitants, according to estimates by the United Nations (UN). The country's demographic density is 53.4 inhabitants/km², with the majority of the population living on the coast and the south of the territory.
The country is mostly rural, with rate of urbanization of 36.5% (UN, 2019). The capital, Conakry, is the city with the highest population concentration, currently with 1,889,200 inhabitants (UN, 2019).
The largest portion of the Guinean population belongs to six ethnic groups. Are they:
Fulani (33.4% of the population)
Malinque (29.4%)
Soso (or Susu, 21.2%)
Guerze (7.8%)
Kissi (6.2%)
Take (1.6%)
Consequently, there is a great linguistic variety in the country: French is the official language, but there are currently around 40 languages spoken in Guinean territory.
Guinea's population is quite young, its median age being 19.1 years. Life expectancy at birth in the country is 61.6 years, a very low value compared to other countries in the world. Its population growth rate (28% in 2020, according to the UN) and birth rate (35.86/1000) are among the 20 highest in the world context.

Guinea Economy
O Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of Guinea is US$ 12.297 billion, according to the World Bank. The service sector accounts for almost half of this amount, while industry and agriculture represent, respectively, 32.1% and 19.8% of the country's economy.
guinea has the world's largest bauxite reserve, ore from which the aluminum. Mining in the country is also distinguished by the presence of high grade iron ore, which attracts the interest of several foreign mining companies, including Brazilian ones. Still in mining, the country is a gold and diamond producer.
The agricultural sector concentrates 76% of the labor force in Guinea. Some of the crops are: rice, cassava, corn, oil palm, peanuts, fonio, banana, sugar cane and sweet potatoes.
Despite its mineral wealth and its high economic potential, Guinea has large portion of the population living below the poverty line. The country's Human Development Index (HDI) is considered low, at 0.477 in 2019.
Read too: The 10 poorest countries in the world
Guinea Flag

Guinea Culture
THE Guinea's cultural wealth is derived from ethnic groups to which its population belongs, which translates into different traditions and religious celebrations, languages spoken, and forms of cultural manifestation.
One of the most important artistic expressions in the country is music, marked by the use of string instruments, such as the kora, and percussion instruments, such as the djembê. Mory Kante was a Guinean musician and an African icon, considered ambassador of AfroPop.
In dance, the Guinea's national company called Les Ballets Africans. Created in the 1950s, it is one of the first in the country and aims to promote traditional African culture|2|.

Guinea Infrastructure
Guinean rivers have high hydraulic potential, and for that reason, most of its energy matrix is formed by hydroelectric. A portion of 67% of the installed energy capacity comes from this source, a value that corresponds to one of the highest in the world (20th place in 2017). The second power supply of the country are the fossil fuels, representing 33% of the installed capacity.
Less than half of Guinea's total population, however, has access to electricity.. In rural areas, the share is only 24% against 84% in urban areas.
In total, the country has 16 airports, of which four have paved roads (data from 2013). In 2017, the railways totaled 1086 km, while the highways totaled 44,301 km, with only 3346 km of them paved (2018 data). Guinea also has 1300 km of waterways.
Guinea Government
O Guinea's current government system is presidentialism. The country's first president came to power in 1958, when the nation declared its independence from France. The 2010 election is considered the first democratic election to take place in the country.
Curiosities about Guinea
The country is also called Guinea-Conakry to differentiate it from its neighbor, Guinea-Bissau.
One of the biggest markets in West Africa, the Marché Medina, is located in Guinea.
Isla de Los is one of the main natural tourist attractions in Guinea.
About 35.6% of Guinea's territory corresponds to protected areas, which include nature reserves, parks and forests.
Grades
|1| ROSARY, José. UN satisfied with first free elections in Guinea-Conakry. Available at: <https://news.un.org/pt/story/2010/08/1351441-onu-satisfeita-com-primeiras-eleicoes-livres-na-guine-conacri>. Accessed on Feb 25 2021.
|2| Les Ballets Africans. Africa collection. Available at: <https://acervoafrica.org.br/artistas/les-ballets-africains/>. Accessed on Feb 25 2021.
Image credit
[1] Guy Debonnet / commons
By Paloma Guitarrara
Geography teacher



