In general, the pure substances are hardly found isolated in nature, being found in the form of mixtures, that is, associated with other substances. This means that we and almost everything around us are examples of mixtures of the most varied pure substances.
In this text we will learn what it is and what the classifications of pure substances and mixtures are.
pure substances
pure substances are materials that have chemical composition and properties constant physical and chemical ones, as they do not change at constant pressure and temperature.
Generally speaking, pure substances can be classified in two ways:
a) Simple substances
They are chemical compounds formed by atoms of the same chemical element. For example:
→ H2 (Hydrogen Gas)
Hydrogen gas molecules are formed by two atoms of the chemical element Hydrogen, so it is a simple substance.
→ O3 (Ozone Gas)
Ozone gas molecules are formed by three atoms of the chemical element Oxygen, so it is a simple substance.
There is also the possibility that atoms of the same chemical element form completely different simple substances, the allotropes. An example of
allotropy this is the case of the chemical element Oxygen, which forms the gas substances oxygen (O2) and ozone gas (O3).Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
B) compound substances
They are chemical compounds formed by atoms of different chemical elements. Examples:
→ CO2 (Carbon Gas or Carbon Dioxide)
Carbon dioxide molecules are formed by one atom of the element carbon and two atoms of the element oxygen. As the chemical elements are different, it is a compound substance.
→ kmnO4 (Potassium permanganate)
O ion-formula of potassium permanganate is formed by one atom of the element potassium, one atom of the element manganese and four atoms of the element oxygen.
Mind Map: Pure Substance and Mixture

* To download the mind map in PDF, Click here!
Mixtures
Mix it is the union of two or more different substances (regardless of whether they are simple or composite). It has physical characteristics (melting point, boiling point, density, toughness, etc.) that are different and variable (not fixed) compared to the substances that comprise it.
A mixture of water and sodium chloride, for example, has a totally different melting point compared to the melting points of water ( 0OC) and sodium chloride (803OC) alone.
a) Homogeneous mixtures
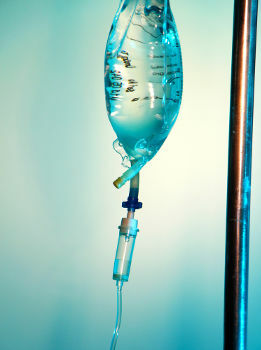
Saline is a homogeneous mixture formed by water, glucose and sodium chloride
Homogeneous mixtures have only one phase (a single visual appearance). They are formed when one material has the ability to dissolve another. Examples:
water and sodium chloride;
water and glucose;
gasoline and ethanol;
atmospheric air (oxygen gas, nitrogen gas, carbon dioxide, water vapor etc.);
acetic acid and water;
petroleum (gasoline, kerosene, lubricating oil, etc.);
saline.
b) Heterogeneous mixtures

Milk is a heterogeneous mixture because it has a liquid phase (water) and a solid phase (fat)
Heterogeneous mixtures have more than one phase (two or more visual aspects). They are formed when one material does not dissolve another. Examples:
Granite;
Milk;
Blood;
Water and sand;
Water this is Leo;
Water and gasoline.
* Mind Map by Victor Ricardo Ferreira
Chemistry teacher
By Me. Diogo Lopes Dias
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
DAYS, Diogo Lopes. "Pure substances and mixtures"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/mistura-e-substancias-puras.htm. Accessed on June 28, 2021.
Chemistry

See the definition of basic Chemistry concepts such as matter, energy, substance, mixture, body, object, mass, volume and system.



